
How can you find the value of $\csc \left( \pi \right)$?
Answer
555.6k+ views
Hint: CSC or the cosecant function is a trigonometric function that depicts the value of the cosecant of any angle. Just visualize the cosecant of $\pi $ where its natural sine function is 0.
Complete step by step solution:
For any triangle, its sin, cos, and tan functions are nothing but a combination of its perpendicular, base, and hypotenuse.
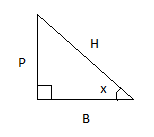
In the figure above, x is the angle whereas P, B and H are perpendicular, base and hypotenuse respectively. Cosecant, popularly known as cosec is nothing but the reciprocal of sine. Here sine is found out by dividing the length of perpendicular by hypotenuse.
$\sin \left( x \right) = \dfrac{P}{H}$
As such cosecant will be
$\cos {\text{ec}}\left( x \right) = \dfrac{H}{P}$
Now, we know that $\sin \left( \pi \right) = 0$. So,
$\
\cos {\text{ec}}\left( \pi \right) = \dfrac{1}{{\sin \left( \pi \right)}} \\
= \dfrac{1}{0} \\
\ $
As such $\cos {\text{ec}}\left( \pi \right)$ is undefined. As such finding the exact value of $\cos {\text{ec}}\left( \pi \right)$ is impossible. However, it can be found out to some extent using limits and continuity where the value of the angle, which is the variable of the function, tends to be $\pi $ but actually it is not. It can be slightly higher or slightly lower than $\pi $ which will give us the value of positive infinity or negative infinity respectively.
Additional information:
Although no one knows the exact value of infinity but when using it in functions where the same angle acting as variable for all the function subparts, it can be equated also. For example,
$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \pi } \left( {\dfrac{{\sin \left( x \right)}}{{\cos \left( {\pi - x} \right)}}} \right) = 1$
It is not infinity upon infinity because first of all, we are using the same function variable and secondly x is tending to $\pi $ and is not actually $\pi $ which prevents it from becoming an indeterminate form.
Note:
Undefined and infinite are two different things and not the same. Undefined is when a value cannot be defined by mathematics such as one divided by zero, whereas infinite is a value that cannot be counted by mathematics like the sum of all numbers on the number line.
Complete step by step solution:
For any triangle, its sin, cos, and tan functions are nothing but a combination of its perpendicular, base, and hypotenuse.

In the figure above, x is the angle whereas P, B and H are perpendicular, base and hypotenuse respectively. Cosecant, popularly known as cosec is nothing but the reciprocal of sine. Here sine is found out by dividing the length of perpendicular by hypotenuse.
$\sin \left( x \right) = \dfrac{P}{H}$
As such cosecant will be
$\cos {\text{ec}}\left( x \right) = \dfrac{H}{P}$
Now, we know that $\sin \left( \pi \right) = 0$. So,
$\
\cos {\text{ec}}\left( \pi \right) = \dfrac{1}{{\sin \left( \pi \right)}} \\
= \dfrac{1}{0} \\
\ $
As such $\cos {\text{ec}}\left( \pi \right)$ is undefined. As such finding the exact value of $\cos {\text{ec}}\left( \pi \right)$ is impossible. However, it can be found out to some extent using limits and continuity where the value of the angle, which is the variable of the function, tends to be $\pi $ but actually it is not. It can be slightly higher or slightly lower than $\pi $ which will give us the value of positive infinity or negative infinity respectively.
Additional information:
Although no one knows the exact value of infinity but when using it in functions where the same angle acting as variable for all the function subparts, it can be equated also. For example,
$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \pi } \left( {\dfrac{{\sin \left( x \right)}}{{\cos \left( {\pi - x} \right)}}} \right) = 1$
It is not infinity upon infinity because first of all, we are using the same function variable and secondly x is tending to $\pi $ and is not actually $\pi $ which prevents it from becoming an indeterminate form.
Note:
Undefined and infinite are two different things and not the same. Undefined is when a value cannot be defined by mathematics such as one divided by zero, whereas infinite is a value that cannot be counted by mathematics like the sum of all numbers on the number line.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




