
From the point \[P\left( {16,7} \right)\] tangent PQ and PR are drawn to the circle \[{x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 4y - 20 = 0\]. If C be the centre of the circle then area of the quadrilateral PQCR is
A) 450 sq. units
B) 15 sq. units
C) 50 sq. units
D) 75 sq. units
Answer
563.4k+ views
Hint:
Here we will first find the coordinates of the center of the circle and the radius of the circle. Then we will find the relation between the area of the quadrilateral PQCR and Area of the triangle PQC. Then we will find the area of the triangle PQC and put its value in the relationship to get the value of the area of the quadrilateral PQCR.
Formula used:
We will use the following formulas:
1) The distance between the two points with coordinate \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right),\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] is given by the formula \[d = \sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}} \].
2) Pythagoras theorem: \[{\left( {{\rm{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\rm{Perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\rm{Base}}} \right)^2}\]
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The equation of the circle is \[{x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 4y - 20 = 0\].
First, we will make the given equation of circle into the standard equation of the circle i.e. \[{(x - {x_0})^2} + {(y - {y_0})^2} = {r^2}\]where, \[{x_0}\]is the x coordinate of the center of the circle and\[{y_0}\]is the y coordinate of the center of the circle and \[r\]is the radius of the circle. Therefore we can write the equation of the given circle as
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 2x + {1^2} + {y^2} - 4y + {2^2} - 20 - 1 - 4 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - 1} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - 2} \right)^2} = {5^2}\]
Now by comparing it with the standard equation of the circle, we get the center of the circle as \[O\left( {1,2} \right)\] and radius of the circle as \[r = 5\].
Now we will draw a circle and the point P along with the two tangents PQ and PR from point P on the circle. Therefore, we get
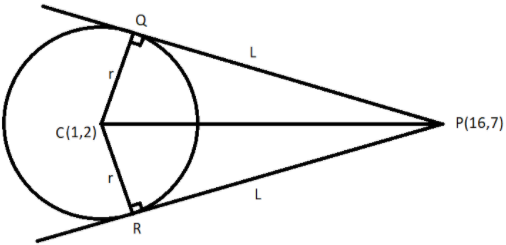
We can clearly see that the area of the quadrilateral PQCR is equal to twice the area of the triangle PQC as area of triangle PQC is equal to the area of triangle PRC
Area of PQCR \[ = 2 \times \] area of \[\Delta PQC\]
So we will now find the area of the triangle PQC. Therefore, we get
Area of \[\Delta PQC = \dfrac{1}{2} \times PQ \times QC = \dfrac{1}{2} \times L \times r\]………………………………….\[\left( 1 \right)\]
So to find the value of \[L\] firstly we will calculate the value of the PC by using the basic distance formula between the two points. So, we get
\[PC = \sqrt {{{\left( {16 - 1} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {7 - 2} \right)}^2}} \]
Subtracting the terms in the bracket, we get
\[ \Rightarrow PC = \sqrt {{{\left( {15} \right)}^2} + {{\left( 5 \right)}^2}} \]
Applying the exponent on terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow PC = \sqrt {225 + 25} \]
Adding the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow PC = \sqrt {250} = 5\sqrt {10} \]
Now we will use the Pythagoras theorem for the triangle PQC to get the value of L.
\[P{C^2} = P{Q^2} + Q{C^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {5\sqrt {10} } \right)^2} = {L^2} + {r^2}\]
Now we will put the value of the \[r\] in the equation to get the value of \[L\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow 250 = {L^2} + {5^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {L^2} = 250 - 25\]
Subtracting the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow L = \sqrt {225} = 15\]
Now we will calculate the area of the triangle PQC.
Substituting \[L = 15\] and \[r = 5\] in the equation \[\left( 1 \right)\], we get
Area of \[\Delta PQC = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 15 \times 5\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of \[\Delta PQC = \dfrac{{75}}{2}\]
Now by using the area of the triangle PQC we will get the area of the quadrilateral PQCR, we get
Area of \[PQCR = 2 \times \] Area of \[\Delta PQC\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of \[PQCR\] \[ = 2 \times \dfrac{{75}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of \[PQCR\] \[ = 75\] sq. units
Hence, the area of the quadrilateral PQCR is 75 sq. units.
