
Give balanced equation for: A displacement reaction involving a metal above hydrogen in the activity series with copper [II] sulphate solution:
Answer
563.4k+ views
Hint: We know that a reaction where displacement of a less reactive metal from its compound occurs by a more reactive metal is termed as displacement reaction. The reactivity of metals is decided by the reactivity series of metals.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s first understand the activity or reactivity series of metals in detail. This series is a list of metals arranged according to their reactivity. The metals present at the top of the list are more reactive than those present at the bottom. The highly reactive metal displaces less reactive metal in displacement reaction. As potassium is the highest reactive metal it can displace all other metal atoms from their compounds. Similarly, zinc can displace iron from iron sulphate as zinc is more reactive than iron.
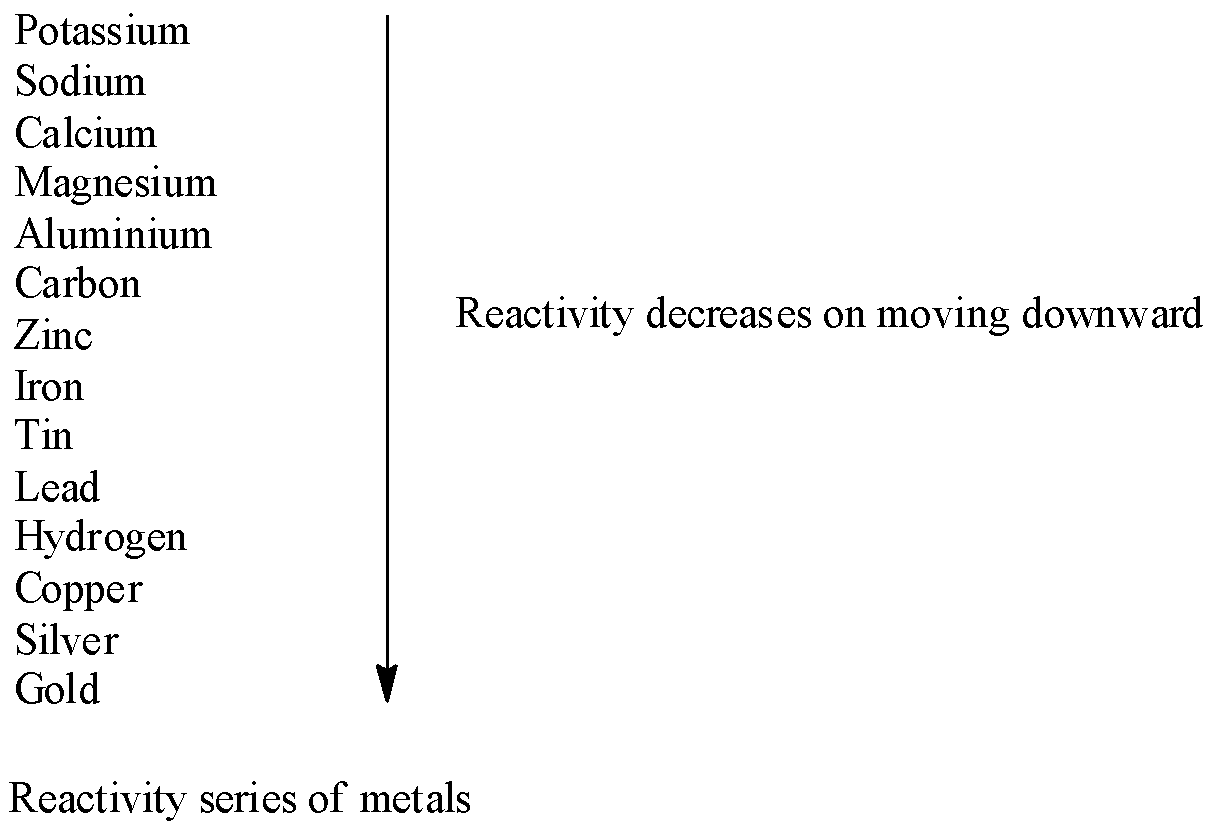
Now come to the question. We have to write a displacement reaction in which a metal above hydrogen in the activity series reacts with copper [II] sulphate solution.
Zinc is the metal which is above hydrogen in the reactivity series. So, we have to write the balanced equation of reaction of zinc and copper sulphate. From the activity series we observe that zinc is more reactive than copper. So, zinc displaces copper from copper sulphate and a displacement reaction takes place.
The balanced equation for the reaction of zinc and copper sulphate is,
${\rm{Zn}} + {\rm{CuS}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}} \to {\rm{ZnS}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}} + {\rm{Cu}}$
Note: Always remember that in a double displacement reaction, the exchange of ions of two ionic compounds takes place. The reaction between potassium nitrate and aluminium chloride represents a double displacement reaction.
\[{\rm{KN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}} + {\rm{AlC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}} \to {\rm{Al}}{\left( {{\rm{N}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_3} + {\rm{KCl}}\]
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s first understand the activity or reactivity series of metals in detail. This series is a list of metals arranged according to their reactivity. The metals present at the top of the list are more reactive than those present at the bottom. The highly reactive metal displaces less reactive metal in displacement reaction. As potassium is the highest reactive metal it can displace all other metal atoms from their compounds. Similarly, zinc can displace iron from iron sulphate as zinc is more reactive than iron.

Now come to the question. We have to write a displacement reaction in which a metal above hydrogen in the activity series reacts with copper [II] sulphate solution.
Zinc is the metal which is above hydrogen in the reactivity series. So, we have to write the balanced equation of reaction of zinc and copper sulphate. From the activity series we observe that zinc is more reactive than copper. So, zinc displaces copper from copper sulphate and a displacement reaction takes place.
The balanced equation for the reaction of zinc and copper sulphate is,
${\rm{Zn}} + {\rm{CuS}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}} \to {\rm{ZnS}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}} + {\rm{Cu}}$
Note: Always remember that in a double displacement reaction, the exchange of ions of two ionic compounds takes place. The reaction between potassium nitrate and aluminium chloride represents a double displacement reaction.
\[{\rm{KN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}} + {\rm{AlC}}{{\rm{l}}_{\rm{3}}} \to {\rm{Al}}{\left( {{\rm{N}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_3} + {\rm{KCl}}\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




