
Find the correct answer $ A\Delta B= $ \[\]
A. $ \left( A\bigcup B \right)-\left( A\bigcap B \right) $ \[\]
B. $ \left( A\bigcup B \right)+\left( A\bigcap B \right) $ \[\]
C. $ \left( A\bigcap B \right)-\left( A\bigcup B \right) $ \[\]
D. None of these \[\]
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: We recall that $ A\Delta B $ represents the symmetric difference of sets which means all the elements which are in either only in set $ A $ or only in set $ B $ but not both sets $ A,B $ that is $ A\Delta B=\left( A-B \right)\bigcup \left( B-A \right) $ . We us the definition of diffr4renc and put $ A-B=A\bigcap {{B}^{'}},B-A={{A}^{'}}\bigcap B $ and then simplify using distributive property $ A\bigcup \left( B\bigcap C \right)=\left( A\bigcup B \right)\bigcap \left( A\bigcap C \right) $ and De-morgan’s law $ {{\left( A\bigcap B \right)}^{'}}={{A}^{'}}\bigcup {{B}^{'}} $ .
\[\]
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the difference of a set $ A $ from $ B $ represents the elements that are only in $ A $ but not in $ B $ and it is denoted by $ A-B. $ Similarly the difference of a set $ B $ from $ A $ represents the elements that are only in $ B $ but not in $ A $ and it is denoted by $ B-A $ . \[\]
The union of the sets $ A-B $ and $ B-A $ is called symmetric of the sets $ A,B $ and represents all the elements that are wither only in $ A $ or only in $ B $ and is denoted by $ A\Delta B $. Mathematically we have;
\[A\Delta B=\left( A-B \right)\bigcup \left( B-A \right)\]
We know that complement of a set $ A $ can obtain as $ {{A}^{'}}=U-A $ where $ U $ is the universal set.
We know that if we take the intersection of set $ A $ and $ {{B}^{'}} $ from $ A $ and have the elements only in set $ A $ as
\[A-B=A\bigcap {{B}^{'}}\]
Similarly if we take the intersection of set $ {{A}^{'}} $ and $ B $ from $ B $ and have the elements only in set $ B $ as
\[B-A={{A}^{'}}\bigcap B\]
We put $ A-B,B-A $ in the definition of symmetric difference to have;
\[\begin{align}
& A\Delta B=\left( A-B \right)\bigcup \left( B-A \right) \\
& \Rightarrow A\Delta B=\left( A\bigcap {{B}^{'}} \right)\bigcup \left( {{A}^{'}}\bigcap B \right) \\
\end{align}\]
We use the distributive property of sets to have;
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow A\Delta B=\left( \left( A\bigcap {{B}^{'}} \right)\bigcup {{A}^{'}} \right)\bigcap \left( \left( A\bigcap {{B}^{'}} \right)\bigcup B \right) \\
& \Rightarrow A\Delta B=\left( \left( A\bigcup {{A}^{'}} \right)\bigcap \left( {{B}^{'}}\bigcup {{A}^{'}} \right) \right)\bigcap \left( \left( A\bigcup B \right)\bigcap \left( {{B}^{'}}\bigcup B \right) \right) \\
\end{align}\]
We use Demorgan’s law and have;
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow A\Delta B=\left( U\bigcap {{\left( A\bigcap B \right)}^{'}} \right)\bigcap \left( \left( A\bigcup B \right)\bigcap U \right) \\
& \Rightarrow A\Delta B={{\left( A\bigcap B \right)}^{'}}\bigcap \left( A\bigcup B \right) \\
& \Rightarrow A\Delta B=\left( A\bigcup B \right)-\left( A\bigcap B \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Hence the correct is option is A and the Venn diagram of $ A\Delta B $ is given below. \[\]
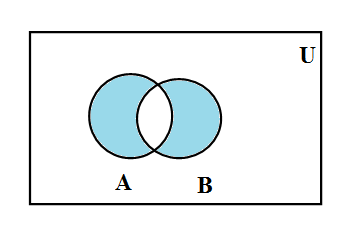
Note:
We note that the union of two sets $ A, B $ represents all the elements that belong to either of the sets $ A $ or $ B $ and is denoted by $ A\bigcup B $ . The intersection of two sets $ A, B $ represents all the elements that belong to both the sets $ A $ and $ B $ and is denoted by $ A\bigcap B $ . Symmetric difference heavily used for indicator function where the function returns 1 or 0 accordingly as output can only belong to two different sets.
\[\]
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the difference of a set $ A $ from $ B $ represents the elements that are only in $ A $ but not in $ B $ and it is denoted by $ A-B. $ Similarly the difference of a set $ B $ from $ A $ represents the elements that are only in $ B $ but not in $ A $ and it is denoted by $ B-A $ . \[\]
The union of the sets $ A-B $ and $ B-A $ is called symmetric of the sets $ A,B $ and represents all the elements that are wither only in $ A $ or only in $ B $ and is denoted by $ A\Delta B $. Mathematically we have;
\[A\Delta B=\left( A-B \right)\bigcup \left( B-A \right)\]
We know that complement of a set $ A $ can obtain as $ {{A}^{'}}=U-A $ where $ U $ is the universal set.
We know that if we take the intersection of set $ A $ and $ {{B}^{'}} $ from $ A $ and have the elements only in set $ A $ as
\[A-B=A\bigcap {{B}^{'}}\]
Similarly if we take the intersection of set $ {{A}^{'}} $ and $ B $ from $ B $ and have the elements only in set $ B $ as
\[B-A={{A}^{'}}\bigcap B\]
We put $ A-B,B-A $ in the definition of symmetric difference to have;
\[\begin{align}
& A\Delta B=\left( A-B \right)\bigcup \left( B-A \right) \\
& \Rightarrow A\Delta B=\left( A\bigcap {{B}^{'}} \right)\bigcup \left( {{A}^{'}}\bigcap B \right) \\
\end{align}\]
We use the distributive property of sets to have;
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow A\Delta B=\left( \left( A\bigcap {{B}^{'}} \right)\bigcup {{A}^{'}} \right)\bigcap \left( \left( A\bigcap {{B}^{'}} \right)\bigcup B \right) \\
& \Rightarrow A\Delta B=\left( \left( A\bigcup {{A}^{'}} \right)\bigcap \left( {{B}^{'}}\bigcup {{A}^{'}} \right) \right)\bigcap \left( \left( A\bigcup B \right)\bigcap \left( {{B}^{'}}\bigcup B \right) \right) \\
\end{align}\]
We use Demorgan’s law and have;
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow A\Delta B=\left( U\bigcap {{\left( A\bigcap B \right)}^{'}} \right)\bigcap \left( \left( A\bigcup B \right)\bigcap U \right) \\
& \Rightarrow A\Delta B={{\left( A\bigcap B \right)}^{'}}\bigcap \left( A\bigcup B \right) \\
& \Rightarrow A\Delta B=\left( A\bigcup B \right)-\left( A\bigcap B \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Hence the correct is option is A and the Venn diagram of $ A\Delta B $ is given below. \[\]

Note:
We note that the union of two sets $ A, B $ represents all the elements that belong to either of the sets $ A $ or $ B $ and is denoted by $ A\bigcup B $ . The intersection of two sets $ A, B $ represents all the elements that belong to both the sets $ A $ and $ B $ and is denoted by $ A\bigcap B $ . Symmetric difference heavily used for indicator function where the function returns 1 or 0 accordingly as output can only belong to two different sets.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




