
Find the locus of the middle points of the chords for the parabola \[{{y}^{2}}=4bx\] , chords which are normal to this parabola.
Answer
614.1k+ views
Hint: To find the locus of middle points of chords for the parabola \[{{y}^{2}}=4bx\], write the equation of chord of the parabola joining any two points on the parabola. Write the equation of normal to the parabola in slope form. Compare the two equations and eliminate the variables to find the midpoint of chords.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have a parabola of the form\[{{y}^{2}}=4bx\]. We have to find the locus of middle points of chords to this parabola, which are normal to the parabola.
We know that the equation of chord of the parabola \[{{y}^{2}}=4bx\] joining its two points \[P({{t}_{1}})=(bt_{1}^{2},2b{{t}_{1}})\] and \[Q({{t}_{2}})=(bt_{2}^{2},2b{{t}_{2}})\] is \[y({{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}})=2x+2b{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}\].
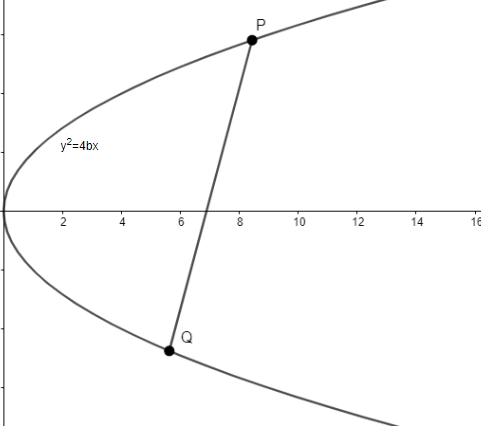
Rewriting the above equation by dividing it by \[({{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}})\], we get \[y=\dfrac{2x}{{{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}}}+\dfrac{2b{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}}{{{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}}}.....\left( 1 \right)\].
We know that the equation of normal to the parabola \[{{y}^{2}}=4bx\] with slope m is\[y=mx-2bm-b{{m}^{3}}.....\left( 2 \right)\].
We know that equation (1) and (2) represent the same line.
Thus, comparing the slope of both lines, we get \[m=\dfrac{2}{{{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}}}\].
Rearranging the terms, we have \[{{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}}=\dfrac{2}{m}.....\left( 3 \right)\].
Comparing the intercept of both lines, we get \[\dfrac{2b{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}}{{{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}}}=-2bm-b{{m}^{3}}\].
Rewriting the above equation by multiplying it by \[({{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}})\], we get \[2b{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}=({{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}})(-2bm-b{{m}^{3}})\].
Substituting the value of equation (3) in the above equation, we get \[2b{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}=\dfrac{2}{m}(-2bm-b{{m}^{3}})\].
Rearranging the terms, we have \[b{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}=-2b-b{{m}^{2}}\].
Thus, we have \[{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}=-2-{{m}^{2}}.....\left( 4 \right)\].
We know that \[t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2}={{({{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}})}^{2}}-2{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}\].
Substituting the values of equation (3) and (4) in above equation, we get \[t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2}={{\left( \dfrac{2}{m} \right)}^{2}}-2(-2-{{m}^{2}})\].
Thus, we have \[t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2}=\dfrac{4}{{{m}^{2}}}+4+2{{m}^{2}}.....\left( 5 \right)\].
We have to find the locus of the middle point of the chords.
We know that the end points of the chords are \[P({{t}_{1}})=(bt_{1}^{2},2b{{t}_{1}})\] and \[Q({{t}_{2}})=(bt_{2}^{2},2b{{t}_{2}})\].
We know that middle point of two points \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\] and \[({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})\] is \[\left( \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2} \right)\].
Substituting \[{{x}_{1}}=bt_{1}^{2},{{y}_{1}}=2b{{t}_{1}},{{x}_{2}}=bt_{2}^{2},{{y}_{2}}=2b{{t}_{2}}\] in the above equation, we get \[\left( \dfrac{b(t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2})}{2},b({{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}}) \right)\] as the middle point of \[P({{t}_{1}})\] and \[Q({{t}_{2}})\].
We know that the middle point of chord is \[\left( \dfrac{b(t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2})}{2},b({{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}}) \right)\].
Let’s assume \[x=\dfrac{b(t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2})}{2},y=b({{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}})\].
Substituting the values in above equation using equations (3) and (5), we get \[x=\dfrac{b(\dfrac{4}{{{m}^{2}}}+4+2{{m}^{2}})}{2}=\dfrac{2b}{{{m}^{2}}}+2b+b{{m}^{2}}\] and \[y=b({{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}})=b\left( \dfrac{2}{m} \right)=\dfrac{2b}{m}\].
Substituting \[m=\dfrac{2b}{y}\] in the equation of x, we get \[x=\dfrac{2b}{{{\left( \dfrac{2b}{y} \right)}^{2}}}+2b+b{{\left( \dfrac{2b}{y} \right)}^{2}}\].