So, option D is the correct option.
Note:
Quadrilateral is a two dimensional geometric shape which has four sides. Area is the amount of surface covered by a two dimensional shape. The Pythagoras theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the square of the other two sides of the triangle.This theorem is applied to only right angled triangles. Right angled triangle is the triangle which has one of its angles equal to \[{90^\circ}\] . Hypotenuse is the longest side of the right angled triangle.
Here we will first find the coordinates of the center of the circle and the radius of the circle. Then we will find the relation between the area of the quadrilateral PQCR and Area of the triangle PQC. Then we will find the area of the triangle PQC and put its value in the relationship to get the value of the area of the quadrilateral PQCR.
Formula used:
We will use the following formulas:
1) The distance between the two points with coordinate \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right),\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] is given by the formula \[d = \sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}} \].
2) Pythagoras theorem: \[{\left( {{\rm{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\rm{Perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\rm{Base}}} \right)^2}\]
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The equation of the circle is \[{x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 4y - 20 = 0\].
First, we will make the given equation of circle into the standard equation of the circle i.e. \[{(x - {x_0})^2} + {(y - {y_0})^2} = {r^2}\]where, \[{x_0}\]is the x coordinate of the center of the circle and\[{y_0}\]is the y coordinate of the center of the circle and \[r\]is the radius of the circle. Therefore we can write the equation of the given circle as
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 2x + {1^2} + {y^2} - 4y + {2^2} - 20 - 1 - 4 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - 1} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - 2} \right)^2} = {5^2}\]
Now by comparing it with the standard equation of the circle, we get the center of the circle as \[O\left( {1,2} \right)\] and radius of the circle as \[r = 5\].
Now we will draw a circle and the point P along with the two tangents PQ and PR from point P on the circle. Therefore, we get

We can clearly see that the area of the quadrilateral PQCR is equal to twice the area of the triangle PQC as area of triangle PQC is equal to the area of triangle PRC
Area of PQCR \[ = 2 \times \] area of \[\Delta PQC\]
So we will now find the area of the triangle PQC. Therefore, we get
Area of \[\Delta PQC = \dfrac{1}{2} \times PQ \times QC = \dfrac{1}{2} \times L \times r\]………………………………….\[\left( 1 \right)\]
So to find the value of \[L\] firstly we will calculate the value of the PC by using the basic distance formula between the two points. So, we get
\[PC = \sqrt {{{\left( {16 - 1} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {7 - 2} \right)}^2}} \]
Subtracting the terms in the bracket, we get
\[ \Rightarrow PC = \sqrt {{{\left( {15} \right)}^2} + {{\left( 5 \right)}^2}} \]
Applying the exponent on terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow PC = \sqrt {225 + 25} \]
Adding the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow PC = \sqrt {250} = 5\sqrt {10} \]
Now we will use the Pythagoras theorem for the triangle PQC to get the value of L.
\[P{C^2} = P{Q^2} + Q{C^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\left( {5\sqrt {10} } \right)^2} = {L^2} + {r^2}\]
Now we will put the value of the \[r\] in the equation to get the value of \[L\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow 250 = {L^2} + {5^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {L^2} = 250 - 25\]
Subtracting the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow L = \sqrt {225} = 15\]
Now we will calculate the area of the triangle PQC.
Substituting \[L = 15\] and \[r = 5\] in the equation \[\left( 1 \right)\], we get
Area of \[\Delta PQC = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 15 \times 5\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of \[\Delta PQC = \dfrac{{75}}{2}\]
Now by using the area of the triangle PQC we will get the area of the quadrilateral PQCR, we get
Area of \[PQCR = 2 \times \] Area of \[\Delta PQC\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of \[PQCR\] \[ = 2 \times \dfrac{{75}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of \[PQCR\] \[ = 75\] sq. units
Hence, the area of the quadrilateral PQCR is 75 sq. units.
So, option D is the correct option.
Note:
Quadrilateral is a two dimensional geometric shape which has four sides. Area is the amount of surface covered by a two dimensional shape. The Pythagoras theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the square of the other two sides of the triangle.This theorem is applied to only right angled triangles. Right angled triangle is the triangle which has one of its angles equal to \[{90^\circ}\] . Hypotenuse is the longest side of the right angled triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




