
How do you find the center and radius of a circle using a polynomial ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-6x+10y+9=0$?
Answer
549.6k+ views
Hint: Convert the given polynomial to the standard form of circle ${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{\left( r \right)}^{2}}$by completing square method. In completing the square method try to get three square terms of ‘x’, ‘y’ and constant. Then find the center and the radius by comparing the obtained expression with the general equation of the circle.
Complete step by step solution:
The standard form of general equation of circle is${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{\left( r \right)}^{2}}$ where (h, k) is the center and ‘r’ is the radius.
The expression we have ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-6x+10y+9=0$
We can convert the given equation to the standard form by completing the square method. For that we have to convert the whole expression to three square terms, one of ‘x’, one of ‘y’ and one of constant.
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-6x+10y+9=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x \right)}^{2}}-2\cdot x\cdot 3+{{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y \right)}^{2}}+2\cdot y\cdot 5+{{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}}+9=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+5 \right)}^{2}}-9-25+9=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+5 \right)}^{2}}=0+25 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-\left( -5 \right) \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now it is in the required form.
Comparing the above equation with the general equation of circle, we get
h=3, k=$-5$ and r=5
Hence, the center of the given circle is (3, $-5$) and radius is ‘5’.
It can be graphed as
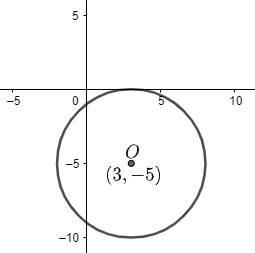
This is the required solution of the given question.
Note: A second degree heterogeneous equation $a{{x}^{2}}+2hxy+b{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0$ may represent a conic if $abc+2fgh-a{{f}^{2}}-b{{g}^{2}}-c{{h}^{2}}\ne 0$. For circle a=b and h=0, so the equation of circle becomes ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0$. In standard form it can be written as ${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{\left( r \right)}^{2}}$ where ‘h’ and ‘k’ represents the ‘x’ and ‘y’ offset from the origin respectively.
Complete step by step solution:
The standard form of general equation of circle is${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{\left( r \right)}^{2}}$ where (h, k) is the center and ‘r’ is the radius.
The expression we have ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-6x+10y+9=0$
We can convert the given equation to the standard form by completing the square method. For that we have to convert the whole expression to three square terms, one of ‘x’, one of ‘y’ and one of constant.
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-6x+10y+9=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x \right)}^{2}}-2\cdot x\cdot 3+{{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y \right)}^{2}}+2\cdot y\cdot 5+{{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}}+9=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+5 \right)}^{2}}-9-25+9=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+5 \right)}^{2}}=0+25 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-3 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-\left( -5 \right) \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Now it is in the required form.
Comparing the above equation with the general equation of circle, we get
h=3, k=$-5$ and r=5
Hence, the center of the given circle is (3, $-5$) and radius is ‘5’.
It can be graphed as

This is the required solution of the given question.
Note: A second degree heterogeneous equation $a{{x}^{2}}+2hxy+b{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0$ may represent a conic if $abc+2fgh-a{{f}^{2}}-b{{g}^{2}}-c{{h}^{2}}\ne 0$. For circle a=b and h=0, so the equation of circle becomes ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+c=0$. In standard form it can be written as ${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{\left( r \right)}^{2}}$ where ‘h’ and ‘k’ represents the ‘x’ and ‘y’ offset from the origin respectively.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




