
Find the square root of the following number by division method: 5329.
Answer
619.8k+ views
Hint:Follow the rules of division method for finding the square root of any number. Put bars from the unit place and use two digits for one bar. Now think of the largest number whose square is even to just less than the first bar digit in the number. Now, subtract and bring down the quotient to the divisor, now add a new digit in quotient and divisor (in front) and repeat it to get the quotient. At last, when the remainder becomes 0, the quotient is the square root of it.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Division method for finding square root can be given as,
(a) First place a bar over every pair of digits starting from unit digit, if the number of digits are odd then the left most single digit will also have a bar.
(b) Think of the largest number whose square is even to just less than the first bar digit. Take this number as divisor and also as quotient.
(c) Next subtract the product of the divisor and the quotient from the first bar digit and bring down the next pair of digits which have a bar to the right side of the remainder, that becomes a new dividend.
(d) Now, the new divisor is obtained by adding the first divisor and the quotient and add a digit to the right side of it that we have to choose (according to the new dividend which is chosen in such a way that product of new divisor and this digit is less than or equal to the new dividend).
(e) Repeat step (b, c, d) till the bar digit has been taken up. Now quotient is the required square root of the given number.
Now, let us apply the above steps to find the square root of 5329.
(1) First place bar at two digits starting from unit place and similarly further as well. So, we get $\overline{53}\overline{29}$.
(2) Now, we know the number by the first two digits is 53. So, we know,
\[{{7}^{2}}<{53}<{{8}^{2}}\]
(3) Hence, we can write
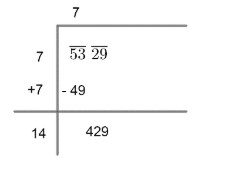
(4) Now, the new dividend is 429 and we need to use the same number in quotient and divisor (starting with 14) to get 429.
We have,
$\begin{align}
& 141\times 1=141 \\
& 142\times 2=284 \\
& 143\times 3=429 \\
\end{align}$
So, we get,
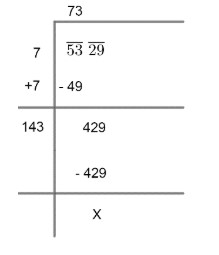
(5) So, the square root of 539 is 73.
Note: Don’t put bars from the starting of a number in the division method. It is a general mistake done by students with this method.
Always put the same digit in divisor and quotient. They should be the same for getting the square root.
Bars should be only on maximum two digits and minimum on one digit.
One can verify the square root by calculating it by prime factorization method. So, we can get 5329 by prime factorization as
$\begin{align}
& 73\left| \!{\underline {\,
5329 \,}} \right. \\
& 73\left| \!{\underline {\,
73 \,}} \right. \\
& \ \ \ \ \ 1 \\
\end{align}$
Now, we can observe that the square root of 5329 by prime factorization is very difficult as one may not be able to guess 73 as a factor of 5329.
So, division method is a more powerful method and efficient method with these types of numbers.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Division method for finding square root can be given as,
(a) First place a bar over every pair of digits starting from unit digit, if the number of digits are odd then the left most single digit will also have a bar.
(b) Think of the largest number whose square is even to just less than the first bar digit. Take this number as divisor and also as quotient.
(c) Next subtract the product of the divisor and the quotient from the first bar digit and bring down the next pair of digits which have a bar to the right side of the remainder, that becomes a new dividend.
(d) Now, the new divisor is obtained by adding the first divisor and the quotient and add a digit to the right side of it that we have to choose (according to the new dividend which is chosen in such a way that product of new divisor and this digit is less than or equal to the new dividend).
(e) Repeat step (b, c, d) till the bar digit has been taken up. Now quotient is the required square root of the given number.
Now, let us apply the above steps to find the square root of 5329.
(1) First place bar at two digits starting from unit place and similarly further as well. So, we get $\overline{53}\overline{29}$.
(2) Now, we know the number by the first two digits is 53. So, we know,
\[{{7}^{2}}<{53}<{{8}^{2}}\]
(3) Hence, we can write

(4) Now, the new dividend is 429 and we need to use the same number in quotient and divisor (starting with 14) to get 429.
We have,
$\begin{align}
& 141\times 1=141 \\
& 142\times 2=284 \\
& 143\times 3=429 \\
\end{align}$
So, we get,

(5) So, the square root of 539 is 73.
Note: Don’t put bars from the starting of a number in the division method. It is a general mistake done by students with this method.
Always put the same digit in divisor and quotient. They should be the same for getting the square root.
Bars should be only on maximum two digits and minimum on one digit.
One can verify the square root by calculating it by prime factorization method. So, we can get 5329 by prime factorization as
$\begin{align}
& 73\left| \!{\underline {\,
5329 \,}} \right. \\
& 73\left| \!{\underline {\,
73 \,}} \right. \\
& \ \ \ \ \ 1 \\
\end{align}$
Now, we can observe that the square root of 5329 by prime factorization is very difficult as one may not be able to guess 73 as a factor of 5329.
So, division method is a more powerful method and efficient method with these types of numbers.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

Who Won 36 Oscar Awards? Record Holder Revealed

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE




