
Give one example of damped vibration.
Answer
605.4k+ views
Hint: If we swing a pendulum, having a certain length of the string, we will see at first oscillation it reaches its maximum height and after that gradually height decreases with the number of oscillations. This is due to opposing forces like air drag. The time comes when the pendulum finally stops. This is the damping of vibration or we can say that it is losing energy. We will see in brief why this happens.
Complete step by step answer:
To give one example of damped oscillation let us understand the damped oscillation first:
Damped Oscillation:
In an ideal condition energy and amplitude of SHM (simple harmonic motion) remains constant. Mathematically, displacement of SHM is given by
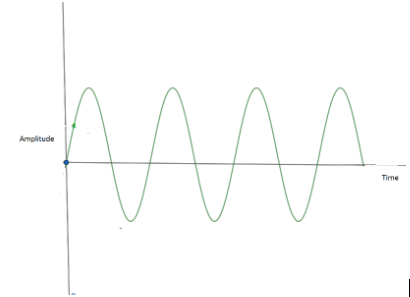
$x=a\sin \left( \omega t+\phi \right)$
Where,
\[x=\]displacement of particle executing SHM
\[a=\] amplitude
\[\phi =\] phase difference
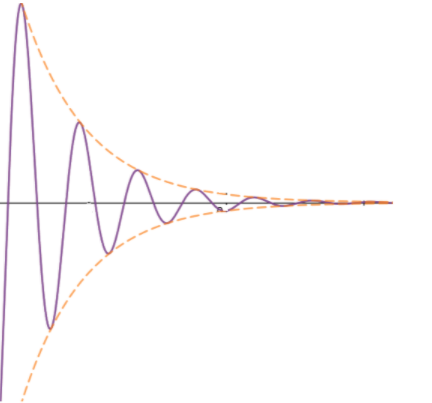
In practical situations a resistance act on the particle which is known as damping force. Damping force is directly proportional to velocity of particle, but its direction is always opposite to velocity due to which amplitude and energy of SHM decrease simultaneously. This is known as damped oscillation of damped vibration.
Let the damping force acting on the particle is F and the velocity of particle be v, then:
\[\begin{align}
& F\propto -v \\
& F=-bv \\
\end{align}\]
Here negative sign indicates damping and b is the damping constant.
As a result of this force we obtain this type of graph
Examples of damped vibrations are: Clock pendulum, Vibrating spring, LRC circuits etc.
Note: If oscillations are damping then to revive damped oscillation we have to give continuous energy to maintain its amplitude with a period of time, and the oscillation obtained is called Forced Oscillation.
Therefore it is to be clear in mind what is damped oscillation and what is Forced oscillation.
Complete step by step answer:
To give one example of damped oscillation let us understand the damped oscillation first:
Damped Oscillation:
In an ideal condition energy and amplitude of SHM (simple harmonic motion) remains constant. Mathematically, displacement of SHM is given by

$x=a\sin \left( \omega t+\phi \right)$
Where,
\[x=\]displacement of particle executing SHM
\[a=\] amplitude
\[\phi =\] phase difference
In practical situations a resistance act on the particle which is known as damping force. Damping force is directly proportional to velocity of particle, but its direction is always opposite to velocity due to which amplitude and energy of SHM decrease simultaneously. This is known as damped oscillation of damped vibration.
Let the damping force acting on the particle is F and the velocity of particle be v, then:
\[\begin{align}
& F\propto -v \\
& F=-bv \\
\end{align}\]
Here negative sign indicates damping and b is the damping constant.
As a result of this force we obtain this type of graph

Examples of damped vibrations are: Clock pendulum, Vibrating spring, LRC circuits etc.
Note: If oscillations are damping then to revive damped oscillation we have to give continuous energy to maintain its amplitude with a period of time, and the oscillation obtained is called Forced Oscillation.
Therefore it is to be clear in mind what is damped oscillation and what is Forced oscillation.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




