
How do you find $\sin \left( \dfrac{-pi}{2} \right)$ ?
Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint: Using trigonometric functions, we have to apply the trigonometric ratios for the particular angle and find its value. We should know about the trigonometric ratios for different angles. Also, we should know about the even and odd functions. In this question, particularly sine function is used.
Complete step by step answer:
Basic trigonometric functions are:
$\Rightarrow $ Sine (sin)
$\Rightarrow $Cosine (cos)
$\Rightarrow $Tangent (tan)
When we say $\sin \theta $, here $\theta $ means angle in degrees.
Derived functions are:
$\Rightarrow $cosec$\theta $ = $\dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }$
$\Rightarrow $sec$\theta $ = $\dfrac{1}{\cos \theta }$
$\Rightarrow $tan$\theta $ = $\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }$ = $\dfrac{1}{\cot \theta }$
$\Rightarrow $cot$\theta $ = $\dfrac{1}{\tan \theta }$ = $\dfrac{\cos \theta }{\sin \theta }$
You know what is sin$\theta $? Let’s find out.
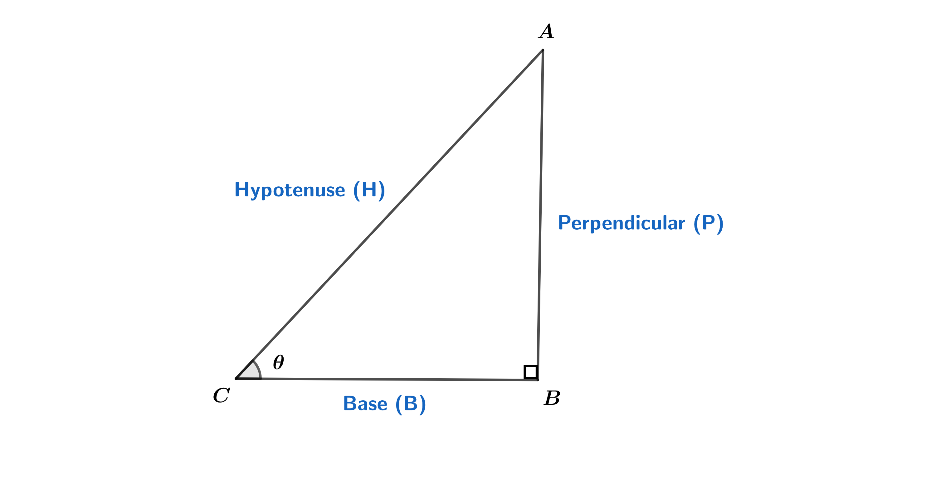
So, from figure, sin$\theta $ = $\dfrac{perpendicular(P)}{hypotenuse(H)}$
Now, let’s see some even and odd functions.
$\Rightarrow $sin(-x) = -sinx
$\Rightarrow $ cos(-x) = cosx
$\Rightarrow $ tan(-x) = -tanx
$\Rightarrow $ cot(-x) = -cotx
$\Rightarrow $ cosec(-x) = -cosecx
$\Rightarrow $sec(-x) = secx
Now, let’s make a table of trigonometric ratios for basic trigonometric functions i.e. sin, cos, tan, cot, sec and cosec.
So, from the trigonometric ratio table, we can see that the value of sin$\theta $ at ${{90}^{\circ }}$is 1.
As we can see in the table, values are given in degrees, but we need the value in radians.
So let’s convert ${{90}^{\circ }}$ to radians.
If we talk about a circle, so 1 revolution about a circle in degrees is ${{360}^{\circ }}$but in radians, it is $2\pi $ radians. So, they both are equal.
$\Rightarrow {{360}^{\circ }}=2\pi $radians
Now, let’s divide $2\pi $ by ${{360}^{\circ }}$:
$\Rightarrow 1=\dfrac{2\pi }{{{360}^{\circ }}}$
$\Rightarrow 1=\dfrac{\pi }{{{180}^{\circ }}}$
Basically, now we will plug in the angle we want to convert units with. So we will multiply with ${{90}^{\circ }}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\pi }{{{180}^{\circ }}}\times {{90}^{\circ }}$
After cancellation we will get:
$\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ rad
Now, we can say if $\sin \dfrac{\pi }{2}=1$ from the table, then $\sin \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2} \right)=-1$ by using the even and odd function here:
$\Rightarrow $sin(-x) = -sinx
So, the final answer is: $\sin \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2} \right)=-1$.
This is the graph of $\sin \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2} \right)=-1$.
Note: Students must know the conversion of degrees to radians. You should remember all the functions and trigonometric ratios before solving any question related to trigonometry. Formula for conversion of degrees to radians is:
Radians = degrees$\times \dfrac{\pi }{{{180}^{\circ }}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Basic trigonometric functions are:
$\Rightarrow $ Sine (sin)
$\Rightarrow $Cosine (cos)
$\Rightarrow $Tangent (tan)
When we say $\sin \theta $, here $\theta $ means angle in degrees.
Derived functions are:
$\Rightarrow $cosec$\theta $ = $\dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }$
$\Rightarrow $sec$\theta $ = $\dfrac{1}{\cos \theta }$
$\Rightarrow $tan$\theta $ = $\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }$ = $\dfrac{1}{\cot \theta }$
$\Rightarrow $cot$\theta $ = $\dfrac{1}{\tan \theta }$ = $\dfrac{\cos \theta }{\sin \theta }$
You know what is sin$\theta $? Let’s find out.

