
Give conversions: Benzaldehyde to alpha-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid
Answer
546.6k+ views
Hint: Draw the structure of benzaldehyde and $\alpha$-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid and observe the change in conversion of benzaldehyde to $\alpha-$Hydroxyphenylacetic acid. First, benzaldehyde undergoes nucleophilic addition reaction with \[{\text{NaCN}}\] in presence of \[{\text{HCl}}\] and give benzaldehyde cyanohydrins. Acid hydrolysis of cyanohydrins gives rise to alphaHydroxyphenylacetic acid.
Complete answer:
First, we will write the desired reaction.
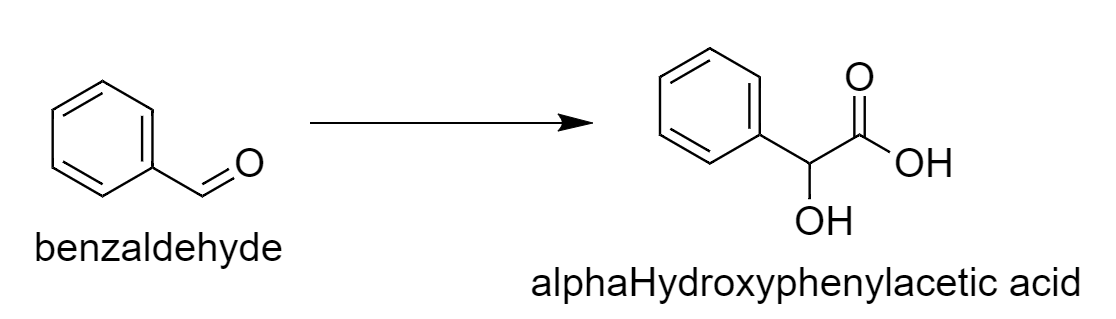
From this reaction, we can say that there is one additional carbon atom of carboxylic acid in the product. So we have to use the reagent that will add one extra carbon atom. So benzaldehyde reacts with \[{\text{NaCN}}\] in presence of \[{\text{HCl}}\] that will increase the carbon atom. The intermediate benzaldehyde cyanohydrins on further reaction with water in presence of acid give rise to alpha-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid.
The detailed mechanism of the reaction is as follows:
Step 1: Nucleophilic addition of \[{\text{NaCN}}\] in presence of \[{\text{HCl}}\] gives Benzaldehyde cyanohydrin.
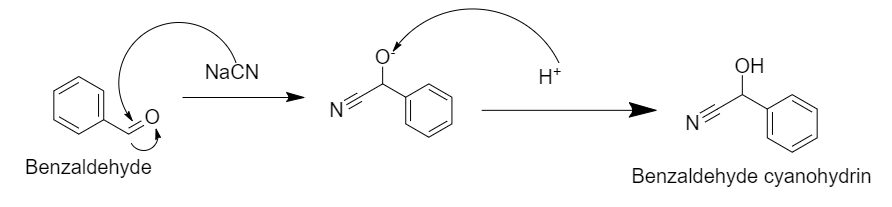
In this reaction, there is a nucleophilic attack of the cyanide group on the carbonyl carbon, which in presence of acid converts into benzaldehyde cyanohydrins.
Step 2: Acid hydrolysis of cyanohydrins gives rise to alpha-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid.
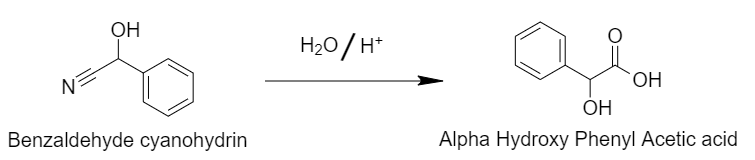
Acid hydrolysis converts the cyanide group of benzaldehyde cyanohydrins to the carboxylic acid group.
Note:
The common name of the alpha-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid is mandelic acid. The IUPAC name of alpha-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid is 2-hydroxy-2-phenyl acetic acid. It has medical applications and is used as an antibacterial agent. Due to the presence of carboxylic and hydroxyl groups, it is a slightly polar compound.
Complete answer:
First, we will write the desired reaction.

From this reaction, we can say that there is one additional carbon atom of carboxylic acid in the product. So we have to use the reagent that will add one extra carbon atom. So benzaldehyde reacts with \[{\text{NaCN}}\] in presence of \[{\text{HCl}}\] that will increase the carbon atom. The intermediate benzaldehyde cyanohydrins on further reaction with water in presence of acid give rise to alpha-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid.
The detailed mechanism of the reaction is as follows:
Step 1: Nucleophilic addition of \[{\text{NaCN}}\] in presence of \[{\text{HCl}}\] gives Benzaldehyde cyanohydrin.

In this reaction, there is a nucleophilic attack of the cyanide group on the carbonyl carbon, which in presence of acid converts into benzaldehyde cyanohydrins.
Step 2: Acid hydrolysis of cyanohydrins gives rise to alpha-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid.

Acid hydrolysis converts the cyanide group of benzaldehyde cyanohydrins to the carboxylic acid group.
Note:
The common name of the alpha-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid is mandelic acid. The IUPAC name of alpha-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid is 2-hydroxy-2-phenyl acetic acid. It has medical applications and is used as an antibacterial agent. Due to the presence of carboxylic and hydroxyl groups, it is a slightly polar compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




