
For square planar complex of platinum (II) , ${{[Pt(N{{H}_{3}})(Br)(Cl)py]}^{0}}$ , how many isomeric forms are possible?
(A) Two
(B) Three
(C) Four
(D) six
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Coordination compounds can form different isomers. Two main types of isomerism exhibited by coordination compounds are stereo isomerism and structural isomerism. Stereoisomers include both geometric and optical isomers. Structural isomers include linkage, ionization, coordination, and hydrate isomers.
Complete step by step solution:
(1) square planar complexes with formula [MABCD] can form three isomers. These isomers are called “A trans to B”.
(2) square planar complex with formula $[M{{A}_{2}}{{B}_{2}}]$ can form two isomers.
Generally, Cis- and trans- refer to the postion of 2 groups relative to each other. In cis- isomer “they are next to each other” , i.e. at 90 degrees in relation to central metal ion, whereas in the trans- isomer they are “opposite to each other”, i.e. 180 degrees relative to the central metal ion.
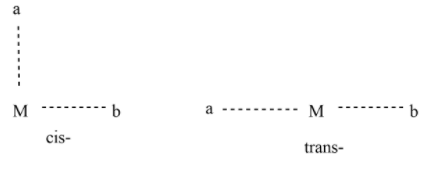
Where, M=central metal ion , ‘a’ and ‘b’ are ligands.
Given complex, ${{[Pt(N{{H}_{3}})(Br)(Cl)py]}^{0}}$, $N{{H}_{3}},Br,Cl\And py$ are mono dentate ligands.
The above complex is related to a square planar with a type of [MABCD] formula. So, this complex can exhibit three isomers.
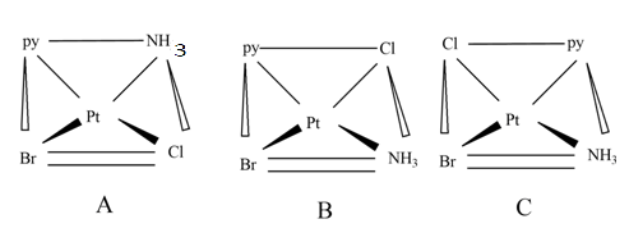
A,B, and C are geometric isomers of a given square planar complex. The A isomer is cis isomer named is cis-aminobromo-cis-chloropyridineplatinum(II). Similarly B and C isomers represent trans isomers.
The first report of the three geometric isomers being isolated and characterized of the type [MABCD] in 1928.
From the above geometric isomers, we can give IUPAC names of the isomers separately.
For example, the figure A, the IUPAC name of the isomer is cis-aminobromo-cis-chloropyridineplatinum(II).
Hence , the correct answer is option C = three.
Note: The reactivity and properties of different isomers are often not the same and contribute to applications of coordination compounds. Metal complxes exhibits geometrical isomerism with ligands adject to other is cis-isomer across from another is trans-isomer. Depending upon the property of ligand, structural isomerism exhibits. By using the isomerism of the coordination compounds, can predict their IUPAC names.
Complete step by step solution:
(1) square planar complexes with formula [MABCD] can form three isomers. These isomers are called “A trans to B”.
(2) square planar complex with formula $[M{{A}_{2}}{{B}_{2}}]$ can form two isomers.
Generally, Cis- and trans- refer to the postion of 2 groups relative to each other. In cis- isomer “they are next to each other” , i.e. at 90 degrees in relation to central metal ion, whereas in the trans- isomer they are “opposite to each other”, i.e. 180 degrees relative to the central metal ion.

Where, M=central metal ion , ‘a’ and ‘b’ are ligands.
Given complex, ${{[Pt(N{{H}_{3}})(Br)(Cl)py]}^{0}}$, $N{{H}_{3}},Br,Cl\And py$ are mono dentate ligands.
The above complex is related to a square planar with a type of [MABCD] formula. So, this complex can exhibit three isomers.

A,B, and C are geometric isomers of a given square planar complex. The A isomer is cis isomer named is cis-aminobromo-cis-chloropyridineplatinum(II). Similarly B and C isomers represent trans isomers.
The first report of the three geometric isomers being isolated and characterized of the type [MABCD] in 1928.
From the above geometric isomers, we can give IUPAC names of the isomers separately.
For example, the figure A, the IUPAC name of the isomer is cis-aminobromo-cis-chloropyridineplatinum(II).
Hence , the correct answer is option C = three.
Note: The reactivity and properties of different isomers are often not the same and contribute to applications of coordination compounds. Metal complxes exhibits geometrical isomerism with ligands adject to other is cis-isomer across from another is trans-isomer. Depending upon the property of ligand, structural isomerism exhibits. By using the isomerism of the coordination compounds, can predict their IUPAC names.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




