
How to find the value of \[\sin {{37}^{\circ }}\] and \[{{24}^{\circ }}\]
Answer
514.8k+ views
Hint: To find the value of \[\sin {{37}^{\circ }}\] we will apply angle sum property and find out the value of \[\angle A\] and then we will assume the values of sides \[AB\] and \[BC\] and then apply Pythagoras theorem and we can find the value of \[\sin {{37}^{\circ }}\] . For \[\sin {{24}^{\circ }}\] we will use a different formula of \[\sin \theta \] Then we will solve each trigonometric function to get the required solution.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The word Trigonometry is derived from the Greek word trigon and metron. Here trigon means figures with three angles and metron means measurement. That is the meaning of the word Trigonometry is a measurement of triangles. In the modern age Trigonometry has broad based meaning. In simple words we define it as that branch of mathematics which deals with the measurement of angles and the problems allied with angles.
Currently trigonometry is used in many areas such as the science of seismology, designing electric circuits, predicting the heights of tides in the ocean, analyzing the musical tone and in many other areas.
We know that the angle between \[{{0}^{\circ }}\] and \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] is called acute angle. Further the angle of \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] is called right angle and the angle lies between \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] and \[{{180}^{\circ }}\] is called obtuse angle.
A series of real valued functions, defined as the ratio of the sides of a triangle is called a Trigonometric Function.
Trigonometric functions are also known as the circular functions.The basic trigonometric functions are sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant and cosecant. The angles of sine, cosine, and tangent are the primary classification of functions of trigonometry. And the three functions which are cotangent, secant and cosecant can be derived from the primary functions.
Now according to the question to find the value of \[\sin {{37}^{\circ }}\]
We know that \[{{37}^{\circ }}<{{90}^{\circ }}\] hence \[{{37}^{\circ }}\] is an acute angle
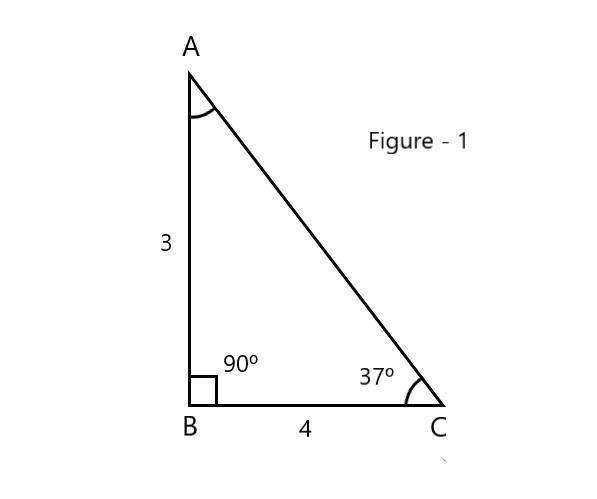
Now from \[\vartriangle ABC\] in figure \[(1)\] , \[\angle C\] is \[{{37}^{\circ }}\] and \[\angle B={{90}^{\circ }}\]
By angle sum property:
\[\Rightarrow \angle A\text{+}\angle B\text{+}\angle C\text{=18}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle A+{{90}^{\circ }}+{{37}^{\circ }}=\text{18}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle A+{{127}^{\circ }}=\text{18}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle A=\text{18}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}-{{127}^{\circ }}\]
\[\therefore \angle A={{53}^{\circ }}\]
Let \[AB=\text{3 units}\] and \[BC=4\text{ units}\]
Now by Pythagoras theorem:
\[\text{hypotenus}{{\text{e}}^{\text{2}}}\text{=perpendicula}{{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+bas}{{\text{e}}^{\text{2}}}\]
According to figure \[(1)\]
\[\Rightarrow A{{C}^{\text{2}}}\text{=A}{{\text{B}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+B}{{\text{C}}^{\text{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow A{{C}^{\text{2}}}\text{=}{{\text{4}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{3}}^{\text{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow A{{C}^{\text{2}}}\text{=16+9}\]
\[\Rightarrow A{{C}^{\text{2}}}\text{=25}\]
\[\Rightarrow AC\text{=}\sqrt{25}\]
We know that
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{perpendicular}{hypotenuse}\]
Hence,
\[\sin {{37}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{AB}{AC}\]
\[\therefore \sin {{37}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{3}{5}\]
Now to find the value of \[\sin {{24}^{\circ }}\]
\[\Rightarrow \sin {{24}^{\circ }}=\sin ({{60}^{\circ }}-{{36}^{\circ }})\]
Apply the formula \[\sin (A-B)=\sin A\cos B-\cos A\sin B\]
Where \[A={{60}^{\circ }}\] and \[B={{36}^{\circ }}\]
\[\Rightarrow \sin ({{60}^{\circ }}-{{36}^{\circ }})=\sin {{60}^{\circ }}\cdot \cos {{36}^{\circ }}-\cos {{60}^{\circ }}\cdot \sin {{36}^{\circ }}\]
We know that
\[\sin {{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\] , \[\cos {{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{1}{2}\] , \[\cos {{36}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}+1}{4}\] , \[\sin {{36}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{\sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}}}{4}\]
Put this value in above equation we get ,
\[\Rightarrow \sin ({{60}^{\circ }}-{{36}^{\circ }})=[\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\cdot (\dfrac{\sqrt{5}+1}{4})-\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot (\dfrac{\sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}}}{4})]\]
\[\Rightarrow \sin ({{60}^{\circ }}-{{36}^{\circ }})=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{15}}{8}-\dfrac{\sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}}}{8}\]
\[\Rightarrow \sin ({{60}^{\circ }}-{{36}^{\circ }})=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{15}-\sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}}}{8}\]
Hence
\[\sin {{24}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{15}-\sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}}}{8}\]
Note: We must keep one thing in mind that \[\sin \theta \] is not the same as \[\sin \times \theta \] because it represents a ratio, not a product and this is true for all the trigonometric ratios. Any trigonometric function of angle \[{{\theta }^{\circ }}\] is equal to the same trigonometric function of any angle \[n\times {{360}^{\circ }}+\theta \], where \[n\] is any integer.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The word Trigonometry is derived from the Greek word trigon and metron. Here trigon means figures with three angles and metron means measurement. That is the meaning of the word Trigonometry is a measurement of triangles. In the modern age Trigonometry has broad based meaning. In simple words we define it as that branch of mathematics which deals with the measurement of angles and the problems allied with angles.
