
Gabriel phthalimide reaction is used for the preparation of:
A. ${{\text{1}}^{\text{o}}}$amine
B. ${{\text{2}}^{\text{o}}}$amine
C. ${{\text{3}}^{\text{o}}}$amine
D. ${4^{\text{o}}}$amine
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: The phthalimide gives nucleophilic substitution with an alkyl halide to form amines. The amine should not be hindered because hindered amine are not formed by Gabriel’s Phthalimide synthesis.
Complete step by step solution:Gabriel’s Phthalimide synthesis is used for the conversion of primary alkyl halide into an amine.
In Gabriel phthalimide synthesis, a base abstract proton from phthalimide gives a nucleophile phthalimide ion which attacks on the unhindered primary alkyl halide. The base hydrolysis of alkylated phthalimide gives the primary unhindered amine and phthalimide ion.
Phthalimide ion itself is a bulky ion, so it prefers attack on less hindered primary alkyl halide.
A general reaction is as follows:
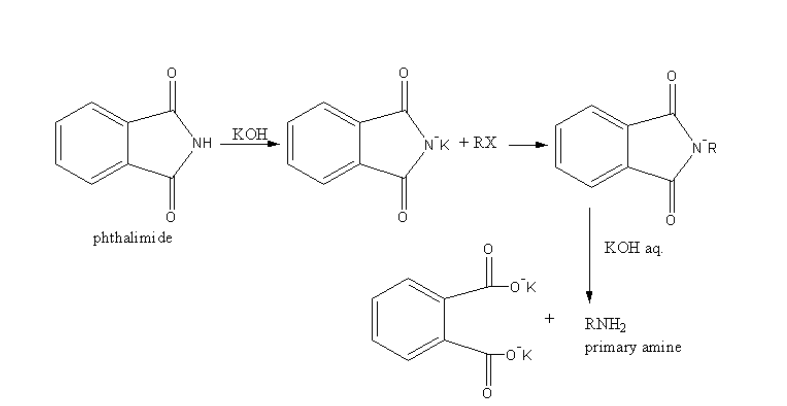
As the primary alkyl halides are used, primary amines are formed. Primary amine will have nitrogen attached with only one carbon and two hydrogens. So, primary amines are synthesised by Gabriel’s Phthalimide synthesis.
Therefore option (A) ${{\text{1}}^{\text{o}}}$amine, is correct.
Note: Gabriel’s Phthalimide synthesis is not used for the preparation of secondary, tertiary aliphatic amines due to steric hindrance. This method is also not used for the preparation of aromatic amines. Gabriel phthalimide synthesis nucleophilic substitution reaction. The general reaction shown by aromatic halide is the electrophilic substitution reaction. Because aromatic halide shows resonance due to resonance they are stable. The nucleophilic substitution destabilizes the resonance of the aromatic compounds.
Complete step by step solution:Gabriel’s Phthalimide synthesis is used for the conversion of primary alkyl halide into an amine.
In Gabriel phthalimide synthesis, a base abstract proton from phthalimide gives a nucleophile phthalimide ion which attacks on the unhindered primary alkyl halide. The base hydrolysis of alkylated phthalimide gives the primary unhindered amine and phthalimide ion.
Phthalimide ion itself is a bulky ion, so it prefers attack on less hindered primary alkyl halide.
A general reaction is as follows:

As the primary alkyl halides are used, primary amines are formed. Primary amine will have nitrogen attached with only one carbon and two hydrogens. So, primary amines are synthesised by Gabriel’s Phthalimide synthesis.
Therefore option (A) ${{\text{1}}^{\text{o}}}$amine, is correct.
Note: Gabriel’s Phthalimide synthesis is not used for the preparation of secondary, tertiary aliphatic amines due to steric hindrance. This method is also not used for the preparation of aromatic amines. Gabriel phthalimide synthesis nucleophilic substitution reaction. The general reaction shown by aromatic halide is the electrophilic substitution reaction. Because aromatic halide shows resonance due to resonance they are stable. The nucleophilic substitution destabilizes the resonance of the aromatic compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




