
Find the equation to the straight line drawn at right angles to the straight line $\dfrac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{a}}}{\text{ - }}\dfrac{{\text{y}}}{{\text{b}}}$ =1 through the point where it meets the axis a of x.
Answer
614.7k+ views
Hint- this question is based on the theory of straight line. So we need to first recall the basics of straight line. As we know any straight line with slope m is written in the form of y = mx +c. and the product of slope of two perpendicular line is -1 i.e. $ m \times {{m}_{1}} = -1 $ in this case as discussed below.
Complete step-by-step solution -
The diagram for the question as follow:
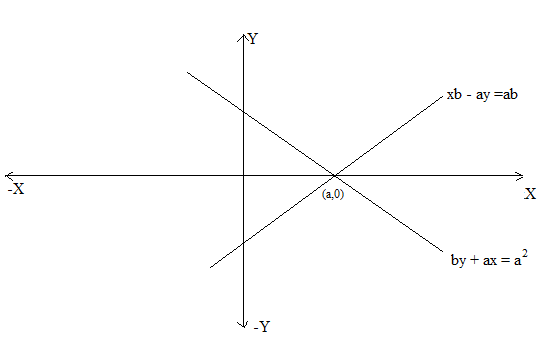
Given line is
$\dfrac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{a}}}{\text{ - }}\dfrac{{\text{y}}}{{\text{b}}}$ =1
Let, Slope of the line is m and its value is
m = $\dfrac{{\text{b}}}{{\text{a}}}$
Then perpendicular slope is ${{\text{m}}_{\text{1}}}$ and its value is
${{\text{m}}_{\text{1}}}$= $\dfrac{{{\text{ - a}}}}{{\text{b}}}$
As we know the equation of straight line with slope ${{\text{m}}_{\text{1}}}$ is y = mx +c.
Then the equation of the line with this slope is y= $\dfrac{ - a}{b}$ x +c ………………… (1)
As (a,0) passes through the above line (Given line meets at x−axis i.e., put y=0)
Then, 0= $\dfrac{{{\text{ - a}}}}{{\text{b}}}$$ \times $a +c
$ \Rightarrow $${\text{c = }}\dfrac{{{{\text{a}}^{\text{2}}}}}{{\text{b}}}$
Put, value of c in equation (1), we get
$\Rightarrow y = \dfrac{-a}{b}\times x + \dfrac{{a}^{2}}{b} $
On taking L.C.M we get the required line $by + ax $ = ${{\text{a}}^{\text{2}}}$.
Note- The important thing is that you should know that the general equation of a straight is given as ax+by = c, where a,b $ \ne $0. You should know that when two lines are perpendicular then the product of their slope is -1 and also if two lines are parallel then their slopes are equal.
Complete step-by-step solution -
The diagram for the question as follow:

Given line is
$\dfrac{{\text{x}}}{{\text{a}}}{\text{ - }}\dfrac{{\text{y}}}{{\text{b}}}$ =1
Let, Slope of the line is m and its value is
m = $\dfrac{{\text{b}}}{{\text{a}}}$
Then perpendicular slope is ${{\text{m}}_{\text{1}}}$ and its value is
${{\text{m}}_{\text{1}}}$= $\dfrac{{{\text{ - a}}}}{{\text{b}}}$
As we know the equation of straight line with slope ${{\text{m}}_{\text{1}}}$ is y = mx +c.
Then the equation of the line with this slope is y= $\dfrac{ - a}{b}$ x +c ………………… (1)
As (a,0) passes through the above line (Given line meets at x−axis i.e., put y=0)
Then, 0= $\dfrac{{{\text{ - a}}}}{{\text{b}}}$$ \times $a +c
$ \Rightarrow $${\text{c = }}\dfrac{{{{\text{a}}^{\text{2}}}}}{{\text{b}}}$
Put, value of c in equation (1), we get
$\Rightarrow y = \dfrac{-a}{b}\times x + \dfrac{{a}^{2}}{b} $
On taking L.C.M we get the required line $by + ax $ = ${{\text{a}}^{\text{2}}}$.
Note- The important thing is that you should know that the general equation of a straight is given as ax+by = c, where a,b $ \ne $0. You should know that when two lines are perpendicular then the product of their slope is -1 and also if two lines are parallel then their slopes are equal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




