
How do you find the area of a regular hexagon with a radius of $5?$ Please show working.
Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint:Area of a regular hexagon with radius “r” is given by \[\dfrac{{{r^2}n\sin \left( {\dfrac{{{{360}^0}}}{n}} \right)}}{2}\] where “n” is the number of sides of the regular hexagon. Show working with the help of a figure and try to derive the above formula.
Complete step by step solution:
Do you know how the area of a regular hexagon is equals to
\[\dfrac{{{r^2}n\sin \left( {\dfrac{{{{360}^0}}}{n}} \right)}}{2}\], let us derive this and see how it comes.
Draw a regular hexagon with side $2a$ and radius $R$ Now in this regular hexagon, we can see from figure $\Delta {\text{ABD}}$, if we find the area of $\Delta {\text{ABD}}$ and multiply it by $6$ then we will get the required area of hexagon. Since, we know that in a regular hexagon two times its length of side $(2a)$ is equals to its diameter $(2R)$
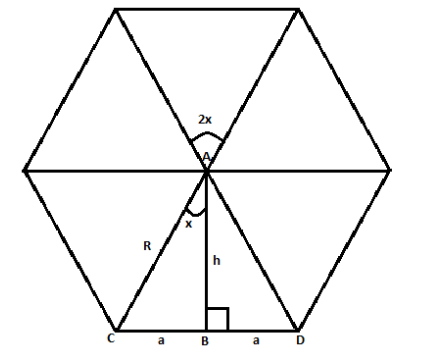
$
\Rightarrow 2R = 2 \times 2a \\
\Rightarrow R = 2a\; - - - - (i) \\
$
Now the area of the $\Delta {\text{ABD}}$ can be written as
\[
= \dfrac{1}{2} \times {\text{base}} \times {\text{heigth}} \\
{\text{ = }}\dfrac{1}{2} \times {\text{CD}} \times {\text{AB}} \\
{\text{ = }}\dfrac{1}{2} \times 2a \times {\text{h}} \\
\]
From equation (i) we know that $R = 2a$ and in $\Delta {\text{ABC}}$ we have
$
\cos x = \dfrac{{{\text{AB}}}}{{{\text{AC}}}} = \dfrac{h}{R} \\
\Rightarrow h = R\cos x \\
$
We can also write $\cos x = \sin ({90^0} - x)$
$ \Rightarrow h = R\sin ({90^0} - x)$
Putting $2a = R\;{\text{and}}\;h = R\sin ({90^0} - x)$ in above area expression,
\[
{\text{ = }}\dfrac{1}{2} \times 2a \times {\text{h}} \\
{\text{ = }}\dfrac{1}{2} \times R \times R\sin ({90^0} - x) \\
{\text{ = }}\dfrac{1}{2} \times {R^2}\sin ({90^0} - x) \\
\]
From figure, we can write \[6 \times 2x = {360^0} \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{{{360}^0}}}{{12}}
\Rightarrow x = {30^0}\] so the above expression will be
\[
{\text{ = }}\dfrac{1}{2} \times {R^2}\sin ({90^0} - x) \\
{\text{ = }}\dfrac{1}{2} \times {R^2}\sin ({90^0} - {30^0}) \\
{\text{ = }}\dfrac{1}{2} \times {R^2}\sin {60^0} \\
\]
So we get the area of $\Delta {\text{ABD}}$, now multiplying it by $n = 6$ (number of triangles) to get area of the hexagon
$ = 6 \times \dfrac{1}{2} \times {R^2}\sin {60^0}$
Now substituting the given value of radius, $R = 5$ we will get
$
= 6 \times \dfrac{1}{2} \times {R^2}\sin {60^0} \\
= 6 \times \dfrac{1}{2} \times {5^2}\sin {60^0} \\
= 6 \times \dfrac{1}{2} \times 25 \times \sin {60^0} \\
= 75 \times \sin {60^0} \\
$
We know the value of $\sin {60^0} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$
$
= 75 \times \sin {60^0} \\
= 75 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} \\
= 64.952\;{\text{uni}}{{\text{t}}^{\text{2}}} \\
$
$\therefore $ the required area of regular hexagon with radius $5\;{\text{units}}\;{\text{ = }}\;{\text{64}}{\text{.952}}\;{\text{uni}}{{\text{t}}^2}$
Note: Apart from regular and irregular hexagon, hexagon is also classified as concave and convex hexagon, concave hexagon has one or more interior angles $ > {180^0}$ whereas in convex hexagon none of its interior angles is $ > {180^0}$ and also the regular hexagon is always a convex one.
Complete step by step solution:
Do you know how the area of a regular hexagon is equals to
\[\dfrac{{{r^2}n\sin \left( {\dfrac{{{{360}^0}}}{n}} \right)}}{2}\], let us derive this and see how it comes.
Draw a regular hexagon with side $2a$ and radius $R$ Now in this regular hexagon, we can see from figure $\Delta {\text{ABD}}$, if we find the area of $\Delta {\text{ABD}}$ and multiply it by $6$ then we will get the required area of hexagon. Since, we know that in a regular hexagon two times its length of side $(2a)$ is equals to its diameter $(2R)$

$
\Rightarrow 2R = 2 \times 2a \\
\Rightarrow R = 2a\; - - - - (i) \\
$
Now the area of the $\Delta {\text{ABD}}$ can be written as
\[
= \dfrac{1}{2} \times {\text{base}} \times {\text{heigth}} \\
{\text{ = }}\dfrac{1}{2} \times {\text{CD}} \times {\text{AB}} \\
{\text{ = }}\dfrac{1}{2} \times 2a \times {\text{h}} \\
\]
From equation (i) we know that $R = 2a$ and in $\Delta {\text{ABC}}$ we have
$
\cos x = \dfrac{{{\text{AB}}}}{{{\text{AC}}}} = \dfrac{h}{R} \\
\Rightarrow h = R\cos x \\
$
We can also write $\cos x = \sin ({90^0} - x)$
$ \Rightarrow h = R\sin ({90^0} - x)$
Putting $2a = R\;{\text{and}}\;h = R\sin ({90^0} - x)$ in above area expression,
\[
{\text{ = }}\dfrac{1}{2} \times 2a \times {\text{h}} \\
{\text{ = }}\dfrac{1}{2} \times R \times R\sin ({90^0} - x) \\
{\text{ = }}\dfrac{1}{2} \times {R^2}\sin ({90^0} - x) \\
\]
From figure, we can write \[6 \times 2x = {360^0} \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{{{360}^0}}}{{12}}
\Rightarrow x = {30^0}\] so the above expression will be
\[
{\text{ = }}\dfrac{1}{2} \times {R^2}\sin ({90^0} - x) \\
{\text{ = }}\dfrac{1}{2} \times {R^2}\sin ({90^0} - {30^0}) \\
{\text{ = }}\dfrac{1}{2} \times {R^2}\sin {60^0} \\
\]
So we get the area of $\Delta {\text{ABD}}$, now multiplying it by $n = 6$ (number of triangles) to get area of the hexagon
$ = 6 \times \dfrac{1}{2} \times {R^2}\sin {60^0}$
Now substituting the given value of radius, $R = 5$ we will get
$
= 6 \times \dfrac{1}{2} \times {R^2}\sin {60^0} \\
= 6 \times \dfrac{1}{2} \times {5^2}\sin {60^0} \\
= 6 \times \dfrac{1}{2} \times 25 \times \sin {60^0} \\
= 75 \times \sin {60^0} \\
$
We know the value of $\sin {60^0} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$
$
= 75 \times \sin {60^0} \\
= 75 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} \\
= 64.952\;{\text{uni}}{{\text{t}}^{\text{2}}} \\
$
$\therefore $ the required area of regular hexagon with radius $5\;{\text{units}}\;{\text{ = }}\;{\text{64}}{\text{.952}}\;{\text{uni}}{{\text{t}}^2}$
Note: Apart from regular and irregular hexagon, hexagon is also classified as concave and convex hexagon, concave hexagon has one or more interior angles $ > {180^0}$ whereas in convex hexagon none of its interior angles is $ > {180^0}$ and also the regular hexagon is always a convex one.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




