
Give examples of unicellular and multicellular organisms.
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: The total cell body is exposed to the environment in unicellular organisms but in the case of multicellular organisms, only the outer cells are exposed to the environment. Also, the former are generally irregular in shape while there is a definite shape in the later.
Complete answer:
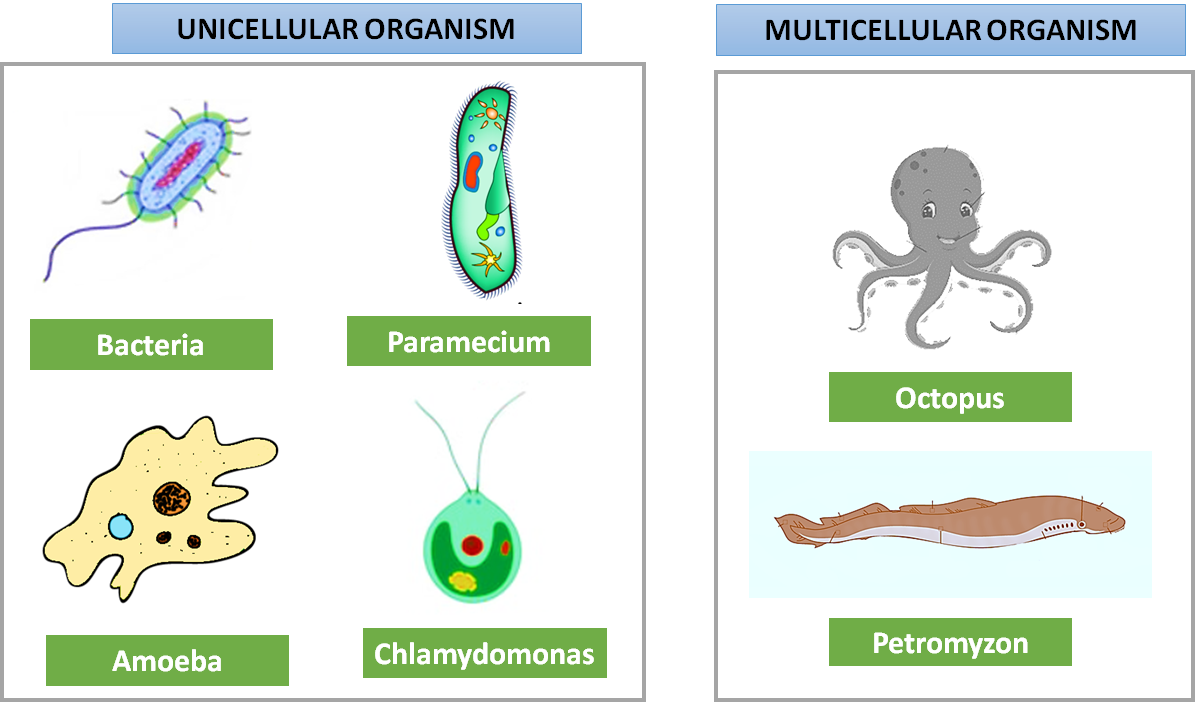
Unicellular organisms are composed of only one cell that can be both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, while the multicellular organisms are composed of more than one cell and include only eukaryotes. Some unicellular prokaryotes are – Salmonella typhi, Escherichia coli, Acetobacter aceti, Lactococcus lactis, and Bacillus anthracis.
Some examples of unicellular eukaryotes are – Amoeba, Euglena, Paramecium, Yeasts, and Mushrooms. These organisms have a simple body organization without the presence of any cell differentiation.
Multicellular organisms are more developed in comparison to the unicellular organisms and in these organisms, there is a clear division of labor at the cellular, tissue, organ, and organ system level. Some examples of multicellular organisms are – Earthworm, Octopus, Petromyzon, Hippocampus, and Frog.
Note: -Unicellular organisms are generally microscopic in nature while multicellular organisms are relatively larger and hence macroscopic.
-Mode of reproduction is primarily asexual in the case of unicellular organisms but multicellular organisms reproduce both sexually and asexually.
-Considering the life span, it is longer in multicellular organisms in comparison to the unicellular organisms.
Complete answer:
Unicellular organisms are composed of only one cell that can be both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, while the multicellular organisms are composed of more than one cell and include only eukaryotes. Some unicellular prokaryotes are – Salmonella typhi, Escherichia coli, Acetobacter aceti, Lactococcus lactis, and Bacillus anthracis.
Some examples of unicellular eukaryotes are – Amoeba, Euglena, Paramecium, Yeasts, and Mushrooms. These organisms have a simple body organization without the presence of any cell differentiation.
Multicellular organisms are more developed in comparison to the unicellular organisms and in these organisms, there is a clear division of labor at the cellular, tissue, organ, and organ system level. Some examples of multicellular organisms are – Earthworm, Octopus, Petromyzon, Hippocampus, and Frog.
Note: -Unicellular organisms are generally microscopic in nature while multicellular organisms are relatively larger and hence macroscopic.
-Mode of reproduction is primarily asexual in the case of unicellular organisms but multicellular organisms reproduce both sexually and asexually.
-Considering the life span, it is longer in multicellular organisms in comparison to the unicellular organisms.

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




