
For the circuit shown in the figure,
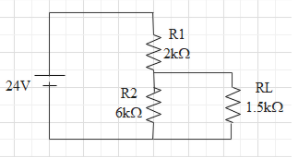
This question has multiple correct options
A. the current I through the battery is 7.5mA
B. the potential difference across ${{R}_{L}}$ is 18V
C. ratio of power dissipated in ${{R}_{1}}$ and ${{R}_{2}}$ is 3
D. if ${{R}_{1}}$ and ${{R}_{2}}$ are interchanged, magnitude of the power dissipated in ${{R}_{L}}$ will decrease by a factor of 9

Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, first obtain the equivalent resistance in the circuit. Then using the voltage, current and resistance relation we can find the current through the circuit. Now, find the voltage across the resistances and use the power, voltage and resistance relation to find the power dissipated through the resistances. With the resistances interchanged, follow the similar procedure to find the required answer.
Complete answer:
Consider the given figure in the question.
The given resistances are,
$\begin{align}
& {{R}_{1}}=2k\Omega =2\times {{10}^{3}}\Omega \\
& {{R}_{2}}=6k\Omega =6\times {{10}^{3}}\Omega \\
& {{R}_{L}}=1.5k\Omega =1.5\times {{10}^{3}}\Omega \\
\end{align}$
Now, to find the current through the battery, we need to find the equivalent resistance through which the current is passed.
The equivalent resistance of ${{R}_{2}}$ and ${{R}_{L}}$ is,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{{{R}'}}=\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{L}}} \\
& \dfrac{1}{{{R}'}}=\dfrac{1}{6k\Omega }+\dfrac{1}{1.5k\Omega }=\dfrac{7.5}{6\times 1.5} \\
& {R}'=\dfrac{6\times 1.5}{7.5} \\
& {R}'=\dfrac{6}{5}k\Omega \\
\end{align}$
The total resistance of the circuit will be,
$\begin{align}
& R={{R}_{1}}+{R}' \\
& R=2k\Omega +\dfrac{6}{5}k\Omega \\
& R=3.2k\Omega \\
\end{align}$
The voltage of the battery connected in the circuit is $V=24V$
Let, the current passing through the battery will be I.
So, the current through the battery will be,
$\begin{align}
& I=\dfrac{V}{R} \\
& I=\dfrac{24V}{3.2K} \\
& I=7.5mA \\
\end{align}$
The potential difference across the resistance ${{R}_{1}}$ is,
${{V}_{1}}=I\times {{R}_{1}}=7.5mA\times 2k\Omega =15V$
The potential difference across the resistance ${{R}_{1}}$ is,
${{V}_{2}}=24V-15V=9V$
So, the potential difference across the resistance ${{R}_{L}}$ will also be 9V.
Now, the ratio of the power dissipated in ${{R}_{1}}$ and ${{R}_{2}}$ is,
$\begin{align}
& {{P}_{1}}:{{P}_{2}}=\dfrac{V_{1}^{2}}{{{R}_{1}}}:\dfrac{V_{2}^{2}}{{{R}_{2}}} \\
& {{P}_{1}}:{{P}_{2}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{{{15}^{2}}}{2}}{\dfrac{{{9}^{2}}}{6}}=\dfrac{225}{2}\times \dfrac{6}{81} \\
& {{P}_{1}}:{{P}_{2}}=\dfrac{25}{3} \\
\end{align}$
In this configuration, the power dissipated through ${{R}_{{{L}_{{}}}}}$will be,
${{P}_{L}}=\dfrac{V_{2}^{2}}{{{R}_{L}}}=\dfrac{{{9}^{2}}}{1.5\times {{10}^{3}}}=54mW$
Now, interchanging the position of the resistances ${{R}_{1}}$ and ${{R}_{2}}$,
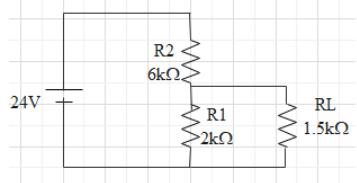
The equivalent resistances of ${{R}_{1}}$and ${{R}_{2}}$ will be,
${R}'=\dfrac{2\times 1.5}{2+1.5}=\dfrac{3}{3.5}$
Now, the voltage through ${{R}_{1}}$ or ${{R}_{L}}$ will be, ${{V}_{L}}=\dfrac{{{R}'}}{{{R}_{2}}+{R}'}\times 24V=\dfrac{\dfrac{3}{3.5}}{6+\dfrac{3}{3.5}}\times 24=3V$
So, the power dissipated through ${{R}_{L}}$ will be,
${{P}_{L}}^{\prime }=\dfrac{{{V}_{L}}^{2}}{{{R}_{L}}}=\dfrac{{{3}^{2}}}{1.5}=6mW$
The ratio of the power ${{P}_{L}}^{\prime }$ and ${{P}_{L}}$ will be,
$\dfrac{{{P}_{L}}^{\prime }}{{{P}_{L}}}=\dfrac{3mW}{54mW}=\dfrac{1}{9}$
After the resistances are interchanged, the power through the resistances are decreased by a factor of 9.
