
What is the function of the contractile vacuole?
A. Excretion
B. Respiration
C. Digestion
D. Nutrition
Answer
575.4k+ views
Hint:The contractile vacuole is a type of vacuole present in the protists or unicellular algae. These vacuoles are involved in osmoregulation in these organisms. Also, it protects these organisms from rupturing through excessive internal pressure.
Complete answer:The vacuoles are organelles that are for storing cellular products. The contractile vacuole is a special type of vacuole that helps in osmoregulation. Like a simple vacuole, it also stores cellular products. It is present in protists or unicellular algae. These organisms are usually found in freshwater environments. The concentration of solutes is less in the environment outside the cell. This makes the cell’s outer environment hypotonic.
Under hypotonic conditions, osmosis occurs. This causes water to accumulate inside the cell from the external environment in contractile vacuoles. Thus, these vacuoles protect the cell from absorbing too much water and rupture due to high internal pressure.
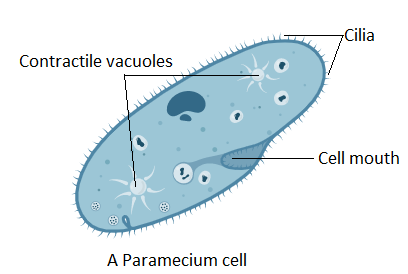
The contractile vacuole contracts and expels water out of the cell. When the water flows into the contractile vacuole the phase is known as diastole. On the other hand, the phase when the water leaves the contractile vacuole is called systole. The water first moves inside the cytoplasm and then to the contractile vacuole. Thus, we can conclude that the contractile vacuoles are involved in the process of excretion. A general example of this is Amoeba. It is a single-celled organism belonging to protists that excrete through contractile vacuoles.
Thus, option A) Excretion is the right answer.
Note: It has been studied that the organisms that lack cell walls are the ones that generally consist of contractile vacuoles. As a result of evolution, contractile vacuoles have been lost in multicellular organisms. But some of the fungi and sponge species exhibit the presence of contractile vacuoles.
Complete answer:The vacuoles are organelles that are for storing cellular products. The contractile vacuole is a special type of vacuole that helps in osmoregulation. Like a simple vacuole, it also stores cellular products. It is present in protists or unicellular algae. These organisms are usually found in freshwater environments. The concentration of solutes is less in the environment outside the cell. This makes the cell’s outer environment hypotonic.
Under hypotonic conditions, osmosis occurs. This causes water to accumulate inside the cell from the external environment in contractile vacuoles. Thus, these vacuoles protect the cell from absorbing too much water and rupture due to high internal pressure.

The contractile vacuole contracts and expels water out of the cell. When the water flows into the contractile vacuole the phase is known as diastole. On the other hand, the phase when the water leaves the contractile vacuole is called systole. The water first moves inside the cytoplasm and then to the contractile vacuole. Thus, we can conclude that the contractile vacuoles are involved in the process of excretion. A general example of this is Amoeba. It is a single-celled organism belonging to protists that excrete through contractile vacuoles.
Thus, option A) Excretion is the right answer.
Note: It has been studied that the organisms that lack cell walls are the ones that generally consist of contractile vacuoles. As a result of evolution, contractile vacuoles have been lost in multicellular organisms. But some of the fungi and sponge species exhibit the presence of contractile vacuoles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