Thus, we have \[x=\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{2b}+2b+\dfrac{4{{b}^{3}}}{{{y}^{2}}}\].
Hence, the locus of the middle points of normal chords for the parabola \[{{y}^{2}}=4bx\] is \[x=\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{2b}+2b+\dfrac{4{{b}^{3}}}{{{y}^{2}}}\].
Note: We can also solve this question by writing the equation of normal to the parabola in parametric form instead of slope form and then finding its point of intersection with the parabolas, to find the midpoint of the chord.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have a parabola of the form\[{{y}^{2}}=4bx\]. We have to find the locus of middle points of chords to this parabola, which are normal to the parabola.
We know that the equation of chord of the parabola \[{{y}^{2}}=4bx\] joining its two points \[P({{t}_{1}})=(bt_{1}^{2},2b{{t}_{1}})\] and \[Q({{t}_{2}})=(bt_{2}^{2},2b{{t}_{2}})\] is \[y({{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}})=2x+2b{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}\].

Rewriting the above equation by dividing it by \[({{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}})\], we get \[y=\dfrac{2x}{{{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}}}+\dfrac{2b{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}}{{{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}}}.....\left( 1 \right)\].
We know that the equation of normal to the parabola \[{{y}^{2}}=4bx\] with slope m is\[y=mx-2bm-b{{m}^{3}}.....\left( 2 \right)\].
We know that equation (1) and (2) represent the same line.
Thus, comparing the slope of both lines, we get \[m=\dfrac{2}{{{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}}}\].
Rearranging the terms, we have \[{{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}}=\dfrac{2}{m}.....\left( 3 \right)\].
Comparing the intercept of both lines, we get \[\dfrac{2b{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}}{{{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}}}=-2bm-b{{m}^{3}}\].
Rewriting the above equation by multiplying it by \[({{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}})\], we get \[2b{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}=({{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}})(-2bm-b{{m}^{3}})\].
Substituting the value of equation (3) in the above equation, we get \[2b{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}=\dfrac{2}{m}(-2bm-b{{m}^{3}})\].
Rearranging the terms, we have \[b{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}=-2b-b{{m}^{2}}\].
Thus, we have \[{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}=-2-{{m}^{2}}.....\left( 4 \right)\].
We know that \[t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2}={{({{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}})}^{2}}-2{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}\].
Substituting the values of equation (3) and (4) in above equation, we get \[t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2}={{\left( \dfrac{2}{m} \right)}^{2}}-2(-2-{{m}^{2}})\].
Thus, we have \[t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2}=\dfrac{4}{{{m}^{2}}}+4+2{{m}^{2}}.....\left( 5 \right)\].
We have to find the locus of the middle point of the chords.
We know that the end points of the chords are \[P({{t}_{1}})=(bt_{1}^{2},2b{{t}_{1}})\] and \[Q({{t}_{2}})=(bt_{2}^{2},2b{{t}_{2}})\].
We know that middle point of two points \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\] and \[({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})\] is \[\left( \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2} \right)\].
Substituting \[{{x}_{1}}=bt_{1}^{2},{{y}_{1}}=2b{{t}_{1}},{{x}_{2}}=bt_{2}^{2},{{y}_{2}}=2b{{t}_{2}}\] in the above equation, we get \[\left( \dfrac{b(t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2})}{2},b({{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}}) \right)\] as the middle point of \[P({{t}_{1}})\] and \[Q({{t}_{2}})\].
We know that the middle point of chord is \[\left( \dfrac{b(t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2})}{2},b({{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}}) \right)\].
Let’s assume \[x=\dfrac{b(t_{1}^{2}+t_{2}^{2})}{2},y=b({{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}})\].
Substituting the values in above equation using equations (3) and (5), we get \[x=\dfrac{b(\dfrac{4}{{{m}^{2}}}+4+2{{m}^{2}})}{2}=\dfrac{2b}{{{m}^{2}}}+2b+b{{m}^{2}}\] and \[y=b({{t}_{1}}+{{t}_{2}})=b\left( \dfrac{2}{m} \right)=\dfrac{2b}{m}\].
Substituting \[m=\dfrac{2b}{y}\] in the equation of x, we get \[x=\dfrac{2b}{{{\left( \dfrac{2b}{y} \right)}^{2}}}+2b+b{{\left( \dfrac{2b}{y} \right)}^{2}}\].
Thus, we have \[x=\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{2b}+2b+\dfrac{4{{b}^{3}}}{{{y}^{2}}}\].
Hence, the locus of the middle points of normal chords for the parabola \[{{y}^{2}}=4bx\] is \[x=\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{2b}+2b+\dfrac{4{{b}^{3}}}{{{y}^{2}}}\].
Note: We can also solve this question by writing the equation of normal to the parabola in parametric form instead of slope form and then finding its point of intersection with the parabolas, to find the midpoint of the chord.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