So, the correct options are (A) and (D).
Note:
As shown in the second part of the question, in the first part also we can directly find the potential differences across the resistances. In the first part we have found out the current because we are asked to find the current in the circuit.
Complete answer:
Consider the given figure in the question.
The given resistances are,
$\begin{align}
& {{R}_{1}}=2k\Omega =2\times {{10}^{3}}\Omega \\
& {{R}_{2}}=6k\Omega =6\times {{10}^{3}}\Omega \\
& {{R}_{L}}=1.5k\Omega =1.5\times {{10}^{3}}\Omega \\
\end{align}$
Now, to find the current through the battery, we need to find the equivalent resistance through which the current is passed.
The equivalent resistance of ${{R}_{2}}$ and ${{R}_{L}}$ is,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{{{R}'}}=\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{R}_{L}}} \\
& \dfrac{1}{{{R}'}}=\dfrac{1}{6k\Omega }+\dfrac{1}{1.5k\Omega }=\dfrac{7.5}{6\times 1.5} \\
& {R}'=\dfrac{6\times 1.5}{7.5} \\
& {R}'=\dfrac{6}{5}k\Omega \\
\end{align}$
The total resistance of the circuit will be,
$\begin{align}
& R={{R}_{1}}+{R}' \\
& R=2k\Omega +\dfrac{6}{5}k\Omega \\
& R=3.2k\Omega \\
\end{align}$
The voltage of the battery connected in the circuit is $V=24V$
Let, the current passing through the battery will be I.
So, the current through the battery will be,
$\begin{align}
& I=\dfrac{V}{R} \\
& I=\dfrac{24V}{3.2K} \\
& I=7.5mA \\
\end{align}$
The potential difference across the resistance ${{R}_{1}}$ is,
${{V}_{1}}=I\times {{R}_{1}}=7.5mA\times 2k\Omega =15V$
The potential difference across the resistance ${{R}_{1}}$ is,
${{V}_{2}}=24V-15V=9V$
So, the potential difference across the resistance ${{R}_{L}}$ will also be 9V.
Now, the ratio of the power dissipated in ${{R}_{1}}$ and ${{R}_{2}}$ is,
$\begin{align}
& {{P}_{1}}:{{P}_{2}}=\dfrac{V_{1}^{2}}{{{R}_{1}}}:\dfrac{V_{2}^{2}}{{{R}_{2}}} \\
& {{P}_{1}}:{{P}_{2}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{{{15}^{2}}}{2}}{\dfrac{{{9}^{2}}}{6}}=\dfrac{225}{2}\times \dfrac{6}{81} \\
& {{P}_{1}}:{{P}_{2}}=\dfrac{25}{3} \\
\end{align}$
In this configuration, the power dissipated through ${{R}_{{{L}_{{}}}}}$will be,
${{P}_{L}}=\dfrac{V_{2}^{2}}{{{R}_{L}}}=\dfrac{{{9}^{2}}}{1.5\times {{10}^{3}}}=54mW$
Now, interchanging the position of the resistances ${{R}_{1}}$ and ${{R}_{2}}$,

The equivalent resistances of ${{R}_{1}}$and ${{R}_{2}}$ will be,
${R}'=\dfrac{2\times 1.5}{2+1.5}=\dfrac{3}{3.5}$
Now, the voltage through ${{R}_{1}}$ or ${{R}_{L}}$ will be, ${{V}_{L}}=\dfrac{{{R}'}}{{{R}_{2}}+{R}'}\times 24V=\dfrac{\dfrac{3}{3.5}}{6+\dfrac{3}{3.5}}\times 24=3V$
So, the power dissipated through ${{R}_{L}}$ will be,
${{P}_{L}}^{\prime }=\dfrac{{{V}_{L}}^{2}}{{{R}_{L}}}=\dfrac{{{3}^{2}}}{1.5}=6mW$
The ratio of the power ${{P}_{L}}^{\prime }$ and ${{P}_{L}}$ will be,
$\dfrac{{{P}_{L}}^{\prime }}{{{P}_{L}}}=\dfrac{3mW}{54mW}=\dfrac{1}{9}$
After the resistances are interchanged, the power through the resistances are decreased by a factor of 9.
So, the correct options are (A) and (D).
Note:
As shown in the second part of the question, in the first part also we can directly find the potential differences across the resistances. In the first part we have found out the current because we are asked to find the current in the circuit.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




