
For self-pollination, flower must be
A.Unisexual
B.Bisexual
C.Monosexual
D.Asexual
Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint: Pollination is a process in which pollen grains are transferred from anther to stigma. It results in fertilization of female gamete with male gamete. There are two types i.e. Self-pollination and cross pollination. Self-pollination takes place within the flower. Cross pollination occurs from one to another flower.
Complete answer:
Pollination is of two types.
(a) Self-pollination (autogamy): It takes place within a flower
(b) Cross-pollination (allogamy): It occurs from one flower to another flower.
It is of two subtypes:
(i) Geitonogamy: It is from one flower to another flower on the same plant. Genetically, it is a self-pollination ecologically a cross-pollination
(ii) Xenogamy: It is a true cross-pollination that occurs from one plant to another plant.
self-pollination : It is true pollination. The pollen grains are tranfered from anther to stigma within same flower which means they need to be bisexual. It does not require pollination.
Adaptations for self-pollination: The most favourable conditions for self-pollination are as under:
(i) Bisexuality: Bisexual flowers ensures self-pollination.
(ii) Homogamy : It is a condition where stamen and carpel mature at the same time.
(iii) Cleistogamy :Cleistogamous flowers never open and seed setting in these flowers occur without the exposition of their sex-organs as these flowers are bisexual. Commelina benghalensis is the striking example of cleistogamy. Other examples include members of family Violaceae, Balsaminaceae and Polygonaceae.
Cleistogamy ensures self-pollination as there are no chances of cross-pollination.
In Commelina benghalensis and Arachis hypogea (groundnut) cleistogamy is accompanied by geocarpy (formation of fruits below the soil).
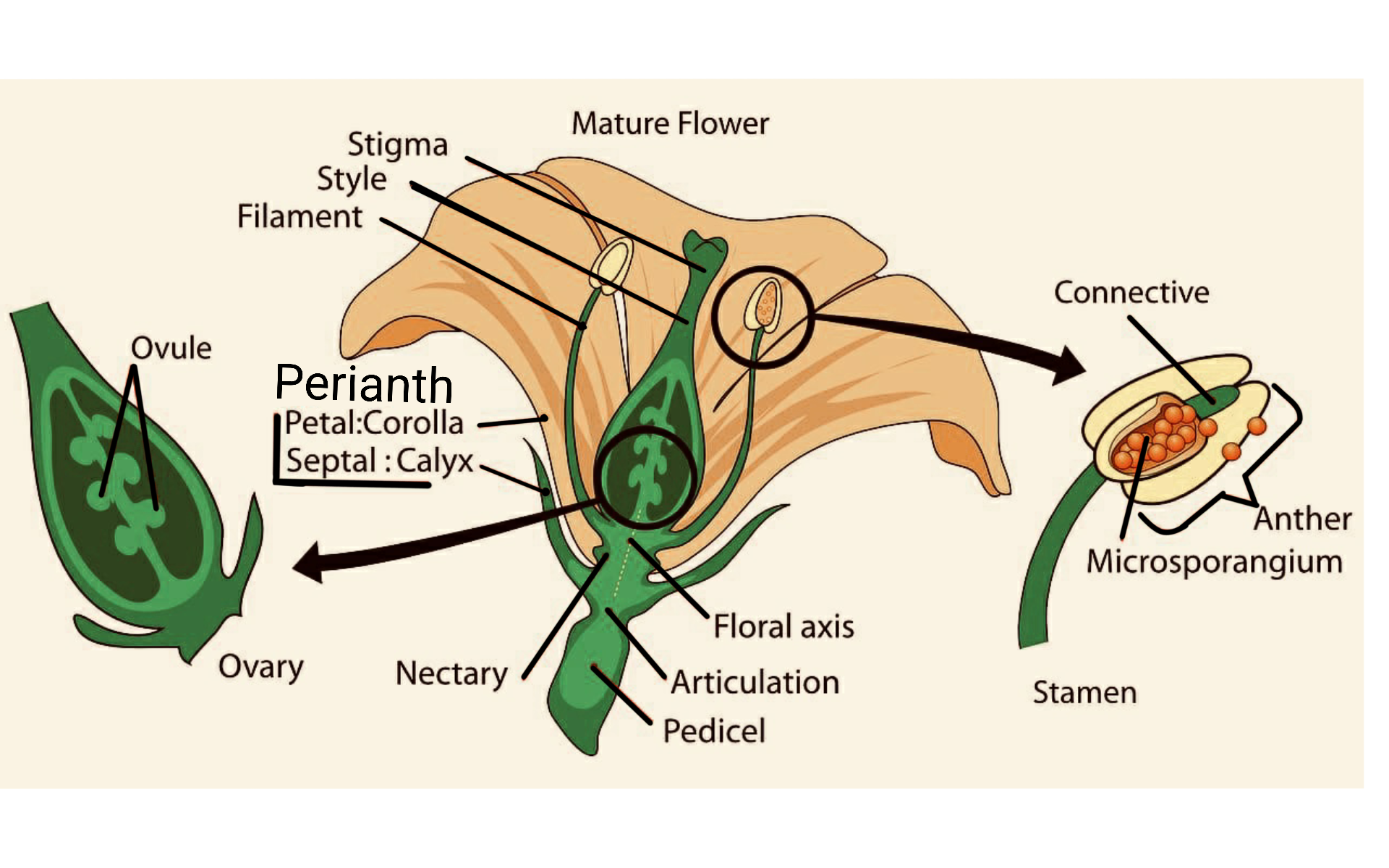
Hence, the correct answer is option (B)
Note: Advantage/Disadvantage of self-pollination
(a) Self-pollination is almost certain in a bisexual flower. It is an independent process.
(b) Another advantage is purity of generation.
(c) The most distinct disadvantage of self-pollination is that it results in a weaker progeny if it continues for several generations.
Complete answer:
Pollination is of two types.
(a) Self-pollination (autogamy): It takes place within a flower
(b) Cross-pollination (allogamy): It occurs from one flower to another flower.
It is of two subtypes:
(i) Geitonogamy: It is from one flower to another flower on the same plant. Genetically, it is a self-pollination ecologically a cross-pollination
(ii) Xenogamy: It is a true cross-pollination that occurs from one plant to another plant.
self-pollination : It is true pollination. The pollen grains are tranfered from anther to stigma within same flower which means they need to be bisexual. It does not require pollination.
Adaptations for self-pollination: The most favourable conditions for self-pollination are as under:
(i) Bisexuality: Bisexual flowers ensures self-pollination.
(ii) Homogamy : It is a condition where stamen and carpel mature at the same time.
(iii) Cleistogamy :Cleistogamous flowers never open and seed setting in these flowers occur without the exposition of their sex-organs as these flowers are bisexual. Commelina benghalensis is the striking example of cleistogamy. Other examples include members of family Violaceae, Balsaminaceae and Polygonaceae.
Cleistogamy ensures self-pollination as there are no chances of cross-pollination.
In Commelina benghalensis and Arachis hypogea (groundnut) cleistogamy is accompanied by geocarpy (formation of fruits below the soil).

Hence, the correct answer is option (B)
Note: Advantage/Disadvantage of self-pollination
(a) Self-pollination is almost certain in a bisexual flower. It is an independent process.
(b) Another advantage is purity of generation.
(c) The most distinct disadvantage of self-pollination is that it results in a weaker progeny if it continues for several generations.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE




