
Find the $\angle PMO$ in the following figure:
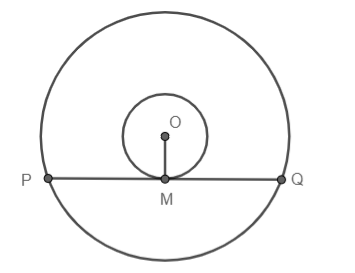
(a) $30{}^\circ $
(b) $45{}^\circ $
(c) $60{}^\circ $
(d) $90{}^\circ $

Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: We know that the tangent and normal at a point to the curve are perpendicular to each other, i.e., the angle between the tangent and the normal at a given point to a curve is $90{}^\circ $ . Also, we know that the normal to a circle always passes through the centre of the circle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us start the solution to the above question by drawing the diagram given in the question for better understanding.
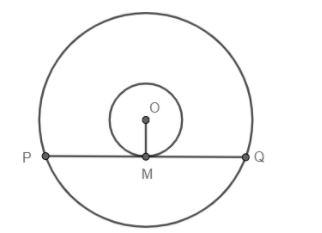
We know that the normal to a circle always passes through the centre of the circle. So, OM is normal to the small circle at M. Also, as PQ touches the smaller circle at a single point, we can say that PQ is the tangent to the small circle meeting the circle at point M.
Now we know that the tangent and normal at a point to the curve are perpendicular to each other, i.e., the angle between the tangent and the normal at a given point to a curve is $90{}^\circ $ . So, we can conclude that $\angle PMO$ , which is an angle between PQ and OM at M is equal to $90{}^\circ $ .
Hence, the answer to the above question is option (d).
Note:The question at the first glance may look related to similarity and congruence of triangles but it won’t be possible to prove the relation between triangle OMP and triangle OMQ as nothing is mentioned in the question, so we cannot get anything from there. So, it is better to go for the approach of tangent and normal as it is easy as well as less time consuming.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us start the solution to the above question by drawing the diagram given in the question for better understanding.

We know that the normal to a circle always passes through the centre of the circle. So, OM is normal to the small circle at M. Also, as PQ touches the smaller circle at a single point, we can say that PQ is the tangent to the small circle meeting the circle at point M.
Now we know that the tangent and normal at a point to the curve are perpendicular to each other, i.e., the angle between the tangent and the normal at a given point to a curve is $90{}^\circ $ . So, we can conclude that $\angle PMO$ , which is an angle between PQ and OM at M is equal to $90{}^\circ $ .
Hence, the answer to the above question is option (d).
Note:The question at the first glance may look related to similarity and congruence of triangles but it won’t be possible to prove the relation between triangle OMP and triangle OMQ as nothing is mentioned in the question, so we cannot get anything from there. So, it is better to go for the approach of tangent and normal as it is easy as well as less time consuming.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