So, from figure, sin$\theta $ = $\dfrac{perpendicular(P)}{hypotenuse(H)}$
Now, let’s see some even and odd functions.
$\Rightarrow $sin(-x) = -sinx
$\Rightarrow $ cos(-x) = cosx
$\Rightarrow $ tan(-x) = -tanx
$\Rightarrow $ cot(-x) = -cotx
$\Rightarrow $ cosec(-x) = -cosecx
$\Rightarrow $sec(-x) = secx
Now, let’s make a table of trigonometric ratios for basic trigonometric functions i.e. sin, cos, tan, cot, sec and cosec.
| Trigonometric ratios(angle $\theta $ in degrees) | ${{0}^{\circ }}$ | ${{30}^{\circ }}$ | ${{45}^{\circ }}$ | ${{60}^{\circ }}$ | ${{90}^{\circ }}$ |
| sin$\theta $ | 0 | $\dfrac{1}{2}$ | $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$ | $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$ | 1 |
| cos$\theta $ | 1 | $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$ | $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$ | $\dfrac{1}{2}$ | 0 |
| tan$\theta $ | 0 | $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$ | 1 | $\sqrt{3}$ | $\infty $ |
| cosec$\theta $ | $\infty $ | 2 | $\sqrt{2}$ | $\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}$ | 1 |
| sec$\theta $ | 1 | $\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}$ | $\sqrt{2}$ | 2 | $\infty $ |
| cot$\theta $ | $\infty $ | $\sqrt{3}$ | 1 | $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$ | 0 |
So, from the trigonometric ratio table, we can see that the value of sin$\theta $ at ${{90}^{\circ }}$is 1.
As we can see in the table, values are given in degrees, but we need the value in radians.
So let’s convert ${{90}^{\circ }}$ to radians.
If we talk about a circle, so 1 revolution about a circle in degrees is ${{360}^{\circ }}$but in radians, it is $2\pi $ radians. So, they both are equal.
$\Rightarrow {{360}^{\circ }}=2\pi $radians
Now, let’s divide $2\pi $ by ${{360}^{\circ }}$:
$\Rightarrow 1=\dfrac{2\pi }{{{360}^{\circ }}}$
$\Rightarrow 1=\dfrac{\pi }{{{180}^{\circ }}}$
Basically, now we will plug in the angle we want to convert units with. So we will multiply with ${{90}^{\circ }}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\pi }{{{180}^{\circ }}}\times {{90}^{\circ }}$
After cancellation we will get:
$\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ rad
Now, we can say if $\sin \dfrac{\pi }{2}=1$ from the table, then $\sin \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2} \right)=-1$ by using the even and odd function here:
$\Rightarrow $sin(-x) = -sinx
So, the final answer is: $\sin \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2} \right)=-1$.
This is the graph of $\sin \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2} \right)=-1$.
Note: Students must know the conversion of degrees to radians. You should remember all the functions and trigonometric ratios before solving any question related to trigonometry. Formula for conversion of degrees to radians is:
Radians = degrees$\times \dfrac{\pi }{{{180}^{\circ }}}$
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

The highest dam in India is A Bhakra dam B Tehri dam class 10 social science CBSE

Describe the process of Unification of Italy class 10 social science CBSE

Who Won 36 Oscar Awards? Record Holder Revealed




