
Give examples of allylic halides.
Answer
518.7k+ views
Hint: Halides is the term used to indicate halogens when they are attached to the carbon chain. The allylic carbon atom is the carbon atom which is $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridized and it is attached to a carbon atom in the chain which is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized or has a double bond.
Complete answer:
There are many types of carbon chains in organic chemistry like straight-chain, branched-chain, allylic carbon chain, vinylic carbon chain, etc. When the carbon atoms have a double bond or a triple bond it is named differently.
So, we are given allylic halides, halides are the term used to indicate the halogens when they are attached to the carbon chain. The allylic carbon atom is the carbon atom which is $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridized and it is attached to a carbon atom in the chain which is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized or has a double bond. Halides include fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), and iodine (I).
Allylic chain means, in the chain, the last carbon atom is attached to the carbon atom having a double bond and when the last carbon atom has one substituent halogen, then it is an allylic halide.
Examples of allylic halides are:
\[C{{H}_{3}}-CH=CH-C{{H}_{2}}Br\]
In this, the carbon atom having the bromine atom is attached with a $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized carbon atom. Other examples are:
$C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CH=CH-C{{H}_{2}}Cl$
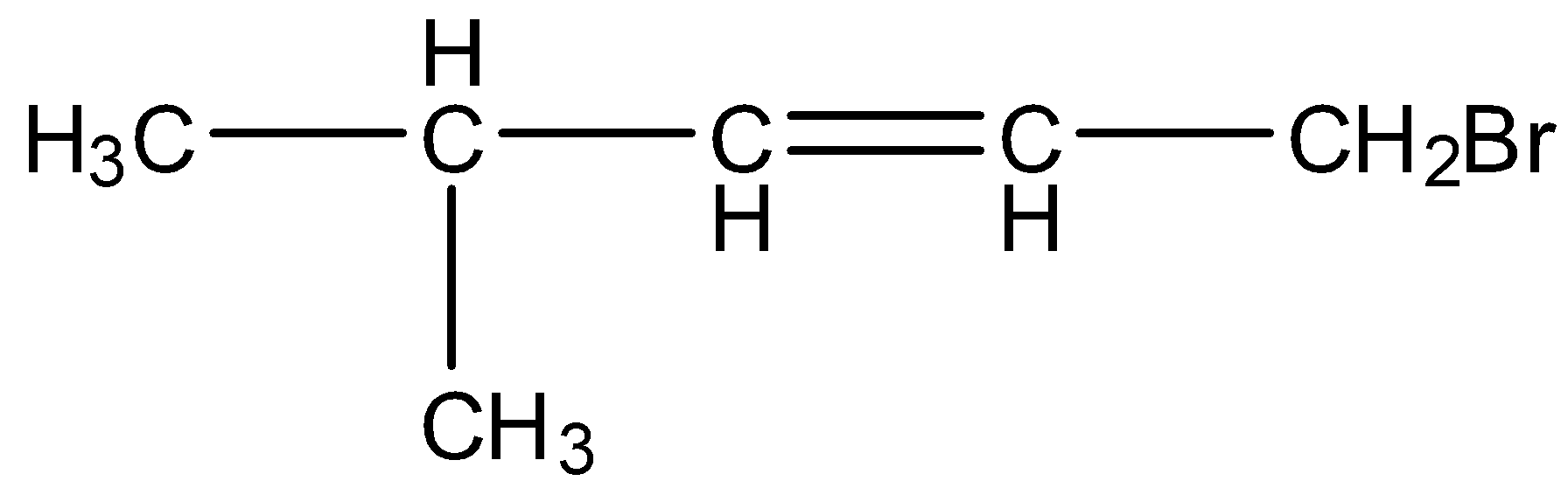
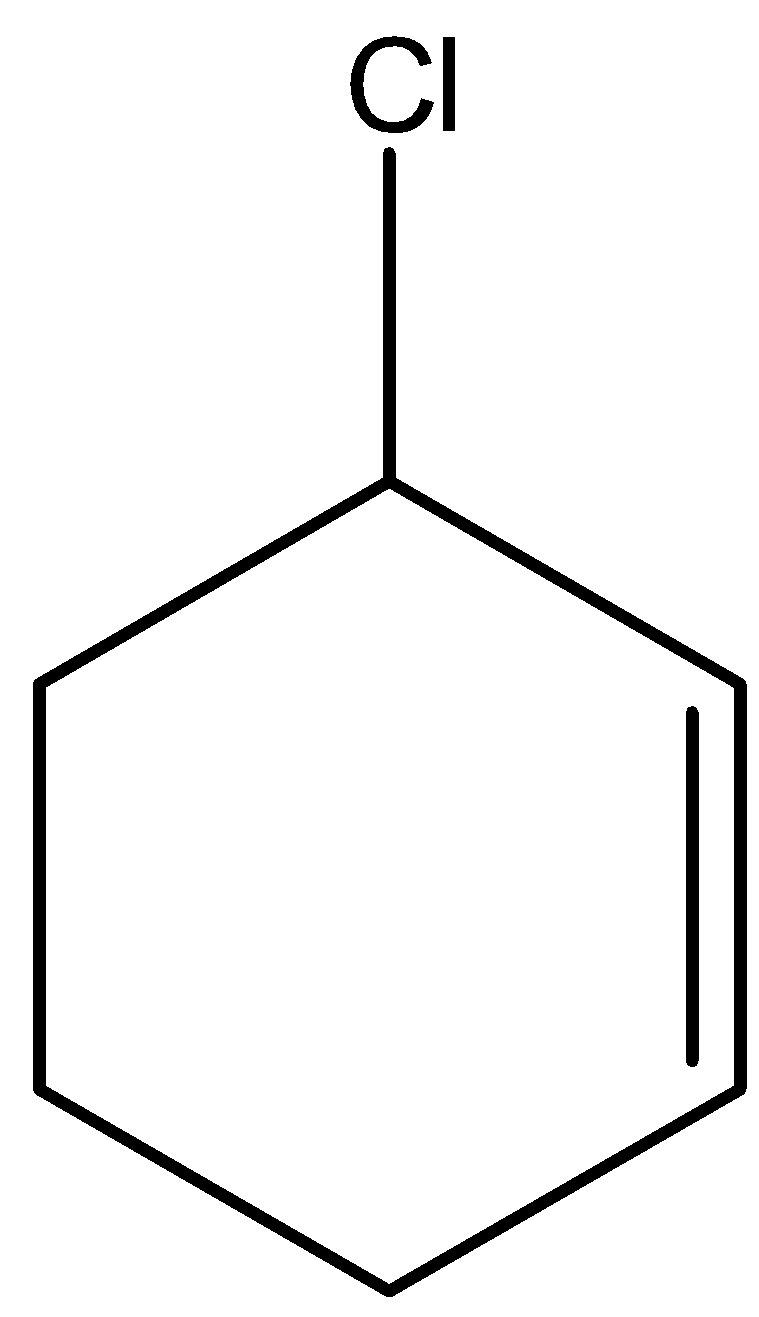
In cyclic form also we can write the allylic halide. An example of cyclic allylic halide is 2-chloro cyclohexene. Its structure is given below:
