
Find the value of $\sin {37^o},\sin {53^o},\tan {37^o},\tan {53^o}$ in terms of fraction.
Answer
481.5k+ views
Hint: In this question, we have to write the given trigonometric function in terms of fraction.
We know, that in a right- angled triangle, there are three sides, perpendicular, base and the hypotenuse.
And, $\sin \theta = \dfrac{P}{H}$ , where, $P$ is the length of perpendicular and $H$ is referred to as the length of hypotenuse, whereas, $\tan \theta = \dfrac{P}{B}$ , where, $P$ is the length of perpendicular and $B$ is the length of base of the triangle.
Complete answer:
Given trigonometric functions $\sin {37^o},\sin {53^o},\tan {37^o},\tan {53^o}$ .
To write these trigonometric functions in terms of fraction.
Consider a right- angled triangle, $\vartriangle ABC$ , with $\angle ACB = {37^o}$ and $\angle ABC = {90^o}$ .
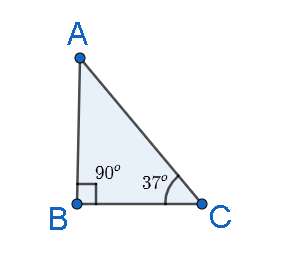
Then, we have, using angle sum property of a triangle, that, $\angle ABC + \angle BAC + \angle ACB = {180^o}$ , i.e., ${37^o} + {90^o} + \angle BAC = {180^o}$ . On solving, we get, $\angle BAC = {180^o} - {127^o}$ i.e., $\angle BAC = {53^o}$ .
Now, let length of side $AB$ is $3units$ and length of side $BC$ is $4units$ , then, by Pythagoras theorem, we have, $A{B^2} + B{C^2} = A{C^2}$ , putting values, we get, ${3^2} + {4^2} = 9 + 16 = 25$ , hence, $AC = 5units$ .
Now, we know, $\sin \theta = \dfrac{P}{H}$ , and for angle $\theta = {37^o}$ , $P = 3$ and $H = 5$ . So, $\sin {37^o} = \dfrac{3}{5}$ .
Similarly, for angle $\theta = {53^o}$ , $P = 4$ and $H = 5$ . So, $\sin {53^o} = \dfrac{4}{5}$ .
Now, for angle $\theta = {37^o}$ , $P = 3$ and $B = 4$ . So, $\tan {37^o} = \dfrac{3}{4}$ .
Similarly, for angle $\theta = {53^o}$ , $P = 4$ and $B = 3$ . So, \[\tan {53^o} = \dfrac{4}{3}\]
Note:
It is not necessary to choose the lengths of sides of the triangle to be $3units$ or $4units$ . We can choose the length of sides of the right- angled triangle by our choices.
If ${x^2} = {a^2}$ , then, taking square root on both sides, we get, $x = \pm a$ , but in this question, we are talking about length of sides and length can never be negative. Hence, we have taken only the positive one.
For any angle, say $\theta $ , the sides opposite to this angle will be the perpendicular side, whereas, the third side except for the hypotenuse, will be the base of the triangle.
We know, that in a right- angled triangle, there are three sides, perpendicular, base and the hypotenuse.
And, $\sin \theta = \dfrac{P}{H}$ , where, $P$ is the length of perpendicular and $H$ is referred to as the length of hypotenuse, whereas, $\tan \theta = \dfrac{P}{B}$ , where, $P$ is the length of perpendicular and $B$ is the length of base of the triangle.
Complete answer:
Given trigonometric functions $\sin {37^o},\sin {53^o},\tan {37^o},\tan {53^o}$ .
To write these trigonometric functions in terms of fraction.
Consider a right- angled triangle, $\vartriangle ABC$ , with $\angle ACB = {37^o}$ and $\angle ABC = {90^o}$ .

Then, we have, using angle sum property of a triangle, that, $\angle ABC + \angle BAC + \angle ACB = {180^o}$ , i.e., ${37^o} + {90^o} + \angle BAC = {180^o}$ . On solving, we get, $\angle BAC = {180^o} - {127^o}$ i.e., $\angle BAC = {53^o}$ .
Now, let length of side $AB$ is $3units$ and length of side $BC$ is $4units$ , then, by Pythagoras theorem, we have, $A{B^2} + B{C^2} = A{C^2}$ , putting values, we get, ${3^2} + {4^2} = 9 + 16 = 25$ , hence, $AC = 5units$ .
Now, we know, $\sin \theta = \dfrac{P}{H}$ , and for angle $\theta = {37^o}$ , $P = 3$ and $H = 5$ . So, $\sin {37^o} = \dfrac{3}{5}$ .
Similarly, for angle $\theta = {53^o}$ , $P = 4$ and $H = 5$ . So, $\sin {53^o} = \dfrac{4}{5}$ .
Now, for angle $\theta = {37^o}$ , $P = 3$ and $B = 4$ . So, $\tan {37^o} = \dfrac{3}{4}$ .
Similarly, for angle $\theta = {53^o}$ , $P = 4$ and $B = 3$ . So, \[\tan {53^o} = \dfrac{4}{3}\]
Note:
It is not necessary to choose the lengths of sides of the triangle to be $3units$ or $4units$ . We can choose the length of sides of the right- angled triangle by our choices.
If ${x^2} = {a^2}$ , then, taking square root on both sides, we get, $x = \pm a$ , but in this question, we are talking about length of sides and length can never be negative. Hence, we have taken only the positive one.
For any angle, say $\theta $ , the sides opposite to this angle will be the perpendicular side, whereas, the third side except for the hypotenuse, will be the base of the triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




