
How do you find the values of \[\sin 2\theta \] and $\cos 2\theta $ when $\cos \theta = \dfrac{{12}}{{13}}?$
Answer
567.9k+ views
Hint: From trigonometric ratios we know that cosine function is adjacent by hypotenuse. So we have the values of adjacent side and hypotenuse side, by using Pythagoras formula given by: $Hypotenus{e^2} = Adjacen{t^2} + Perpendicula{r^2}$ we can find the other side. By using trigonometric ratios we can find the required answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, we have given $\cos \theta = \dfrac{{12}}{{13}}$ , from the trigonometric ratios we know that cosine function is nothing but $\dfrac{{adjacent}}{{hypotenuse}}$ which can be represented as in the below diagram
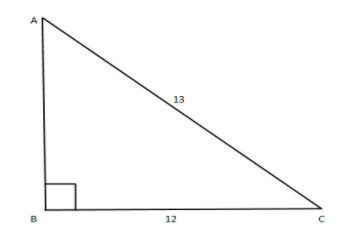
So in a triangle we know the values of adjacent and hypotenuse sides, the other side that is perpendicular or opposite can be find by using Pythagoras theorem formula given by $Hypotenus{e^2} = Adjacen{t^2} + Perpendicula{r^2}$
Now, adjacent side $BC$ value is $12$ and hypotenuse $AC$ is $13$ let, $x$ be the perpendicular $AB$ .
Therefore, we can write as $A{C^2} = B{C^2} + A{B^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {13^2} = {12^2} + {x^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {13^2} - {12^2} = {x^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} = 169 - 144$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} = 25$
$ \Rightarrow x = 5$
Therefore, the perpendicular value is $5$ .
Now, the diagram is as follows:

By using trigonometric ratios we can write as follows:
Sine function is given by: $\dfrac{{opposite}}{{hypotenuse}}$ $ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{5}{{13}}$
Tangent function is given by: $\dfrac{{opposite}}{{adjacent}}$ $ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{5}{{12}}$
In the question they have asked to find the values of \[\sin 2\theta \] and $\cos 2\theta $.
We have a formula for \[\sin 2\theta \] which is given as \[\sin 2\theta = 2\sin \theta \cos \theta \]
By substituting the values in the above formula, we get
\[\sin 2\theta = 2 \times \dfrac{5}{{13}} \times \dfrac{{12}}{{13}}\]
On simplification, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \sin 2\theta = \dfrac{{120}}{{169}}\]
To find $\cos 2\theta $ , we have a formula for $\cos 2\theta $ given by $\cos 2\theta = {\cos ^2}\theta - {\sin ^2}\theta $
By substituting the known values in the above $\cos 2\theta $ formula, we get
$\cos 2\theta = {\left( {\dfrac{{12}}{{13}}} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{5}{{13}}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \cos 2\theta = \left( {\dfrac{{144}}{{169}}} \right) - \left( {\dfrac{{25}}{{169}}} \right)$
On simplification, we get
$ \Rightarrow \cos 2\theta = \dfrac{{119}}{{169}}$
Therefore \[\sin 2\theta = \dfrac{{120}}{{169}}\] and $\cos 2\theta = \dfrac{{119}}{{169}}$.
Note: Whenever we have this type of problem we have to remember the trigonometric ratios for all the functions and also the double angle formulas which makes it easy to solve the problem. The double angle formula for cosine function, we can also use $\cos 2\theta = 1 - 2{\sin ^2}\theta $ we get the same answer. But you need to remember the formulas.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, we have given $\cos \theta = \dfrac{{12}}{{13}}$ , from the trigonometric ratios we know that cosine function is nothing but $\dfrac{{adjacent}}{{hypotenuse}}$ which can be represented as in the below diagram

So in a triangle we know the values of adjacent and hypotenuse sides, the other side that is perpendicular or opposite can be find by using Pythagoras theorem formula given by $Hypotenus{e^2} = Adjacen{t^2} + Perpendicula{r^2}$
Now, adjacent side $BC$ value is $12$ and hypotenuse $AC$ is $13$ let, $x$ be the perpendicular $AB$ .
Therefore, we can write as $A{C^2} = B{C^2} + A{B^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {13^2} = {12^2} + {x^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {13^2} - {12^2} = {x^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} = 169 - 144$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} = 25$
$ \Rightarrow x = 5$
Therefore, the perpendicular value is $5$ .
Now, the diagram is as follows:

By using trigonometric ratios we can write as follows:
Sine function is given by: $\dfrac{{opposite}}{{hypotenuse}}$ $ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{5}{{13}}$
Tangent function is given by: $\dfrac{{opposite}}{{adjacent}}$ $ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{5}{{12}}$
In the question they have asked to find the values of \[\sin 2\theta \] and $\cos 2\theta $.
We have a formula for \[\sin 2\theta \] which is given as \[\sin 2\theta = 2\sin \theta \cos \theta \]
By substituting the values in the above formula, we get
\[\sin 2\theta = 2 \times \dfrac{5}{{13}} \times \dfrac{{12}}{{13}}\]
On simplification, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \sin 2\theta = \dfrac{{120}}{{169}}\]
To find $\cos 2\theta $ , we have a formula for $\cos 2\theta $ given by $\cos 2\theta = {\cos ^2}\theta - {\sin ^2}\theta $
By substituting the known values in the above $\cos 2\theta $ formula, we get
$\cos 2\theta = {\left( {\dfrac{{12}}{{13}}} \right)^2} - {\left( {\dfrac{5}{{13}}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \cos 2\theta = \left( {\dfrac{{144}}{{169}}} \right) - \left( {\dfrac{{25}}{{169}}} \right)$
On simplification, we get
$ \Rightarrow \cos 2\theta = \dfrac{{119}}{{169}}$
Therefore \[\sin 2\theta = \dfrac{{120}}{{169}}\] and $\cos 2\theta = \dfrac{{119}}{{169}}$.
Note: Whenever we have this type of problem we have to remember the trigonometric ratios for all the functions and also the double angle formulas which makes it easy to solve the problem. The double angle formula for cosine function, we can also use $\cos 2\theta = 1 - 2{\sin ^2}\theta $ we get the same answer. But you need to remember the formulas.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




