
Give significance of gastrulation.
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: We already know that the gestation is the time from the fertilization i.e., the fusion of sperm and ovum to birth. However, the fertilization results in the formation of a single cell zygote that must grow into a multicellular organism.
Complete answer:
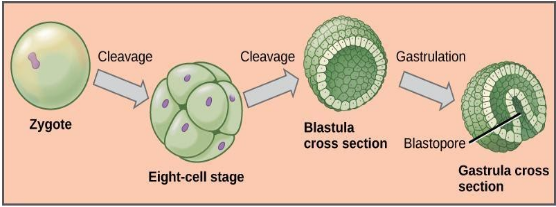
(a) Embryonic development (embryogenesis) begins with fertilization of the ovum by the sperm. The haploid gametes fuse to form a diploid single-celled zygote. This zygote undergoes rapid cell-cycles without increasing in size while increasing the total number of cells in the zygote (this process is also called cleavage i.e. dividing in half). Following these rapid cleavages the zygote develops into a ball of undifferentiated cells, ‘morula’.
(b) Further growth of morula leads to the formation of a hollow spherical structure, ‘blastula’ in which the center of the zygote is now occupied by a fluid-filled cavity (blastocoel) lined by a continuous layer of epithelial cells (blastomeres). Blastula formation is followed by the maturation and formation of a multi-layered structure ‘gastrula’. This stage is especially important from the embryo genetic point of view since,
a) During this stage, the undifferentiated cells undergo massive folding and reorganization hence it can be considered as the beginning point of cellular differentiation and morphogenesis.
b) During this stage, Blastula folds inwards and begins growing in size. While the overall growth patterns may vary across the animal kingdom, this stage is marked by significant cellular movements including invagination (inward bending, in form of a “v”), ingression (cells from the epithelial layer migrate into blastocoel), involution (epithelial sheets roll inwards to now constitute an internal layer)and epiboly (cells don’t move or divide but increase and surface area by thinning).
c) Gastrulation results in differentiation of the blastocoel and archenteron (or the gut tube) that eventually gives rise to endoderm and mesoderm layers.
d) By the end of gastrulation, the zygote has differentiated into distinct germ layers ( ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm). These layers are precursors to organs and different body parts during the next stage I.e. organogenesis. The ectoderm gives rise to the epidermis and neural systems. The endoderm develops into epithelium and organs of the digestive and respiratory systems among other things. The mesoderm develops into multiple cell types including blood, bone, muscle, etc.
e) Gastrulation is also the point in embryogenesis when basic axes (dorsal-ventral, anterior-posterior, etc.) of the organism’s body are laid down.
Note: “gastrula” and ‘gastrulation’ were first used by the renowned German biologist Ernst Haeckel in 1872. Due to its significance in embryogenesis, Lewis Wolpert (1986), a pioneer of developmental biology has noted “It is not birth, marriage, or death, but gastrulation which is truly the most important time in your life.
Complete answer:
(a) Embryonic development (embryogenesis) begins with fertilization of the ovum by the sperm. The haploid gametes fuse to form a diploid single-celled zygote. This zygote undergoes rapid cell-cycles without increasing in size while increasing the total number of cells in the zygote (this process is also called cleavage i.e. dividing in half). Following these rapid cleavages the zygote develops into a ball of undifferentiated cells, ‘morula’.
(b) Further growth of morula leads to the formation of a hollow spherical structure, ‘blastula’ in which the center of the zygote is now occupied by a fluid-filled cavity (blastocoel) lined by a continuous layer of epithelial cells (blastomeres). Blastula formation is followed by the maturation and formation of a multi-layered structure ‘gastrula’. This stage is especially important from the embryo genetic point of view since,
a) During this stage, the undifferentiated cells undergo massive folding and reorganization hence it can be considered as the beginning point of cellular differentiation and morphogenesis.
b) During this stage, Blastula folds inwards and begins growing in size. While the overall growth patterns may vary across the animal kingdom, this stage is marked by significant cellular movements including invagination (inward bending, in form of a “v”), ingression (cells from the epithelial layer migrate into blastocoel), involution (epithelial sheets roll inwards to now constitute an internal layer)and epiboly (cells don’t move or divide but increase and surface area by thinning).
c) Gastrulation results in differentiation of the blastocoel and archenteron (or the gut tube) that eventually gives rise to endoderm and mesoderm layers.
d) By the end of gastrulation, the zygote has differentiated into distinct germ layers ( ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm). These layers are precursors to organs and different body parts during the next stage I.e. organogenesis. The ectoderm gives rise to the epidermis and neural systems. The endoderm develops into epithelium and organs of the digestive and respiratory systems among other things. The mesoderm develops into multiple cell types including blood, bone, muscle, etc.
e) Gastrulation is also the point in embryogenesis when basic axes (dorsal-ventral, anterior-posterior, etc.) of the organism’s body are laid down.

Note: “gastrula” and ‘gastrulation’ were first used by the renowned German biologist Ernst Haeckel in 1872. Due to its significance in embryogenesis, Lewis Wolpert (1986), a pioneer of developmental biology has noted “It is not birth, marriage, or death, but gastrulation which is truly the most important time in your life.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




