
Find the value of other five trigonometric ratios:
$\cot x = \dfrac{3}{4}$ , x lies in the third quadrant.
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: Given that x lies in third quadrant. Now if x lies in the third quadrant, only \[\tan x\] and \[\cot x\] is positive.
Also, note the following important formulae:
$\cos x = \dfrac{1}{{\sec x}}$ , $\sin x = \dfrac{1}{{\cos ecx}}$ , $\tan x = \dfrac{1}{{\cot x}}$
${\sin ^2}x + {\cos ^2}x = 1$
\[{\sec ^2}x - {\tan ^2}x = 1\]
\[{\operatorname{cosec} ^2}x - {\cot ^2}x = 1\]
Now, the value of \[\cot x\] is given. Therefore find the value of the other five trigonometric ratios with the help of before mentioned formulae.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given, $\cot x = \dfrac{3}{4}$
Therefore $\tan x = \dfrac{1}{{\cot x}} = \dfrac{4}{3}$
\[\because {\sec ^2}x - {\tan ^2}x = 1\], we get,
\[ \Rightarrow {\sec ^2}x = 1 + {\tan ^2}x\]
On taking square root we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \sec x = \pm \sqrt {1 + {{\tan }^2}x} \]
On substituting the value of \[\tan x\]we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \sec x = \pm \sqrt {1 + {{\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)}^2}} \]
On simplification we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \sec x = - \dfrac{5}{3}\]
Here as, x lies in the third Quadrant, therefore \[\sec x\] is negative.
Therefore $\cos x = \dfrac{1}{{\sec x}} = - \dfrac{3}{5}$
Again,
${\sin ^2}x + {\cos ^2}x = 1$
$ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}x = 1 - {\cos ^2}x$
On taking square root we get,
$ \Rightarrow \sin x = \pm \sqrt {1 - {{\cos }^2}x} $
On substituting the value of \[\cos x\]we get,
$ \Rightarrow \sin x = \pm \sqrt {1 - {{\left( { - \dfrac{3}{5}} \right)}^2}} $
On solving we get,
$ \Rightarrow \sin x = \pm \sqrt {1 - \dfrac{9}{{25}}} = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{16}}{{25}}} $
On simplification we get,
$ \Rightarrow \sin x = - \dfrac{4}{5}$
Here as, x lies in the third quadrant so the value of\[\;\sin x\] will be negative.
Therefore, $\operatorname{cosecx} = \dfrac{1}{{\sin x}} = - \dfrac{5}{4}$
Hence when $\cot x = \dfrac{3}{4}$ , and x lies in third quadrant, the other five trigonometric ratios are :
\[\tan x = \dfrac{4}{3}\], $\sin x = - \dfrac{4}{5}$ , $\cos x = - \dfrac{3}{5}$, \[\sec x = - \dfrac{5}{3}\] and $\operatorname{cosecx} = - \dfrac{5}{4}$
Note: Note the following important formulae:
1.$\cos x = \dfrac{1}{{\sec x}}$ , $\sin x = \dfrac{1}{{\cos ecx}}$ , $\tan x = \dfrac{1}{{\cot x}}$
2.${\sin ^2}x + {\cos ^2}x = 1$
3.\[{\sec ^2}x - {\tan ^2}x = 1\]
4.\[{\operatorname{cosec} ^2}x - {\cot ^2}x = 1\]
5.$\sin ( - x) = - \sin x$
6.$\cos ( - x) = \cos x$
7.$\tan ( - x) = - \tan x$
8.$\sin \left( {2n\pi \pm x} \right) = \sin x{\text{ , period 2}}\pi {\text{ or 3}}{60^ \circ }$
9.$\cos \left( {2n\pi \pm x} \right) = \cos x{\text{ , period 2}}\pi {\text{ or 3}}{60^ \circ }$
