
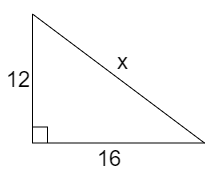
How do I find the value of $x$ ? Do the side lengths form a Pythagorean triple?

Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint: Here, the triangle given is right-angled. Hence, the best way to find the length of one side when two other sides are given in a right-angled triangle is by using the Pythagoras theorem. The integer values that satisfy the Pythagoras theorem are known as Pythagorean Triplets.
Formula used: Pythagoras Theorem: $A{B^2} + B{C^2} = A{C^2}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
Pythagoras theorem is used whenever we need to find one of the sides of a right-angled triangle
The Pythagoras theorem states, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the length opposite to the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the remaining two sides that form a right angle.
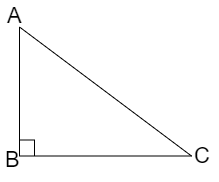
Considering the triangle given here $\;AC$ is the hypotenuse while $\;AB$ and $\;BC$ form the right angle
Hence the Pythagoras theorem is shown as, $A{B^2} + B{C^2} = A{C^2}$ .
Comparing this figure with the figure given, we can obtain the following details
AB = $\;12$ , BC = $\;16$ , and AC = $x$
Now, substituting these values in the Pythagoras theorem,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {12} \right)^2} + {\left( {16} \right)^2} = {\left( x \right)^2}$
Calculating the squares of these values,
$ \Rightarrow 144 + 256 = {x^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 400 = {x^2}$
Now, we know that $\;400$ is a perfect square of $\;20$ .
$ \Rightarrow {(20)^2} = {x^2}$
Applying root on both sides
$ \Rightarrow x = 20$
Thus, the length of the third side or hypotenuse of the right-angled triangle is $\;20$ units.
Now, as we obtained these values through the Pythagoras theorem, we can say that these values satisfy the Pythagoras theorem and thus these values can be called a Pythagorean triplet
The Pythagorean triplet is shown as $\left( {12,16,20} \right)$
Note:
Here, one must only remember the order of writing the values in the Pythagoras theorem. The hypotenuse is on one side while the remaining two sides are on the other side. In the Pythagorean triplet here, if we remove a common factor $\;4$ from each value then we get $\left( {3,4,5} \right)$ , which is the most basic Pythagorean triplet.
Formula used: Pythagoras Theorem: $A{B^2} + B{C^2} = A{C^2}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
Pythagoras theorem is used whenever we need to find one of the sides of a right-angled triangle
The Pythagoras theorem states, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the length opposite to the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the remaining two sides that form a right angle.

Considering the triangle given here $\;AC$ is the hypotenuse while $\;AB$ and $\;BC$ form the right angle
Hence the Pythagoras theorem is shown as, $A{B^2} + B{C^2} = A{C^2}$ .
Comparing this figure with the figure given, we can obtain the following details
AB = $\;12$ , BC = $\;16$ , and AC = $x$
Now, substituting these values in the Pythagoras theorem,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {12} \right)^2} + {\left( {16} \right)^2} = {\left( x \right)^2}$
Calculating the squares of these values,
$ \Rightarrow 144 + 256 = {x^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 400 = {x^2}$
Now, we know that $\;400$ is a perfect square of $\;20$ .
$ \Rightarrow {(20)^2} = {x^2}$
Applying root on both sides
$ \Rightarrow x = 20$
Thus, the length of the third side or hypotenuse of the right-angled triangle is $\;20$ units.
Now, as we obtained these values through the Pythagoras theorem, we can say that these values satisfy the Pythagoras theorem and thus these values can be called a Pythagorean triplet
The Pythagorean triplet is shown as $\left( {12,16,20} \right)$
Note:
Here, one must only remember the order of writing the values in the Pythagoras theorem. The hypotenuse is on one side while the remaining two sides are on the other side. In the Pythagorean triplet here, if we remove a common factor $\;4$ from each value then we get $\left( {3,4,5} \right)$ , which is the most basic Pythagorean triplet.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

The highest dam in India is A Bhakra dam B Tehri dam class 10 social science CBSE

Describe the process of Unification of Italy class 10 social science CBSE

Who Won 36 Oscar Awards? Record Holder Revealed




