
What is the function of the tail of human sperm?
Answer
492k+ views
Hint: In anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction, sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce spermatozoa, which are motile sperm with a flagellum tail, whereas red algae and fungi produce spermatia, which are non-motile sperm cells.
Complete answer:
The human gamete consists of three main parts: head, middle piece, and tail. The foremost operation of the tail is to provide motility to the gamete. With its whipping movement, it propels the gamete towards the egg.
The tip of the gamete head is that portion mentioned because of the process that permits the gamete to penetrate the egg. The midpiece contains the mitochondria that provide the energy the tail must move. The tail moves with whip-like movements back and forth to propel the gamete towards the egg.
The tail provides sperm movement. It whips and undulates so that the cell will travel the egg. Following gamete deposition within the female generative tract, activation of tail movement is suppressed till the gamete is carried to at intervals a relatively short distance of the egg.
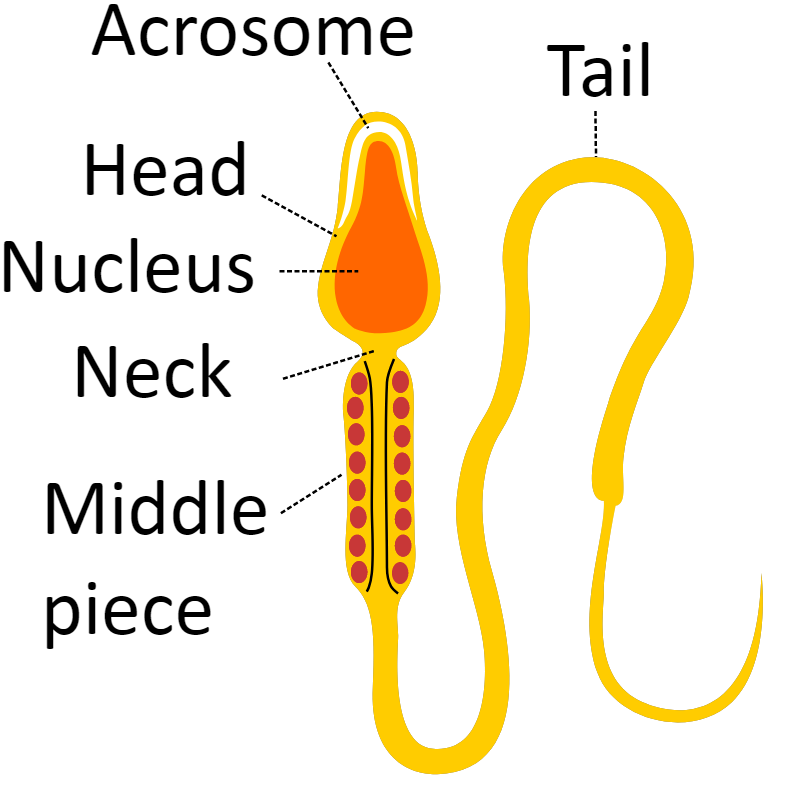
Thus, The tail's primary function is to provide sperm motility. It propels the sperm towards the egg with its whipping motion.
Note:
Sperm cells are unable to divide and have a short lifespan, but after fusing with egg cells during fertilization, a new organism emerges, beginning as a totipotent zygote. Human sperm cells are haploid, which means that their 23 chromosomes can join with the 23 chromosomes of the female egg to form a diploid cell with 46 paired chromosomes.
Complete answer:
The human gamete consists of three main parts: head, middle piece, and tail. The foremost operation of the tail is to provide motility to the gamete. With its whipping movement, it propels the gamete towards the egg.
The tip of the gamete head is that portion mentioned because of the process that permits the gamete to penetrate the egg. The midpiece contains the mitochondria that provide the energy the tail must move. The tail moves with whip-like movements back and forth to propel the gamete towards the egg.
The tail provides sperm movement. It whips and undulates so that the cell will travel the egg. Following gamete deposition within the female generative tract, activation of tail movement is suppressed till the gamete is carried to at intervals a relatively short distance of the egg.

Thus, The tail's primary function is to provide sperm motility. It propels the sperm towards the egg with its whipping motion.
Note:
Sperm cells are unable to divide and have a short lifespan, but after fusing with egg cells during fertilization, a new organism emerges, beginning as a totipotent zygote. Human sperm cells are haploid, which means that their 23 chromosomes can join with the 23 chromosomes of the female egg to form a diploid cell with 46 paired chromosomes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




