
Find the probability of \[{x^2} - 3x + 2 \geqslant 0\] in \[x \in \left[ {0,5} \right]\].
A. \[\dfrac{4}{5}\]
B. \[\dfrac{1}{5}\]
C. \[\dfrac{2}{5}\]
D. \[\dfrac{3}{5}\]
Answer
618.3k+ views
Hint: To find the probability of the given equation, first we have to solve the inequality. After solving the inequality, draw it on a number line in the given boundaries. So, use this concept to reach the solution of the given problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given \[x \in \left[ {0,5} \right]\]
Consider \[{x^2} - 3x + 2 \geqslant 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 3x + 2 \geqslant 0\]
By splitting the terms of \[x\], we have
\[
\Rightarrow {x^2} - x - 2x + 2 \geqslant 0 \\
\Rightarrow x\left( {x - 1} \right) - 2\left( {x - 1} \right) \geqslant 0 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {x - 1} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right) \geqslant 0 \\
\]
We know that the inequality \[\left( {x - a} \right)\left( {x - b} \right) \geqslant 0\] can be rewrite as \[x \leqslant a{\text{ and }}x \geqslant b\]
So, the inequality can be rewrite as
\[x \leqslant 1{\text{ and }}x \geqslant 2\]
If we draw it on number line, from points 0 to 5, we have
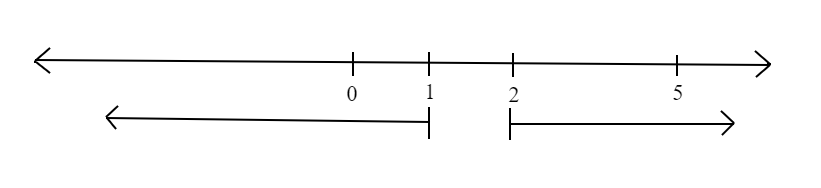
Clearly, from the number line diagram we can see that \[\dfrac{4}{5}\] of the part is covered.
So, the required probability is \[\dfrac{4}{5}\].
Thus, the correct option is A. \[\dfrac{4}{5}\]
Note: The probability of an event is always lying between 0 and 1 i.e., \[0 \leqslant P\left( E \right) \leqslant 1\]. Here the obtained answer is also lying between 0 and 1. Here students may forget to include boundary conditions.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given \[x \in \left[ {0,5} \right]\]
Consider \[{x^2} - 3x + 2 \geqslant 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 3x + 2 \geqslant 0\]
By splitting the terms of \[x\], we have
\[
\Rightarrow {x^2} - x - 2x + 2 \geqslant 0 \\
\Rightarrow x\left( {x - 1} \right) - 2\left( {x - 1} \right) \geqslant 0 \\
\Rightarrow \left( {x - 1} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right) \geqslant 0 \\
\]
We know that the inequality \[\left( {x - a} \right)\left( {x - b} \right) \geqslant 0\] can be rewrite as \[x \leqslant a{\text{ and }}x \geqslant b\]
So, the inequality can be rewrite as
\[x \leqslant 1{\text{ and }}x \geqslant 2\]
If we draw it on number line, from points 0 to 5, we have

Clearly, from the number line diagram we can see that \[\dfrac{4}{5}\] of the part is covered.
So, the required probability is \[\dfrac{4}{5}\].
Thus, the correct option is A. \[\dfrac{4}{5}\]
Note: The probability of an event is always lying between 0 and 1 i.e., \[0 \leqslant P\left( E \right) \leqslant 1\]. Here the obtained answer is also lying between 0 and 1. Here students may forget to include boundary conditions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