Note:
If in the chain the halogen atom is attached with the carbon atom having the double bond then it is classified as vinylic halides. An example of vinyl halide is chloroethene having formula $C{{H}_{2}}=CHCl$.
Complete answer:
There are many types of carbon chains in organic chemistry like straight-chain, branched-chain, allylic carbon chain, vinylic carbon chain, etc. When the carbon atoms have a double bond or a triple bond it is named differently.
So, we are given allylic halides, halides are the term used to indicate the halogens when they are attached to the carbon chain. The allylic carbon atom is the carbon atom which is $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridized and it is attached to a carbon atom in the chain which is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized or has a double bond. Halides include fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), and iodine (I).
Allylic chain means, in the chain, the last carbon atom is attached to the carbon atom having a double bond and when the last carbon atom has one substituent halogen, then it is an allylic halide.
Examples of allylic halides are:
\[C{{H}_{3}}-CH=CH-C{{H}_{2}}Br\]
In this, the carbon atom having the bromine atom is attached with a $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridized carbon atom. Other examples are:
$C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CH=CH-C{{H}_{2}}Cl$

In cyclic form also we can write the allylic halide. An example of cyclic allylic halide is 2-chloro cyclohexene. Its structure is given below:

Note:
If in the chain the halogen atom is attached with the carbon atom having the double bond then it is classified as vinylic halides. An example of vinyl halide is chloroethene having formula $C{{H}_{2}}=CHCl$.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




