
Given that . $\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta XYZ$ are similar.
A. calculate the area of $\Delta ABC$.
B. the scale factor of enlargement.
C. the area of $\Delta XYZ$.


Answer
536.1k+ views
Hint: We first define the base and the height of the $\Delta ABC$. The perpendicular line from one vertex to its opposite side is its height. We use the formula of area $A=\dfrac{1}{2}\times height\times base$ to find the solution. Then from the length of BC and YZ we find the scale factor of enlargement and using that we find the area of $\Delta XYZ$.
Complete step by step solution:
The triangles $\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta XYZ$ are similar. Therefore, the ratio of their sides is equal.
So, $\dfrac{AB}{XY}=\dfrac{BC}{YZ}=\dfrac{AC}{XZ}$.
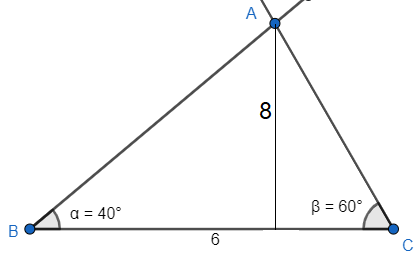
The given triangle $\Delta ABC$ has a base with length 6 unit.
The two angles of the triangles are given where $\angle ABC={{40}^{\circ }};\angle ACB={{60}^{\circ }}$.
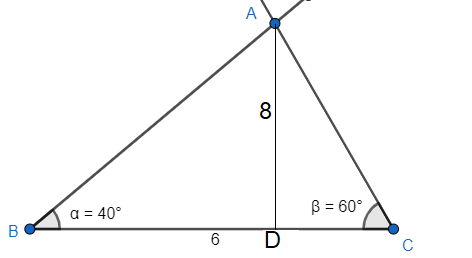
Now we use the formula of the area of the triangle which gives $A=\dfrac{1}{2}\times height\times base$.
For our $\Delta ABC$, the area will be $A=\dfrac{1}{2}\times AD\times BC=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 8\times 6=24$ square units.
Therefore, the area of $\Delta ABC$ is 24 square units.
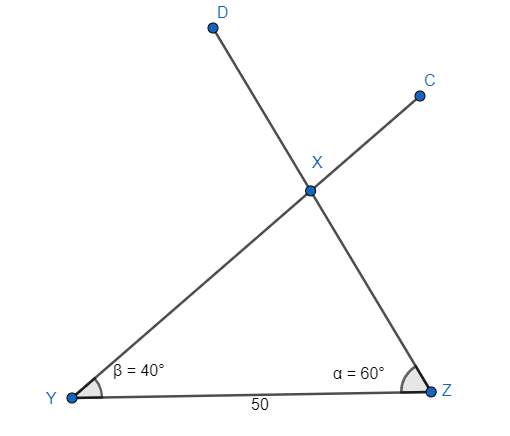
Now for BC and YZ the ratio of the sides is the scale factor of enlargement.
Therefore, $\dfrac{YZ}{BC}=\dfrac{50}{6}=\dfrac{25}{3}$.
We also know that If two triangles are similar, then the ratio of the area of both triangles is proportional to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides.
So, $\dfrac{\Delta XYZ}{\Delta ABC}=\dfrac{Y{{Z}^{2}}}{B{{C}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{50}^{2}}}{{{6}^{2}}}=\dfrac{625}{9}$. We have $\Delta ABC=24$ which gives $\Delta XYZ=\dfrac{625}{9}\times \Delta ABC$.
The area of $\Delta XYZ$ is $\Delta XYZ=\dfrac{625}{9}\times 24=\dfrac{5000}{3}$ square units.
Note: We have to be careful in finding the base for the area. The base will always be the one on which the perpendicular is standing. It can be its extended version also. The vertex will always be in its opposite side.
Complete step by step solution:
The triangles $\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta XYZ$ are similar. Therefore, the ratio of their sides is equal.
So, $\dfrac{AB}{XY}=\dfrac{BC}{YZ}=\dfrac{AC}{XZ}$.
The given triangle $\Delta ABC$ has a base with length 6 unit.
The two angles of the triangles are given where $\angle ABC={{40}^{\circ }};\angle ACB={{60}^{\circ }}$.

Now we use the formula of the area of the triangle which gives $A=\dfrac{1}{2}\times height\times base$.
For our $\Delta ABC$, the area will be $A=\dfrac{1}{2}\times AD\times BC=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 8\times 6=24$ square units.
Therefore, the area of $\Delta ABC$ is 24 square units.
Now for BC and YZ the ratio of the sides is the scale factor of enlargement.
Therefore, $\dfrac{YZ}{BC}=\dfrac{50}{6}=\dfrac{25}{3}$.
We also know that If two triangles are similar, then the ratio of the area of both triangles is proportional to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides.
So, $\dfrac{\Delta XYZ}{\Delta ABC}=\dfrac{Y{{Z}^{2}}}{B{{C}^{2}}}=\dfrac{{{50}^{2}}}{{{6}^{2}}}=\dfrac{625}{9}$. We have $\Delta ABC=24$ which gives $\Delta XYZ=\dfrac{625}{9}\times \Delta ABC$.
The area of $\Delta XYZ$ is $\Delta XYZ=\dfrac{625}{9}\times 24=\dfrac{5000}{3}$ square units.
Note: We have to be careful in finding the base for the area. The base will always be the one on which the perpendicular is standing. It can be its extended version also. The vertex will always be in its opposite side.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




