
What is the formula of cyclohexene and iodine?
Answer
495.6k+ views
Hint: Formula for a chemical compound can be expressed in two ways i.e., structural formula and molecular formula. The molecular formula of a chemical compound specifies the actual number of atoms of each element present in a molecule whereas the structural formula indicates bonding as well as arrangement of atoms in the molecule.
Complete answer:
As per question, the given molecules are cyclohexene and iodine. Let us discuss the formula for each molecule separately.
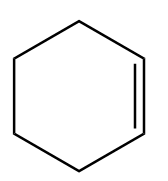
Cyclohexene: It is a cyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula $ {C_6}{H_{10}} $ and is produced by partial hydrogenation of benzene. Structurally, the formula represents that cyclohexene is a six membered carbon ring which consists of a double bond between two of the carbon atoms. The carbon atoms bonded via a double bond are planar and hence, equivalent to eclipsed conformation at that bond.
Thus, the molecular formula of cyclohexene is $ {C_6}{H_{10}} $ and its structural formula is:
Iodine: The molecule of iodine in its gaseous phase exists as $ {I_2} $ . It is a nonpolar covalent molecule in which each iodine atom shares two electrons equally. It tends to sublime at temperature $ {114^o}C $ and melts only under pressure. The reason for low melting and boiling points or low change in enthalpies is due to the weak intermolecular forces existing between the atoms in the molecule.
Thus, the molecular formula of iodine in its gaseous phase is $ {I_2} $ and structurally, it is represented as $ I - I $ .
Note:
Remember that the molecular formula can be used for the nomenclature of simple molecules while the structural formula can be used for the nomenclature of complex molecules and to predict the chemical and physical properties such as polarity for the molecule.
Complete answer:
As per question, the given molecules are cyclohexene and iodine. Let us discuss the formula for each molecule separately.
Cyclohexene: It is a cyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula $ {C_6}{H_{10}} $ and is produced by partial hydrogenation of benzene. Structurally, the formula represents that cyclohexene is a six membered carbon ring which consists of a double bond between two of the carbon atoms. The carbon atoms bonded via a double bond are planar and hence, equivalent to eclipsed conformation at that bond.
Thus, the molecular formula of cyclohexene is $ {C_6}{H_{10}} $ and its structural formula is:

Iodine: The molecule of iodine in its gaseous phase exists as $ {I_2} $ . It is a nonpolar covalent molecule in which each iodine atom shares two electrons equally. It tends to sublime at temperature $ {114^o}C $ and melts only under pressure. The reason for low melting and boiling points or low change in enthalpies is due to the weak intermolecular forces existing between the atoms in the molecule.
Thus, the molecular formula of iodine in its gaseous phase is $ {I_2} $ and structurally, it is represented as $ I - I $ .
Note:
Remember that the molecular formula can be used for the nomenclature of simple molecules while the structural formula can be used for the nomenclature of complex molecules and to predict the chemical and physical properties such as polarity for the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