Currently trigonometry is used in many areas such as the science of seismology, designing electric circuits, predicting the heights of tides in the ocean, analyzing the musical tone and in many other areas.
We know that the angle between \[{{0}^{\circ }}\] and \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] is called acute angle. Further the angle of \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] is called right angle and the angle lies between \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] and \[{{180}^{\circ }}\] is called obtuse angle.
A series of real valued functions, defined as the ratio of the sides of a triangle is called a Trigonometric Function.
Trigonometric functions are also known as the circular functions.The basic trigonometric functions are sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant and cosecant. The angles of sine, cosine, and tangent are the primary classification of functions of trigonometry. And the three functions which are cotangent, secant and cosecant can be derived from the primary functions.
Now according to the question to find the value of \[\sin {{37}^{\circ }}\]
We know that \[{{37}^{\circ }}<{{90}^{\circ }}\] hence \[{{37}^{\circ }}\] is an acute angle

Now from \[\vartriangle ABC\] in figure \[(1)\] , \[\angle C\] is \[{{37}^{\circ }}\] and \[\angle B={{90}^{\circ }}\]
By angle sum property:
\[\Rightarrow \angle A\text{+}\angle B\text{+}\angle C\text{=18}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle A+{{90}^{\circ }}+{{37}^{\circ }}=\text{18}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle A+{{127}^{\circ }}=\text{18}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle A=\text{18}{{\text{0}}^{\text{o}}}-{{127}^{\circ }}\]
\[\therefore \angle A={{53}^{\circ }}\]
Let \[AB=\text{3 units}\] and \[BC=4\text{ units}\]
Now by Pythagoras theorem:
\[\text{hypotenus}{{\text{e}}^{\text{2}}}\text{=perpendicula}{{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+bas}{{\text{e}}^{\text{2}}}\]
According to figure \[(1)\]
\[\Rightarrow A{{C}^{\text{2}}}\text{=A}{{\text{B}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+B}{{\text{C}}^{\text{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow A{{C}^{\text{2}}}\text{=}{{\text{4}}^{\text{2}}}\text{+}{{\text{3}}^{\text{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow A{{C}^{\text{2}}}\text{=16+9}\]
\[\Rightarrow A{{C}^{\text{2}}}\text{=25}\]
\[\Rightarrow AC\text{=}\sqrt{25}\]
We know that
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{perpendicular}{hypotenuse}\]
Hence,
\[\sin {{37}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{AB}{AC}\]
\[\therefore \sin {{37}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{3}{5}\]
Now to find the value of \[\sin {{24}^{\circ }}\]
\[\Rightarrow \sin {{24}^{\circ }}=\sin ({{60}^{\circ }}-{{36}^{\circ }})\]
Apply the formula \[\sin (A-B)=\sin A\cos B-\cos A\sin B\]
Where \[A={{60}^{\circ }}\] and \[B={{36}^{\circ }}\]
\[\Rightarrow \sin ({{60}^{\circ }}-{{36}^{\circ }})=\sin {{60}^{\circ }}\cdot \cos {{36}^{\circ }}-\cos {{60}^{\circ }}\cdot \sin {{36}^{\circ }}\]
We know that
\[\sin {{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\] , \[\cos {{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{1}{2}\] , \[\cos {{36}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{\sqrt{5}+1}{4}\] , \[\sin {{36}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{\sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}}}{4}\]
Put this value in above equation we get ,
\[\Rightarrow \sin ({{60}^{\circ }}-{{36}^{\circ }})=[\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\cdot (\dfrac{\sqrt{5}+1}{4})-\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot (\dfrac{\sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}}}{4})]\]
\[\Rightarrow \sin ({{60}^{\circ }}-{{36}^{\circ }})=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{15}}{8}-\dfrac{\sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}}}{8}\]
\[\Rightarrow \sin ({{60}^{\circ }}-{{36}^{\circ }})=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{15}-\sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}}}{8}\]
Hence
\[\sin {{24}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{15}-\sqrt{10-2\sqrt{5}}}{8}\]
Note: We must keep one thing in mind that \[\sin \theta \] is not the same as \[\sin \times \theta \] because it represents a ratio, not a product and this is true for all the trigonometric ratios. Any trigonometric function of angle \[{{\theta }^{\circ }}\] is equal to the same trigonometric function of any angle \[n\times {{360}^{\circ }}+\theta \], where \[n\] is any integer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




