
How do you find the period and graph the function \[y = 4\tan x\]?
Answer
563.1k+ views
Hint: We know that the distance between the repetitions of any function is called the period of the function.
For a trigonometric function, the length of one complete cycle is called a period.
If we have a function \[{\text{f}}\left( {\text{a}} \right) = {\text{tan}}\left( {{\text{as}}} \right)\], where \[s > 0\], then the graph of the function makes complete cycles between \[ - \dfrac{\pi }{2},0\] and \[0,\dfrac{\pi }{2}\] each of the function have the period of \[p = \dfrac{\pi }{s}\]
Substitute the value of \[s\], we can find the period.
Complete step-by-step solution:
It is given that; \[y = 4\tan x\]
We have to find the period and graph of the given function.
We know that the distance between the repetitions of any function is called the period of the function. For a trigonometric function, the length of one complete cycle is called a period.
If we have a function\[{\text{f}}\left( {\text{a}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ tan}}\left( {{\text{as}}} \right)\], where\[s > 0\], then the graph of the function makes complete cycles between \[ - \dfrac{\pi }{2},0\] and \[0,\dfrac{\pi }{2}\] each of the function have the period of \[p = \dfrac{\pi }{s}\]
Here, \[s = 4\]
So, the period of the given function \[y = 4\tan x\] is \[\dfrac{\pi }{4}\].
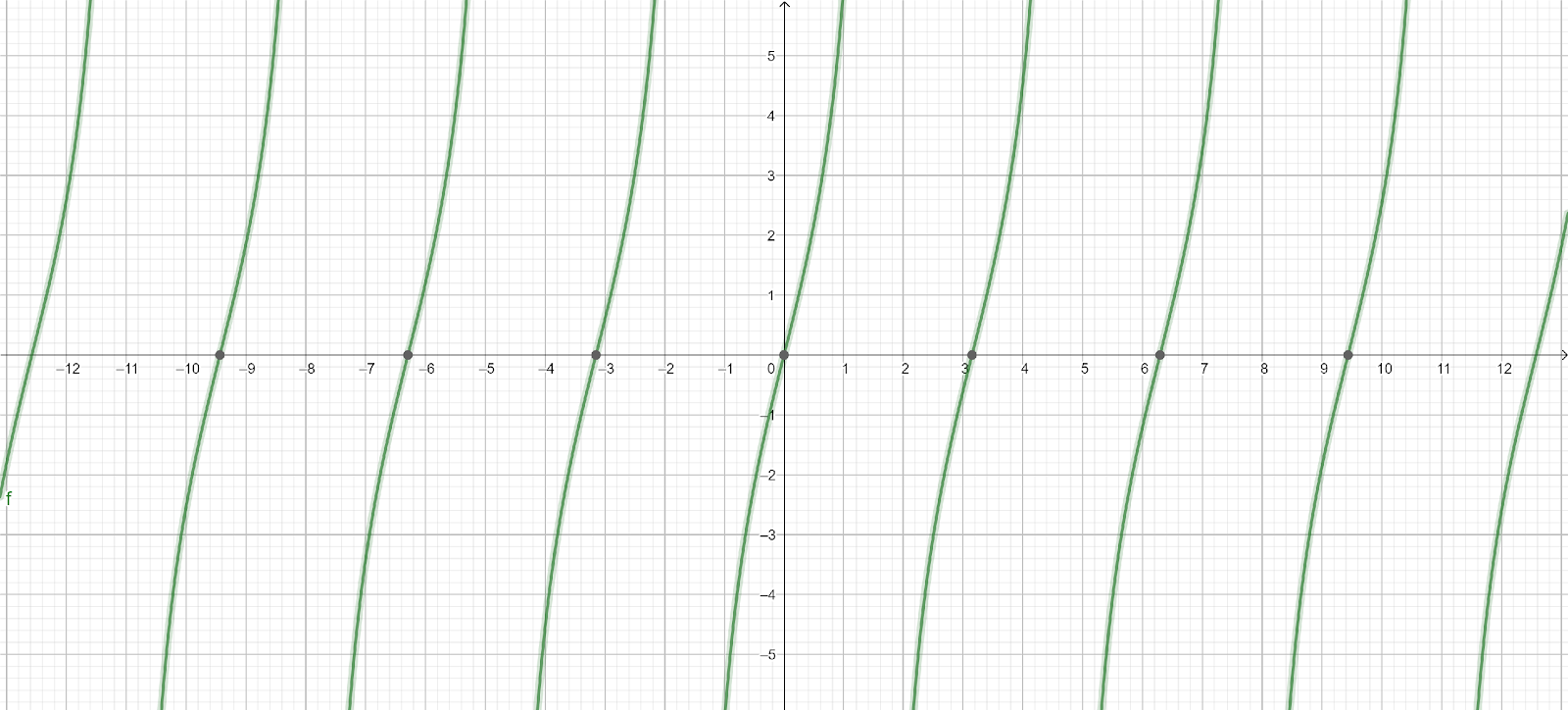
Answer, here’s the graph of \[y = 4\tan x\]
Note: The time interval between two waves is known as a Period whereas a function that repeats its values at regular intervals or periods is known as a Periodic Function. In other words, a periodic function is a function that repeats its values after every particular interval.
If a function repeats over at a constant period, we say that is a periodic function.
It is represented like \[f(x) = f(x + p)\], p is the real number and this is the period of the function.
Period means the time interval between the two occurrences of the wave.
For a trigonometric function, the length of one complete cycle is called a period.
If we have a function \[{\text{f}}\left( {\text{a}} \right) = {\text{tan}}\left( {{\text{as}}} \right)\], where \[s > 0\], then the graph of the function makes complete cycles between \[ - \dfrac{\pi }{2},0\] and \[0,\dfrac{\pi }{2}\] each of the function have the period of \[p = \dfrac{\pi }{s}\]
Substitute the value of \[s\], we can find the period.
Complete step-by-step solution:
It is given that; \[y = 4\tan x\]
We have to find the period and graph of the given function.
We know that the distance between the repetitions of any function is called the period of the function. For a trigonometric function, the length of one complete cycle is called a period.
If we have a function\[{\text{f}}\left( {\text{a}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ tan}}\left( {{\text{as}}} \right)\], where\[s > 0\], then the graph of the function makes complete cycles between \[ - \dfrac{\pi }{2},0\] and \[0,\dfrac{\pi }{2}\] each of the function have the period of \[p = \dfrac{\pi }{s}\]
Here, \[s = 4\]
So, the period of the given function \[y = 4\tan x\] is \[\dfrac{\pi }{4}\].
Answer, here’s the graph of \[y = 4\tan x\]

Note: The time interval between two waves is known as a Period whereas a function that repeats its values at regular intervals or periods is known as a Periodic Function. In other words, a periodic function is a function that repeats its values after every particular interval.
If a function repeats over at a constant period, we say that is a periodic function.
It is represented like \[f(x) = f(x + p)\], p is the real number and this is the period of the function.
Period means the time interval between the two occurrences of the wave.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




