
Find the value of $x$ from the given figure in which O is the center of the circle.
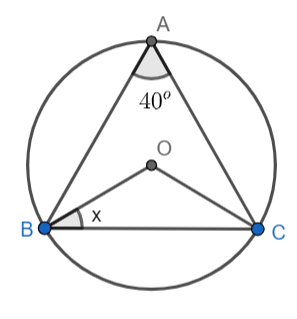
A. x=50o
B. x=60o
C. x=80o
D. x=90o

Answer
624.9k+ views
Hint: We can find the value of $x$ in the given figure by using the property of circles - that the angle subtended by an arc which is at the center of the circle is double to the angle subtended by the same arc on the other perimeters of the same circle.Then, we use the property of a triangle that the sum of all the three angles of a triangle is $180{}^\circ $.Hence calculate the value of x.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given in the question that the arc ‘$BC$’ subtends an angle of $40{}^\circ $ at point A and the same arc ‘$BC$’ subtends an angle $BOC$ at the center of the circle, then we have to find the value of $x$ or we can use angle $OBC$.
If we observe the figure carefully, then from the figure we can conclude that $ABC$ and $OBC$ are two triangles and $ABC$ is a triangle circumscribed in the circle having radius $OB$ or $OC$. Also, in triangle $OBC$ we have side $OB$ is equal to side $OC$ as both of them are radii of the same circle.
Now, we know that the angle subtended by an arc which is at the center of the circle is double of the angle subtended by the same arc on the other perimeters of the same circle.
Looking closely at the figure, we can see that angles $\angle BAC$ and $\angle BOC$ are the angles subtended by the same arc .It is at centre and is at the circumference of the circle.
By using this theorem of circle, we get that $\angle BAC=2\times \angle BOC$.
Thus, we can write $\angle BOC=\dfrac{\angle BAC}{2}$.
From this, we get $\angle BOC=2\times \angle BAC$.
Also, it is given in the question that $\angle BAC=40{}^\circ $. Thus, on putting the value of $\angle BAC$ as $40{}^\circ $, we get
$\angle BOC=2\times 40{}^\circ $
$\angle BOC=80{}^\circ $
Now, we know that the sum of all the sides of a triangle is $180{}^\circ $. So, in triangle BOC, we have
$\angle OBC+\angle OCB+\angle CBO=180{}^\circ $
We have already discussed that side $OB$ is equal to side $OC$ as both of them are the radii of the same circle. So, from this we can say that $\angle OCB$ is equal to $\angle OBC$ as the angle opposite to the equal sides of a triangle are equal. So, we get
$\angle OBC=\angle OCB=x$
On putting the value of $\angle OBC$ and $\angle OCB$ as $x$ and $\angle BOC=80{}^\circ $, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x+x+80{}^\circ =180{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow 2x+80{}^\circ =180{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=180{}^\circ -80{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=100{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{100{}^\circ }{2} \\
& \Rightarrow x=50{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
Thus, $\angle OBC=\angle OCB=50{}^\circ $.
Therefore the value of $x$ in the figure is $50{}^\circ $. We get option A $(x=50{}^\circ )$ as the correct answer.
Note: In such types of questions try to implement theorems of the circle which are already defined. This will reduce your effort to solve the same problem. If you don’t apply them then you have to derive all the concepts individually which will consume your lots of time and also, the probability of error will be increased.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given in the question that the arc ‘$BC$’ subtends an angle of $40{}^\circ $ at point A and the same arc ‘$BC$’ subtends an angle $BOC$ at the center of the circle, then we have to find the value of $x$ or we can use angle $OBC$.
If we observe the figure carefully, then from the figure we can conclude that $ABC$ and $OBC$ are two triangles and $ABC$ is a triangle circumscribed in the circle having radius $OB$ or $OC$. Also, in triangle $OBC$ we have side $OB$ is equal to side $OC$ as both of them are radii of the same circle.
Now, we know that the angle subtended by an arc which is at the center of the circle is double of the angle subtended by the same arc on the other perimeters of the same circle.
Looking closely at the figure, we can see that angles $\angle BAC$ and $\angle BOC$ are the angles subtended by the same arc .It is at centre and is at the circumference of the circle.
By using this theorem of circle, we get that $\angle BAC=2\times \angle BOC$.
Thus, we can write $\angle BOC=\dfrac{\angle BAC}{2}$.
From this, we get $\angle BOC=2\times \angle BAC$.
Also, it is given in the question that $\angle BAC=40{}^\circ $. Thus, on putting the value of $\angle BAC$ as $40{}^\circ $, we get
$\angle BOC=2\times 40{}^\circ $
$\angle BOC=80{}^\circ $
Now, we know that the sum of all the sides of a triangle is $180{}^\circ $. So, in triangle BOC, we have
$\angle OBC+\angle OCB+\angle CBO=180{}^\circ $
We have already discussed that side $OB$ is equal to side $OC$ as both of them are the radii of the same circle. So, from this we can say that $\angle OCB$ is equal to $\angle OBC$ as the angle opposite to the equal sides of a triangle are equal. So, we get
$\angle OBC=\angle OCB=x$
On putting the value of $\angle OBC$ and $\angle OCB$ as $x$ and $\angle BOC=80{}^\circ $, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x+x+80{}^\circ =180{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow 2x+80{}^\circ =180{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=180{}^\circ -80{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=100{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{100{}^\circ }{2} \\
& \Rightarrow x=50{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
Thus, $\angle OBC=\angle OCB=50{}^\circ $.
Therefore the value of $x$ in the figure is $50{}^\circ $. We get option A $(x=50{}^\circ )$ as the correct answer.
Note: In such types of questions try to implement theorems of the circle which are already defined. This will reduce your effort to solve the same problem. If you don’t apply them then you have to derive all the concepts individually which will consume your lots of time and also, the probability of error will be increased.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




