
Find out the names of three metals and nonmetals from the box given in fig:


Answer
501k+ views
Hint: Metals appear on the left side of the periodic table and compromise $ 70% $ all known elements.
Metals are solid at room temperature (mercury is an exception and gallium and caesium have very low melting points.
Nonmetals are placed at the top right-hand side of the periodic table. We go left to right periodically in periodic table property changes metal to nonmetal. Nonmetals are solid or gas at room temperature.
Complete answer:
Metal- We know that metals are placed at the left side of the periodic table and there are $ 70% $ metals in the periodic table. Metals are rich in electrons hence form positive ions.
Properties of metals-
-Metals are solid at room temperature.
-Metals have very high melting and boiling points.
-Metals are good conductors of electricity and heat.
-Metals are malleable and ductile.
Exception (mercury is liquid).
Some examples of metals are - Gold, Silver, Copper, Nickel, Aluminum, Mercury, Titanium, Iron, etc.
Nonmetals- Nonmetals are placed at the top right of the periodic table. Nonmetals form negative ions which means they accept electrons.
Properties of nonmetal-
-Nonmetals are gas or solid at room temperature.
-Nonmetals are good insulators of heat and electricity.
-Nonmetals are non-ductile and non-malleable.
-Nonmetals have low melting and boiling points.
Some examples of Non-metals- Carbon, Phosphorus, Sulphur, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Chlorine, Hydrogen.
Now we can find what metals and nonmetals in the above box are given. We will check horizontally and vertically and find some names.
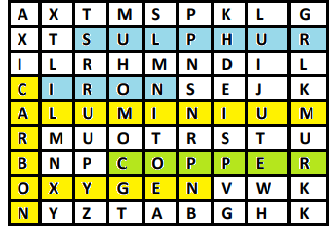
So the in the above-given box-
Nonmetals - Sulphur, Carbon, Oxygen.
Metals - Copper, Aluminum, Iron.
Note:
Look carefully for the correct names in the given box. Before solving this question you should know about the concept of metals and nonmetals and how they are placed in the periodic table. Remember at least some of the very common and useful metals and nonmetal's names. This is memory-based.
Metals are solid at room temperature (mercury is an exception and gallium and caesium have very low melting points.
Nonmetals are placed at the top right-hand side of the periodic table. We go left to right periodically in periodic table property changes metal to nonmetal. Nonmetals are solid or gas at room temperature.
Complete answer:
Metal- We know that metals are placed at the left side of the periodic table and there are $ 70% $ metals in the periodic table. Metals are rich in electrons hence form positive ions.
Properties of metals-
-Metals are solid at room temperature.
-Metals have very high melting and boiling points.
-Metals are good conductors of electricity and heat.
-Metals are malleable and ductile.
Exception (mercury is liquid).
Some examples of metals are - Gold, Silver, Copper, Nickel, Aluminum, Mercury, Titanium, Iron, etc.
Nonmetals- Nonmetals are placed at the top right of the periodic table. Nonmetals form negative ions which means they accept electrons.
Properties of nonmetal-
-Nonmetals are gas or solid at room temperature.
-Nonmetals are good insulators of heat and electricity.
-Nonmetals are non-ductile and non-malleable.
-Nonmetals have low melting and boiling points.
Some examples of Non-metals- Carbon, Phosphorus, Sulphur, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Chlorine, Hydrogen.
Now we can find what metals and nonmetals in the above box are given. We will check horizontally and vertically and find some names.

So the in the above-given box-
Nonmetals - Sulphur, Carbon, Oxygen.
Metals - Copper, Aluminum, Iron.
Note:
Look carefully for the correct names in the given box. Before solving this question you should know about the concept of metals and nonmetals and how they are placed in the periodic table. Remember at least some of the very common and useful metals and nonmetal's names. This is memory-based.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




