
What is the focal length of a double convex lens for which the radius of curvature of each surface is 60 cm (n=1.5)?
A. 50 cm
B. 60 cm
C. 90 cm
D. 30 cm
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: Generally, if nothing is given about the lens, we take it to be thin and having focal length independent of the refractive index. In that case, we take focal length as half of the radius of curvature. But practically, the lens has thickness and the parameters depend upon the refractive index also.
Formula used:
$\dfrac 1f = \left( \dfrac{n_2}{n_1} -1\right) \left( \dfrac{1}{R_1} - \dfrac{1}{R_2}\right)$
Complete step by step answer:
For computing the focal length of any lens, we practically use the formula called lens makers formula. This formula is given by $\dfrac 1f = \left( \dfrac{n_2}{n_1} -1\right) \left( \dfrac{1}{R_1} - \dfrac{1}{R_2}\right)$
Here, $R_1\ and\ R_2$are radii of curvature of two faces of the lens. $n_2$ is the refractive index of material and $n_1$ is the refractive index of the medium in which the lens is kept, as shown in the figure.
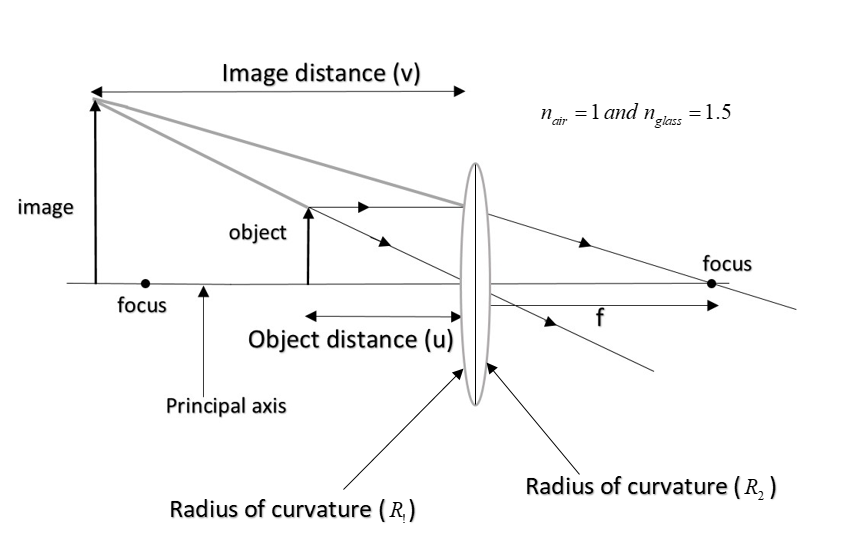
Given, $n_2 = 1.5,\ n_1 = 1\ (by\ default)$
Also given that the radii of curvature for both sides is the same. But, for the left side, we will take radius to be positive whereas for the right side, we will take radius to be negative (as per the sign conventions).
Hence $R_1 = -60cm\ and\ R_2 = +60cm$
Putting the values in the equation: $\dfrac1f = \left( \dfrac{n_2}{n_1} -1\right) \left( \dfrac{1}{R_1} - \dfrac{1}{R_2}\right)$, we get:
$\dfrac1f = \left( \dfrac{1.5}{1} -1\right) \left( \dfrac{1}{-60} - \dfrac{1}{60}\right)$
$\implies \dfrac1f = (0.5)\left( -\dfrac{2}{60} \right) = \dfrac{-1}{60}$
Or $f = -60 cm$
Hence, the focal length of the double convex lens is -60 cm.
Note:
Students should note that in case of a thin lens, we directly take ‘f’ as half of ‘R’. But in this question, we have the value of ‘R’ and ‘f’ is the same. One must not confuse between a thin and practical lens. Whenever the refractive index of the material is given and the lens is not thin, we have to calculate the focal length of the lens using the lens makers formula.
Formula used:
$\dfrac 1f = \left( \dfrac{n_2}{n_1} -1\right) \left( \dfrac{1}{R_1} - \dfrac{1}{R_2}\right)$
Complete step by step answer:
For computing the focal length of any lens, we practically use the formula called lens makers formula. This formula is given by $\dfrac 1f = \left( \dfrac{n_2}{n_1} -1\right) \left( \dfrac{1}{R_1} - \dfrac{1}{R_2}\right)$
Here, $R_1\ and\ R_2$are radii of curvature of two faces of the lens. $n_2$ is the refractive index of material and $n_1$ is the refractive index of the medium in which the lens is kept, as shown in the figure.

Given, $n_2 = 1.5,\ n_1 = 1\ (by\ default)$
Also given that the radii of curvature for both sides is the same. But, for the left side, we will take radius to be positive whereas for the right side, we will take radius to be negative (as per the sign conventions).
Hence $R_1 = -60cm\ and\ R_2 = +60cm$
Putting the values in the equation: $\dfrac1f = \left( \dfrac{n_2}{n_1} -1\right) \left( \dfrac{1}{R_1} - \dfrac{1}{R_2}\right)$, we get:
$\dfrac1f = \left( \dfrac{1.5}{1} -1\right) \left( \dfrac{1}{-60} - \dfrac{1}{60}\right)$
$\implies \dfrac1f = (0.5)\left( -\dfrac{2}{60} \right) = \dfrac{-1}{60}$
Or $f = -60 cm$
Hence, the focal length of the double convex lens is -60 cm.
Note:
Students should note that in case of a thin lens, we directly take ‘f’ as half of ‘R’. But in this question, we have the value of ‘R’ and ‘f’ is the same. One must not confuse between a thin and practical lens. Whenever the refractive index of the material is given and the lens is not thin, we have to calculate the focal length of the lens using the lens makers formula.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




