
What is the function of ATP in cell metabolism? Explain with the aid of a diagram, how its structure makes it possible.
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: They are the chemical compound composed of the phosphate groups, adenine, and also the sugar ribose. These molecules provide energy for various biochemical processes within the body.
Complete answer:
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), an energy-carrying molecule found within the cells of all living things. ATP captures energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes.
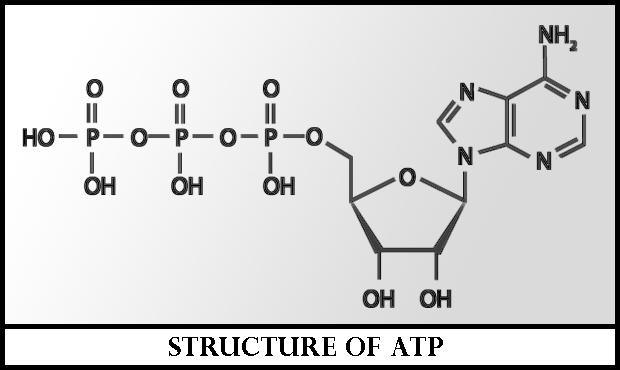
ATP is a nucleotide, which is especially composed of the molecule adenosine and three phosphate groups. It is soluble in water and features a high energy content, which is primarily because of the presence of two phosphoanhydride bonds connected to the three phosphate groups.
The triphosphate tail of ATP is the actual power source in which the cell taps. The available energy is contained within the bonds between the phosphates and is released once they are broken or split into molecules. This happens through the addition of a water molecule (hydrolysis). Usually, only the outer phosphate group is faraway from ATP to yield energy; when this happens, ATP – ATP is converted into ADP – adenosine diphosphate, it's the shape of the nucleotide having only two phosphates.
Additional Information: ATP molecules are mainly composed of three important components.
-The pentose sugar molecule i.e. ribose sugar.
-Nitrogen base- Adenine, attached to the primary carbon of this sugar molecule.
-The three phosphate groups are attached during a chain to the 5th carbon of the pentose sugar. The phosphoryl groups, starting with the group closest to the ribose sugar, are mentioned because of the alpha, beta, and gamma phosphates. These phosphates play a crucial role in the activity of ATP.
Note: ATP is called the energy currency of the cell. ATP molecules are synthesized by Mitochondria, therefore it's called the powerhouse of the cell. The ATP molecule was discovered in 1929 by German chemist Karl Lohmann. Later in the year 1948, Scottish biochemist Alexander Todd was the first person to synthesize the ATP molecule.
Complete answer:
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), an energy-carrying molecule found within the cells of all living things. ATP captures energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes.
ATP is a nucleotide, which is especially composed of the molecule adenosine and three phosphate groups. It is soluble in water and features a high energy content, which is primarily because of the presence of two phosphoanhydride bonds connected to the three phosphate groups.
The triphosphate tail of ATP is the actual power source in which the cell taps. The available energy is contained within the bonds between the phosphates and is released once they are broken or split into molecules. This happens through the addition of a water molecule (hydrolysis). Usually, only the outer phosphate group is faraway from ATP to yield energy; when this happens, ATP – ATP is converted into ADP – adenosine diphosphate, it's the shape of the nucleotide having only two phosphates.
Additional Information: ATP molecules are mainly composed of three important components.
-The pentose sugar molecule i.e. ribose sugar.
-Nitrogen base- Adenine, attached to the primary carbon of this sugar molecule.
-The three phosphate groups are attached during a chain to the 5th carbon of the pentose sugar. The phosphoryl groups, starting with the group closest to the ribose sugar, are mentioned because of the alpha, beta, and gamma phosphates. These phosphates play a crucial role in the activity of ATP.

Note: ATP is called the energy currency of the cell. ATP molecules are synthesized by Mitochondria, therefore it's called the powerhouse of the cell. The ATP molecule was discovered in 1929 by German chemist Karl Lohmann. Later in the year 1948, Scottish biochemist Alexander Todd was the first person to synthesize the ATP molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




