
Find the critical angle of the ray of light at glass water interface if the refractive indices of glass and water are 1.62 and 1.32 respectively.
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: The above stated problem is an easy application of the Snell’s law of refraction. Snell's law is a formula used when applied to light or other waves moving across a barrier between two distinct isotropic media, such as water, glass or air, to establish the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction. If a certain critical point is achieved by the angle of incidence in water, the refracted ray lies around the boundary, having a 90-degree refraction angle. This angle of incidence is referred to as the critical angle; it is the greatest angle of incidence that can still be refracted.
Formula used:
For solving this question, we will be using the formula from Snell’s Law for refraction is
${{\mu }_{1}}\sin {{\theta }_{1}}={{\mu }_{2}}\sin {{\theta }_{2}}$
Complete answer:
Before we start solving the problem that has been stated to us above, let us take a look at all the parameters that have been given to us
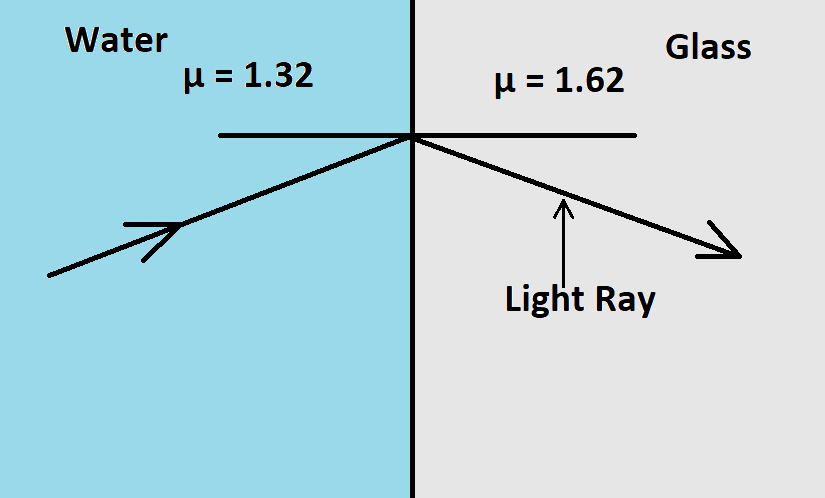
Let the refractive index of the glass be ${{\mu }_{1}}$
Then, ${{\mu }_{1}}$= 1.62
Also, let us assume the refractive index of the water to be ${{\mu }_{2}}$
Then, again
${{\mu }_{1}}$= 1.32
Now,
By applying the Snell’s law for refraction,
We have
${{\mu }_{1}}\sin {{\theta }_{1}}={{\mu }_{2}}\sin {{\theta }_{2}}$
Where ${{\theta }_{1}}$ and ${{\theta }_{2}}$ are the angle of incidence and angle of refraction
Now,
If the ray is going from water to glass,
Then, the critical angle will be
$\Rightarrow {{\theta }_{c}}={{\sin }^{-1}}(\dfrac{{{\mu }_{1}}}{{{\mu }_{2}}})$
So, now
By substituting the values we have in the above formula
We have
$\Rightarrow {{\theta }_{c}}=\sin (\dfrac{1.32}{1.62})$
$\Rightarrow {{\theta }_{c}}={{54.57}^{\circ }}$
So, the critical angle of the ray of light at glass water interface if the refractive indices of glass and water are 1.62 and 1.32 respectively will be ${{54.57}^{\circ }}$
Note:
If the ray of light was entering from glass to the water, then the critical angle will not exist as the ratio of the two refractive indices will be greater than 1, and sin function does not exist for a value greater than 1.
Formula used:
For solving this question, we will be using the formula from Snell’s Law for refraction is
${{\mu }_{1}}\sin {{\theta }_{1}}={{\mu }_{2}}\sin {{\theta }_{2}}$
Complete answer:
Before we start solving the problem that has been stated to us above, let us take a look at all the parameters that have been given to us

Let the refractive index of the glass be ${{\mu }_{1}}$
Then, ${{\mu }_{1}}$= 1.62
Also, let us assume the refractive index of the water to be ${{\mu }_{2}}$
Then, again
${{\mu }_{1}}$= 1.32
Now,
By applying the Snell’s law for refraction,
We have
${{\mu }_{1}}\sin {{\theta }_{1}}={{\mu }_{2}}\sin {{\theta }_{2}}$
Where ${{\theta }_{1}}$ and ${{\theta }_{2}}$ are the angle of incidence and angle of refraction
Now,
If the ray is going from water to glass,
Then, the critical angle will be
$\Rightarrow {{\theta }_{c}}={{\sin }^{-1}}(\dfrac{{{\mu }_{1}}}{{{\mu }_{2}}})$
So, now
By substituting the values we have in the above formula
We have
$\Rightarrow {{\theta }_{c}}=\sin (\dfrac{1.32}{1.62})$
$\Rightarrow {{\theta }_{c}}={{54.57}^{\circ }}$
So, the critical angle of the ray of light at glass water interface if the refractive indices of glass and water are 1.62 and 1.32 respectively will be ${{54.57}^{\circ }}$
Note:
If the ray of light was entering from glass to the water, then the critical angle will not exist as the ratio of the two refractive indices will be greater than 1, and sin function does not exist for a value greater than 1.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




