
For the complex ion \[{[Fe{(CN)_6}]^{ - 3}}\], state:
(A) The type of hybridisation
(B) The magnetic behaviour
(C) The oxidation number of the central metal atom.
Answer
542.4k+ views
Hint: The strong field ligands in a compound cause large splitting while the weak field ligands in a compound cause small splitting. The large splitted compounds are low spin complexes while the small splitted compounds are high spin complexes.
Complete answer:
\[{[Fe{(CN)_6}]^{ - 3}}\]anion is known as ferricyanide. It is also known as hexacyanoferrate (III). The most common salt of this anion is potassium ferricyanide, a red crystalline material that is used as an oxidant.
\[{[Fe{(CN)_6}]^{ - 3}}\] consists of \[F{e^{3 + }}\] as the central atom bound in octahedral geometry to six cyanide ligands. The iron is low spin due to the presence of six strong field ligands. Compared to normal cyanides like potassium cyanide, ferrocyanides are much less toxic because of the tight hold of the cyanide ions to the iron centre. The structure of \[{[Fe{(CN)_6}]^{ - 3}}\] is:

(A) In \[{[Fe{(CN)_6}]^{ - 3}}\]complex, the cyano group i.e., CN is a strong field ligand. Therefore, Cyano group being a strong field ligand will form a low spin complex using inner 3d orbitals. As there are six ligands present, it will form octahedral geometry. Therefore, the hybridisation present in \[{[Fe{(CN)_6}]^{ - 3}}\]is \[{d^2}s{p^3}\].
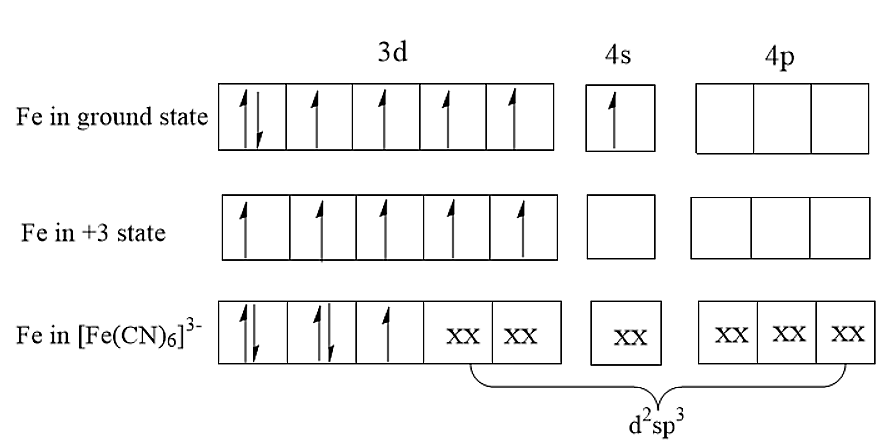
(B) The central atom has an oxidation number of +3. Thus, \[F{e^{3 + }}\]has an unpaired electron. Thus, the complex will be paramagnetic.
(C) The oxidation number of the central metal atom is +3, which can be calculated by the equation
x + 6(-1) = -3
x = +3
Note:
Remember that the presence of one unpaired electron is sufficient for paramagnetism. Make sure to check the configuration of each atom for paramagnetism also, with the molecule as a whole.
Complete answer:
\[{[Fe{(CN)_6}]^{ - 3}}\]anion is known as ferricyanide. It is also known as hexacyanoferrate (III). The most common salt of this anion is potassium ferricyanide, a red crystalline material that is used as an oxidant.
\[{[Fe{(CN)_6}]^{ - 3}}\] consists of \[F{e^{3 + }}\] as the central atom bound in octahedral geometry to six cyanide ligands. The iron is low spin due to the presence of six strong field ligands. Compared to normal cyanides like potassium cyanide, ferrocyanides are much less toxic because of the tight hold of the cyanide ions to the iron centre. The structure of \[{[Fe{(CN)_6}]^{ - 3}}\] is:

(A) In \[{[Fe{(CN)_6}]^{ - 3}}\]complex, the cyano group i.e., CN is a strong field ligand. Therefore, Cyano group being a strong field ligand will form a low spin complex using inner 3d orbitals. As there are six ligands present, it will form octahedral geometry. Therefore, the hybridisation present in \[{[Fe{(CN)_6}]^{ - 3}}\]is \[{d^2}s{p^3}\].

(B) The central atom has an oxidation number of +3. Thus, \[F{e^{3 + }}\]has an unpaired electron. Thus, the complex will be paramagnetic.
(C) The oxidation number of the central metal atom is +3, which can be calculated by the equation
x + 6(-1) = -3
x = +3
Note:
Remember that the presence of one unpaired electron is sufficient for paramagnetism. Make sure to check the configuration of each atom for paramagnetism also, with the molecule as a whole.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




