
For the principal values, evaluate \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\].
Answer
580.5k+ views
Hint: To solve the question given above, first we will draw the rough graphs of \[y={{\tan }^{-1}}\left( x \right)\] and \[y={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( x \right)\] and we will determine the nature of these graphs. Then we will find the value of \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)\] in terms of \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)\]. And the values of \[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\] in terms of \[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\]. After that, we will find the value of \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\] by putting the respective values.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Before solving the question, we must know what is the nature of \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( x \right)\] and \[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( x \right)\]. For determining the nature of these inverse trigonometric functions, we will draw their respective graphs. The graph of \[{{\tan }^{-1}}x\] is:
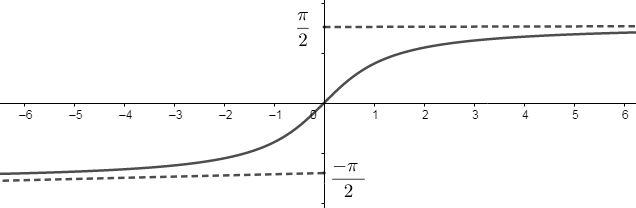
From the above graphs, we can see that the function \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( x \right)\] is an odd function. If a function \[f\left( x \right)\] is an odd function then we have the following relation:
So, \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -x \right)=-{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( x \right)\]
Now, we will draw the graph of \[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( x \right)\]:
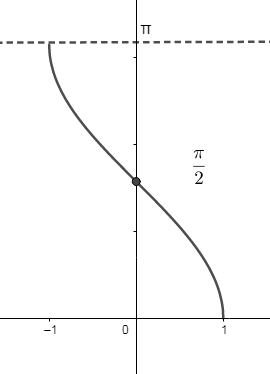
We can see from the above graph that \[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -x \right)=\pi -{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( x \right)\].
Now, we will find the value of \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)\]. We know that,
We have shown above that \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -x \right)=-{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( x \right)\] so using this relation in solving \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)\] we get,
\[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)=-{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)\]…………. Eq. (1)
We know that, the principal value for ${{\tan }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)$ is equal to:
$\dfrac{\pi }{4}$
So, substituting this principal value in eq. (1) we get,
\[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)=-\dfrac{\pi }{4}\]……… Eq. (2)
Now, we will find the value of \[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\]. We have shown above the following relation:
\[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -x \right)=\pi -{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( x \right)\] so using this relation in \[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\] we get,
\[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\pi -{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\]……… Eq. (3)
We know that the principal value for:
${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{4}$
On putting the value of \[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\] in eq. (3), we will get:
\[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\pi -\dfrac{\pi }{4}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\dfrac{3\pi }{4}\] ……… Eq. (4)
Now, we will add equations (2) and (4). After doing this, we will get:
\[\begin{align}
& {{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\dfrac{-\pi }{4}+\dfrac{3\pi }{4} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Note: The above question can be solved in an alternate way as shown: We know that \[\cos \dfrac{\pi }{4}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\]\[\Rightarrow {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{4}\]. Now, we can also say that, \[{{\cot }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{4}\]. Now, \[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)={{\cot }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)\]. Now, we will subtract \[\pi \] on both sides. Thus we will get:
\[\begin{align}
& {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)-\pi ={{\cot }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)-\pi \\
& \Rightarrow \pi -{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\pi -{{\cot }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)={{\cot }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now the value of \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\] = \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)+{{\cot }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)\]. Now we will apply the identity: \[{{\cot }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)+{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{2}\]. So, we will get, \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{2}\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
Before solving the question, we must know what is the nature of \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( x \right)\] and \[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( x \right)\]. For determining the nature of these inverse trigonometric functions, we will draw their respective graphs. The graph of \[{{\tan }^{-1}}x\] is:

From the above graphs, we can see that the function \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( x \right)\] is an odd function. If a function \[f\left( x \right)\] is an odd function then we have the following relation:
So, \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -x \right)=-{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( x \right)\]
Now, we will draw the graph of \[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( x \right)\]:

We can see from the above graph that \[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -x \right)=\pi -{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( x \right)\].
Now, we will find the value of \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)\]. We know that,
We have shown above that \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -x \right)=-{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( x \right)\] so using this relation in solving \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)\] we get,
\[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)=-{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)\]…………. Eq. (1)
We know that, the principal value for ${{\tan }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)$ is equal to:
$\dfrac{\pi }{4}$
So, substituting this principal value in eq. (1) we get,
\[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)=-\dfrac{\pi }{4}\]……… Eq. (2)
Now, we will find the value of \[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\]. We have shown above the following relation:
\[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -x \right)=\pi -{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( x \right)\] so using this relation in \[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\] we get,
\[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\pi -{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\]……… Eq. (3)
We know that the principal value for:
${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{4}$
On putting the value of \[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\] in eq. (3), we will get:
\[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\pi -\dfrac{\pi }{4}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\dfrac{3\pi }{4}\] ……… Eq. (4)
Now, we will add equations (2) and (4). After doing this, we will get:
\[\begin{align}
& {{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\dfrac{-\pi }{4}+\dfrac{3\pi }{4} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Note: The above question can be solved in an alternate way as shown: We know that \[\cos \dfrac{\pi }{4}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\]\[\Rightarrow {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{4}\]. Now, we can also say that, \[{{\cot }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{4}\]. Now, \[{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)={{\cot }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)\]. Now, we will subtract \[\pi \] on both sides. Thus we will get:
\[\begin{align}
& {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)-\pi ={{\cot }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right)-\pi \\
& \Rightarrow \pi -{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\pi -{{\cot }^{-1}}\left( 1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)={{\cot }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Now the value of \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)\] = \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)+{{\cot }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)\]. Now we will apply the identity: \[{{\cot }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)+{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{2}\]. So, we will get, \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( -1 \right)+{{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\dfrac{\pi }{2}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