10.$\tan \left( {n\pi \pm x} \right) = \tan x{\text{ , period }}\pi {\text{ or 18}}{0^ \circ }$
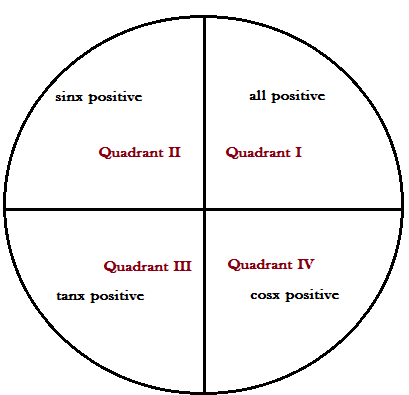
Sign convention:
Also, note the following important formulae:
$\cos x = \dfrac{1}{{\sec x}}$ , $\sin x = \dfrac{1}{{\cos ecx}}$ , $\tan x = \dfrac{1}{{\cot x}}$
${\sin ^2}x + {\cos ^2}x = 1$
\[{\sec ^2}x - {\tan ^2}x = 1\]
\[{\operatorname{cosec} ^2}x - {\cot ^2}x = 1\]
Now, the value of \[\cot x\] is given. Therefore find the value of the other five trigonometric ratios with the help of before mentioned formulae.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given, $\cot x = \dfrac{3}{4}$
Therefore $\tan x = \dfrac{1}{{\cot x}} = \dfrac{4}{3}$
\[\because {\sec ^2}x - {\tan ^2}x = 1\], we get,
\[ \Rightarrow {\sec ^2}x = 1 + {\tan ^2}x\]
On taking square root we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \sec x = \pm \sqrt {1 + {{\tan }^2}x} \]
On substituting the value of \[\tan x\]we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \sec x = \pm \sqrt {1 + {{\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)}^2}} \]
On simplification we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \sec x = - \dfrac{5}{3}\]
Here as, x lies in the third Quadrant, therefore \[\sec x\] is negative.
Therefore $\cos x = \dfrac{1}{{\sec x}} = - \dfrac{3}{5}$
Again,
${\sin ^2}x + {\cos ^2}x = 1$
$ \Rightarrow {\sin ^2}x = 1 - {\cos ^2}x$
On taking square root we get,
$ \Rightarrow \sin x = \pm \sqrt {1 - {{\cos }^2}x} $
On substituting the value of \[\cos x\]we get,
$ \Rightarrow \sin x = \pm \sqrt {1 - {{\left( { - \dfrac{3}{5}} \right)}^2}} $
On solving we get,
$ \Rightarrow \sin x = \pm \sqrt {1 - \dfrac{9}{{25}}} = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{16}}{{25}}} $
On simplification we get,
$ \Rightarrow \sin x = - \dfrac{4}{5}$
Here as, x lies in the third quadrant so the value of\[\;\sin x\] will be negative.
Therefore, $\operatorname{cosecx} = \dfrac{1}{{\sin x}} = - \dfrac{5}{4}$
Hence when $\cot x = \dfrac{3}{4}$ , and x lies in third quadrant, the other five trigonometric ratios are :
\[\tan x = \dfrac{4}{3}\], $\sin x = - \dfrac{4}{5}$ , $\cos x = - \dfrac{3}{5}$, \[\sec x = - \dfrac{5}{3}\] and $\operatorname{cosecx} = - \dfrac{5}{4}$
Note: Note the following important formulae:
1.$\cos x = \dfrac{1}{{\sec x}}$ , $\sin x = \dfrac{1}{{\cos ecx}}$ , $\tan x = \dfrac{1}{{\cot x}}$
2.${\sin ^2}x + {\cos ^2}x = 1$
3.\[{\sec ^2}x - {\tan ^2}x = 1\]
4.\[{\operatorname{cosec} ^2}x - {\cot ^2}x = 1\]
5.$\sin ( - x) = - \sin x$
6.$\cos ( - x) = \cos x$
7.$\tan ( - x) = - \tan x$
8.$\sin \left( {2n\pi \pm x} \right) = \sin x{\text{ , period 2}}\pi {\text{ or 3}}{60^ \circ }$
9.$\cos \left( {2n\pi \pm x} \right) = \cos x{\text{ , period 2}}\pi {\text{ or 3}}{60^ \circ }$
10.$\tan \left( {n\pi \pm x} \right) = \tan x{\text{ , period }}\pi {\text{ or 18}}{0^ \circ }$
Sign convention:

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




