
Find the GCD of 735 and 85 by using Euclid's algorithm.
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Here we have to find the GCD of 785 and 85. For that, we will divide the given two numbers by a long division method and then we will write a larger number in the quotient remainder form, then we will equate the GCD of the given numbers with the GCD of the divisor obtained and the remainder obtained. We will repeat the method again and again until we make the second term zero.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know the rules of Euclidean Algorithm for finding $GCD(A,B)$ which are:-
If $A=0$ then$GCD(A,B)=B$ , as the$GCD(0,B)=B$ ,
Similarly, if $B=0$ then$GCD(A,B)=A$ , as the$GCD(A,0)=A$,
Here we will make one of the numbers of the GCD by using a long division method.
We have to find the GCD of 735 and 85.
Here $A=735\And B=85$
Here $A\ne 0$ and $B\ne 0$
So we will divide 785 by 85 by long division method.
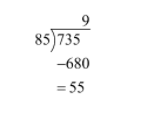
We get 55 as a remainder.
Now, we will write 735 in quotient remainder form.
$\therefore 735=85\times 8+55$
We know from the rule of Euclidean algorithm,
$GCD(A,B)=GCD(B,\text{Remainder})$
Since the remainder here is 55.
Therefore,
$GCD(735,85)=GCD(85,55)$
Now, we will again find GCD $(85,55)$ as neither A here is zero nor B is zero.
Here,$A=85\And B=55$ , which is not zero.
Now, we will again divide 85 by 55
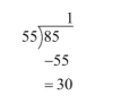
So the remainder is 30.
Now, we will write 85 in the quotient remainder form.
$\therefore 85=55\times 1+30$
Since the remainder here is 30.
Thus,$GCD(85,55)=GCD(55,30)$ from the Euclidean Algorithm rule.
Now, we will again find GCD $(55,30)$ as neither A here is zero nor B is zero.
Here, $A=55\And B=30$ , which is not zero.
Now, we will again divide 55 by 30 by using a long division method.
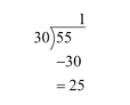
So the remainder is 25.
Now, we will write 55 in the quotient remainder form.
$\therefore 55=30\times 1+25$
Since the remainder here is 25.
Thus, $GCD(85,55)=GCD(30,25)$ from the Euclidean Algorithm rule.
Now, we will again find GCD $(30,25)$ as neither A here is zero nor B is zero.
Here, $A=30\And B=25$ , which is not zero.
Now, we will again divide 30 by 25
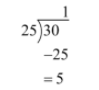
So the remainder is 5.
Now, we will write 30 in the quotient remainder form.
$\therefore 30=25\times 1+5$
Since the remainder here is 5.
Thus, $GCD(30,25)=GCD(25,5)$ from the Euclidean Algorithm rule.
Now we will again find GCD $(25,5)$ as neither A here is zero nor B is zero.
Here, $A=25\And B=5$ , which is not zero.
Now, we will again divide 30 by 25
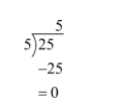
So the remainder is 0.
Thus, $GCD(25,5)=GCD(5,0)$ from the Euclidean Algorithm rule.
And we know;
$GCD(5,0)=5$
Therefore, GCD of 735 and 85 is 5.
Note: Since we have calculated GCD here, let’s define it properly.
The full form of GCD is Greatest Common Divisor. GCD of the two numbers is equal to the largest divisor that will divide both of the integers.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know the rules of Euclidean Algorithm for finding $GCD(A,B)$ which are:-
If $A=0$ then$GCD(A,B)=B$ , as the$GCD(0,B)=B$ ,
Similarly, if $B=0$ then$GCD(A,B)=A$ , as the$GCD(A,0)=A$,
Here we will make one of the numbers of the GCD by using a long division method.
We have to find the GCD of 735 and 85.
Here $A=735\And B=85$
Here $A\ne 0$ and $B\ne 0$
So we will divide 785 by 85 by long division method.
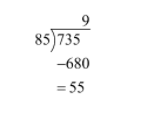
We get 55 as a remainder.
Now, we will write 735 in quotient remainder form.
$\therefore 735=85\times 8+55$
We know from the rule of Euclidean algorithm,
$GCD(A,B)=GCD(B,\text{Remainder})$
Since the remainder here is 55.
Therefore,
$GCD(735,85)=GCD(85,55)$
Now, we will again find GCD $(85,55)$ as neither A here is zero nor B is zero.
Here,$A=85\And B=55$ , which is not zero.
Now, we will again divide 85 by 55
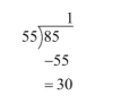
So the remainder is 30.
Now, we will write 85 in the quotient remainder form.
$\therefore 85=55\times 1+30$
Since the remainder here is 30.
Thus,$GCD(85,55)=GCD(55,30)$ from the Euclidean Algorithm rule.
Now, we will again find GCD $(55,30)$ as neither A here is zero nor B is zero.
Here, $A=55\And B=30$ , which is not zero.
Now, we will again divide 55 by 30 by using a long division method.
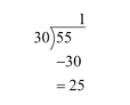
So the remainder is 25.
Now, we will write 55 in the quotient remainder form.
$\therefore 55=30\times 1+25$
Since the remainder here is 25.
Thus, $GCD(85,55)=GCD(30,25)$ from the Euclidean Algorithm rule.
Now, we will again find GCD $(30,25)$ as neither A here is zero nor B is zero.
Here, $A=30\And B=25$ , which is not zero.
Now, we will again divide 30 by 25
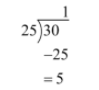
So the remainder is 5.
Now, we will write 30 in the quotient remainder form.
$\therefore 30=25\times 1+5$
Since the remainder here is 5.
Thus, $GCD(30,25)=GCD(25,5)$ from the Euclidean Algorithm rule.
Now we will again find GCD $(25,5)$ as neither A here is zero nor B is zero.
Here, $A=25\And B=5$ , which is not zero.
Now, we will again divide 30 by 25
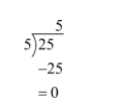
So the remainder is 0.
Thus, $GCD(25,5)=GCD(5,0)$ from the Euclidean Algorithm rule.
And we know;
$GCD(5,0)=5$
Therefore, GCD of 735 and 85 is 5.
Note: Since we have calculated GCD here, let’s define it properly.
The full form of GCD is Greatest Common Divisor. GCD of the two numbers is equal to the largest divisor that will divide both of the integers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




