
How do I find the directrix of a hyperbola?
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: Here we need to draw the figure of general hyperbola which is $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ and then we must know how to calculate the focus which is given by $\left( {c,0} \right)$ and here ${c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2}$ now we can simply apply the formula to calculate the straight line that represent the directrix and this will be equal to $x = \dfrac{a}{e}{\text{ or }}\dfrac{{{a^2}}}{c}$ where $e$ is eccentricity and given by $e = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{a^2} + {b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}} $.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we need to find the equation of the directrix of the hyperbola. For this, we must know what the equation and the representation of hyperbola are. So let us consider hyperbola as represented below:
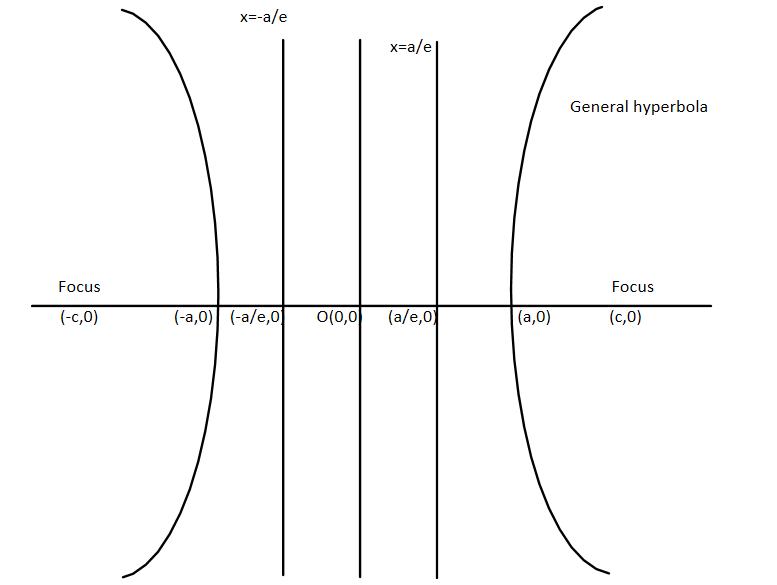
Here we can see that this is the general hyperbola and its general equation is given by:
$\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$
Here the axis on which the vertex is there is called the transverse axis and another is called the conjugate axis.
Now we can see that focus is given by $\left( {c,0} \right)$ and ${c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2}$ where $\left( {a,0} \right){\text{ and }}\left( { - a,0} \right)$ are the two vertices.
The directrix is the line which is parallel to y axis and is given by $x = \dfrac{a}{e}{\text{ or }}\dfrac{{{a^2}}}{c}$ and here $e = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{a^2} + {b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}} $ and represents the eccentricity of the hyperbola.
This can be made clear with an example:
Let us have the hyperbola where we have \[\]
$\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{16}} - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{9} = 1$
So we can compare this above equation with $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ and we will get:
$
a = 4 \\
b = 3 \\
$
Hence we can now calculate the value of $c$ by using the formula which is given by:
${c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2}$
$
{c^2} = {4^2} + {3^2} \\
{c^2} = 16 + 9 = 25 \\
c = \pm 5 \\
$
Now we know that directrix of hyperbola is given by $x = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{c}$
Substituting the values we get:
$x = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{c} = \dfrac{{{4^2}}}{5} = \dfrac{{16}}{5} = 3.2$
So $x = 3.2$ is the directrix of this hyperbola.
Note:
Here the student must know every formula of the general hyperbola because this will be helpful to calculate the results faster and also when we shift the hyperbola centre from origin to any other point.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we need to find the equation of the directrix of the hyperbola. For this, we must know what the equation and the representation of hyperbola are. So let us consider hyperbola as represented below:

Here we can see that this is the general hyperbola and its general equation is given by:
$\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$
Here the axis on which the vertex is there is called the transverse axis and another is called the conjugate axis.
Now we can see that focus is given by $\left( {c,0} \right)$ and ${c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2}$ where $\left( {a,0} \right){\text{ and }}\left( { - a,0} \right)$ are the two vertices.
The directrix is the line which is parallel to y axis and is given by $x = \dfrac{a}{e}{\text{ or }}\dfrac{{{a^2}}}{c}$ and here $e = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{a^2} + {b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}} $ and represents the eccentricity of the hyperbola.
This can be made clear with an example:
Let us have the hyperbola where we have \[\]
$\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{16}} - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{9} = 1$
So we can compare this above equation with $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} - \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ and we will get:
$
a = 4 \\
b = 3 \\
$
Hence we can now calculate the value of $c$ by using the formula which is given by:
${c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2}$
$
{c^2} = {4^2} + {3^2} \\
{c^2} = 16 + 9 = 25 \\
c = \pm 5 \\
$
Now we know that directrix of hyperbola is given by $x = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{c}$
Substituting the values we get:
$x = \dfrac{{{a^2}}}{c} = \dfrac{{{4^2}}}{5} = \dfrac{{16}}{5} = 3.2$
So $x = 3.2$ is the directrix of this hyperbola.
Note:
Here the student must know every formula of the general hyperbola because this will be helpful to calculate the results faster and also when we shift the hyperbola centre from origin to any other point.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




