
How do you find the important points to graph \[f(x) = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}\]?
Answer
507.6k+ views
Hint: In the given equation, we are given an equation and we are asked to find the important points of the given equation. To get the y-intercept we will put x=0 and then to get the x-intercept we will put y=0. Since, we have the main points of the given equation, we can plot the required graph.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that, the function \[f(x) = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}\] we need to find the important points of the graph i.e. domain, range, standard form of the equation, non-defined points, etc.
First, we have to find the Domain of the function (\[{D_f}\]):
And for this, the denominator of the function should not become zero.
When the denominator of the function approaches 0, the function approaches infinity.
\[ \Rightarrow x - 3 \ne 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow x \ne 3\]
Here, \[{D_f}:x \in R - \{ 3\} \]
Thus, \[x \to 3 \Rightarrow f(x) \to \infty \]
Second, we should check the Range of the function (\[{R_f}\]):
Let, \[y = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow yx - 3y = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow yx = 1 + 3y\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{1 + 3y}}{y}\]
Here, \[{R_f}:y \in R - \{ 0\} \]
Thus, \[y \to 0 \Rightarrow x \to \infty \]
Next, we should check for the standard form of equation:
Let, \[y = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow yx - 3y = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow yx = 1 + 3y\]
\[ \Rightarrow xy = 1 + 3y\]
It resembles \[xy = c\] which is the equation for the rectangular hyperbola.
Thus, this equation is in the standard form of rectangular hyperbola.
Also, we will find important points by finding the intercepts (both x and y).
(a) When \[x = 0\]
\[f(x) = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow f(0) = \dfrac{1}{{0 - 3}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow f(0) = - \dfrac{1}{3}\]
Here, the y – intercept is \[0\].
Thus, the co-ordinates we get are \[(0, - \dfrac{1}{3})\].
(b) Let \[y = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}\]
When \[y = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow 0 = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 0 = 1\] which is not possible.
This means, when $y=0$, $x$ value can’t be determined.
The graph of the function \[f(x) = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}\] will look like this:
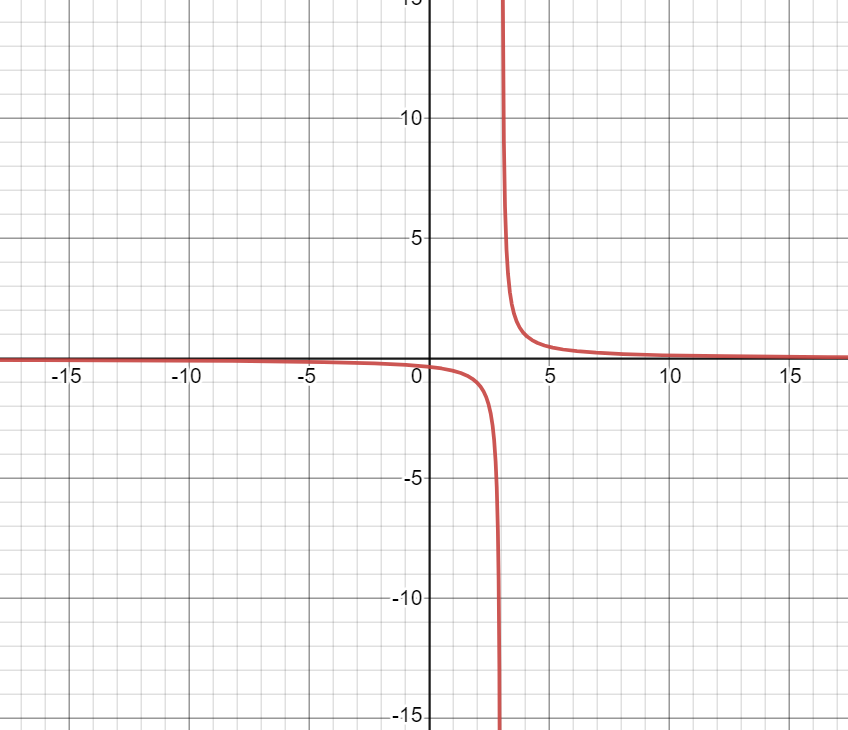
Note:
> In the above graph, when $y=0$, the value of $x$ seems to be approaching zero but it is not zero.
> The intercepts should be correctly known and accordingly only the graph will come out correctly. Also, the equation \[y = {x^2}\] gives the parabola which is open upwards. And, for the equation \[y = - {x^2}\] gives the parabola which is open downwards. We can find the vertex point by making the given equation in the form of the standard equation of the parabola.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that, the function \[f(x) = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}\] we need to find the important points of the graph i.e. domain, range, standard form of the equation, non-defined points, etc.
First, we have to find the Domain of the function (\[{D_f}\]):
And for this, the denominator of the function should not become zero.
When the denominator of the function approaches 0, the function approaches infinity.
\[ \Rightarrow x - 3 \ne 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow x \ne 3\]
Here, \[{D_f}:x \in R - \{ 3\} \]
Thus, \[x \to 3 \Rightarrow f(x) \to \infty \]
Second, we should check the Range of the function (\[{R_f}\]):
Let, \[y = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow yx - 3y = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow yx = 1 + 3y\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{1 + 3y}}{y}\]
Here, \[{R_f}:y \in R - \{ 0\} \]
Thus, \[y \to 0 \Rightarrow x \to \infty \]
Next, we should check for the standard form of equation:
Let, \[y = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow yx - 3y = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow yx = 1 + 3y\]
\[ \Rightarrow xy = 1 + 3y\]
It resembles \[xy = c\] which is the equation for the rectangular hyperbola.
Thus, this equation is in the standard form of rectangular hyperbola.
Also, we will find important points by finding the intercepts (both x and y).
(a) When \[x = 0\]
\[f(x) = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow f(0) = \dfrac{1}{{0 - 3}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow f(0) = - \dfrac{1}{3}\]
Here, the y – intercept is \[0\].
Thus, the co-ordinates we get are \[(0, - \dfrac{1}{3})\].
(b) Let \[y = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}\]
When \[y = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow 0 = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 0 = 1\] which is not possible.
This means, when $y=0$, $x$ value can’t be determined.
The graph of the function \[f(x) = \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}}\] will look like this:

Note:
> In the above graph, when $y=0$, the value of $x$ seems to be approaching zero but it is not zero.
> The intercepts should be correctly known and accordingly only the graph will come out correctly. Also, the equation \[y = {x^2}\] gives the parabola which is open upwards. And, for the equation \[y = - {x^2}\] gives the parabola which is open downwards. We can find the vertex point by making the given equation in the form of the standard equation of the parabola.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




