
How do you find the exact solutions of $\cos 2x - \cos x = 0$ in the interval $\left[ {0,2\pi } \right)$?
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint:
Here we can turn the above given equation into the quadratic equation in $\cos x$ and then we can find the different values of the $\cos x$ and then according to its value we can find the value of $x$ from the graph of the $\cos x$
Complete step by step solution:
Here we need to find the value of $x$ but in the interval which is given as $\left[ {0,2\pi } \right)$
In this interval we must know that this open bracket means that $2\pi $ is not included in the interval and towards the left we have the closed bracket which means $0$ is included in the interval. Hence we cannot take $2\pi $ as our answer.
So here we are given the equation as:
$\cos 2x - \cos x = 0$$ - - - (1)$
We know that $\cos 2x = {\cos ^2}x - {\sin ^2}x$$ - - - - - (2)$
Also we know that
$
{\sin ^2}x + {\cos ^2}x = 1 \\
{\sin ^2}x = 1 - {\cos ^2}x \\
$
Now we can substitute this value in the equation (2) and get:
$
\cos 2x = {\cos ^2}x - (1 - {\cos ^2}x) \\
\cos 2x = 2{\cos ^2}x - 1{\text{ }} - - - - - (3) \\
$
Now substituting this value we get in equation (3) in the equation (1) we will get:
$
2{\cos ^2}x - 1{\text{ }} - \cos x = 0 \\
2{\cos ^2}x - \cos x - 1 = 0 \\
$
Now we get the quadratic equation in $\cos x$
Now we can write in above equation that $\left( { - \cos x} \right) = \left( { - 2\cos x + \cos x} \right)$
We will get:
$2{\cos ^2}x - 2\cos x + \cos x - 1 = 0$
Simplifying it further we will get:
$2\cos x(\cos x - 1) + (\cos x - 1) = 0$
$\left( {2\cos x + 1} \right)\left( {\cos x - 1} \right) = 0$
So we can say either $\cos x = - \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{ or }}\cos x = 1$
Now we can plot the graph of $\cos x$ which is as:
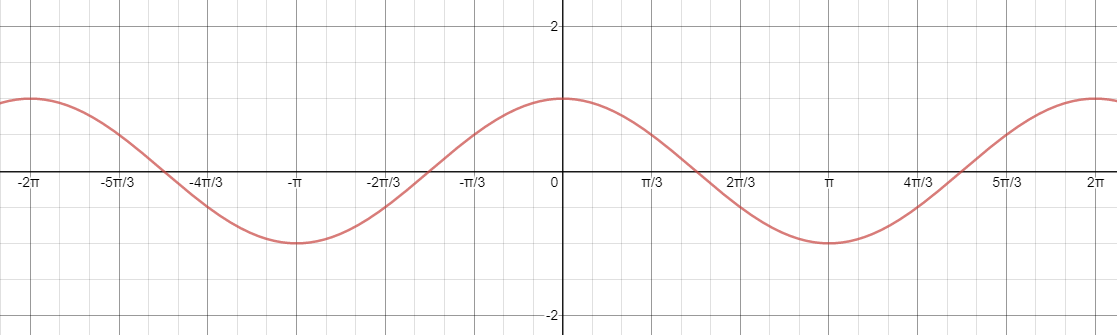
Now we know that from the graph we can see:
$\cos x = - \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{ or }}\cos x = 1$
$
\cos x = 1 \\
x = 0 \\
$
$\cos x = - \dfrac{1}{2}$
From the graph we can notice that:
For $\cos x = - \dfrac{1}{2}$
$x = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3},\dfrac{{4\pi }}{3}$
Hence we get the values as $x = 0,\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3},\dfrac{{4\pi }}{3}$
Note:
If we do not know the graph we can use the properties of cosine function which says that:
$\cos \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3} = \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} + \dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right)$
Now we know that $\cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} + x} \right) = - \sin x$
So we get $\cos \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3} = \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} + \dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right) = - \sin \dfrac{\pi }{6} = - \dfrac{1}{2}$
Hence we must know the properties of all the trigonometric functions in order to solve such problems.
Here we can turn the above given equation into the quadratic equation in $\cos x$ and then we can find the different values of the $\cos x$ and then according to its value we can find the value of $x$ from the graph of the $\cos x$
Complete step by step solution:
Here we need to find the value of $x$ but in the interval which is given as $\left[ {0,2\pi } \right)$
In this interval we must know that this open bracket means that $2\pi $ is not included in the interval and towards the left we have the closed bracket which means $0$ is included in the interval. Hence we cannot take $2\pi $ as our answer.
So here we are given the equation as:
$\cos 2x - \cos x = 0$$ - - - (1)$
We know that $\cos 2x = {\cos ^2}x - {\sin ^2}x$$ - - - - - (2)$
Also we know that
$
{\sin ^2}x + {\cos ^2}x = 1 \\
{\sin ^2}x = 1 - {\cos ^2}x \\
$
Now we can substitute this value in the equation (2) and get:
$
\cos 2x = {\cos ^2}x - (1 - {\cos ^2}x) \\
\cos 2x = 2{\cos ^2}x - 1{\text{ }} - - - - - (3) \\
$
Now substituting this value we get in equation (3) in the equation (1) we will get:
$
2{\cos ^2}x - 1{\text{ }} - \cos x = 0 \\
2{\cos ^2}x - \cos x - 1 = 0 \\
$
Now we get the quadratic equation in $\cos x$
Now we can write in above equation that $\left( { - \cos x} \right) = \left( { - 2\cos x + \cos x} \right)$
We will get:
$2{\cos ^2}x - 2\cos x + \cos x - 1 = 0$
Simplifying it further we will get:
$2\cos x(\cos x - 1) + (\cos x - 1) = 0$
$\left( {2\cos x + 1} \right)\left( {\cos x - 1} \right) = 0$
So we can say either $\cos x = - \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{ or }}\cos x = 1$
Now we can plot the graph of $\cos x$ which is as:

Now we know that from the graph we can see:
$\cos x = - \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{ or }}\cos x = 1$
$
\cos x = 1 \\
x = 0 \\
$
$\cos x = - \dfrac{1}{2}$
From the graph we can notice that:
For $\cos x = - \dfrac{1}{2}$
$x = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3},\dfrac{{4\pi }}{3}$
Hence we get the values as $x = 0,\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3},\dfrac{{4\pi }}{3}$
Note:
If we do not know the graph we can use the properties of cosine function which says that:
$\cos \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3} = \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} + \dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right)$
Now we know that $\cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} + x} \right) = - \sin x$
So we get $\cos \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3} = \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{2} + \dfrac{\pi }{6}} \right) = - \sin \dfrac{\pi }{6} = - \dfrac{1}{2}$
Hence we must know the properties of all the trigonometric functions in order to solve such problems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




