
Find number of solutions of the equation $ \sin x={{x}^{2}}+x+1 $ .
Answer
602.7k+ views
Hint: To solve the question given above, we will first find out the range of the function $ f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}+x+1 $ . To find the range, we will find out its maximum value and minimum value as infinite and for an equation $ a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0\ as\ -\left( \dfrac{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}{4a} \right) $ . Then, we will find out at what x, $ f\left( x \right) $ us minimum using $ x=\dfrac{-b}{2a} $ . Then, at that value of x, we will check whether the $ \sin x $ is more than the minimum value of $ f\left( x \right) $ or not. On this basis, we will determine how many solutions are there for the above equations.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To start with, we will first find out the range of the function $ f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}+x+1 $ . Now, to find the range of $ f\left( x \right) $ we will find its maximum value and minimum value. We can clearly see that the maximum value of $ f\left( x \right) $ will be infinite. Now, we know that the minimum value of the equation $ a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0\ as\ -\left( \dfrac{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}{4a} \right) $ . In our case, a = 1, b = 1 and c = 1. Thus, minimum value of $ f\left( x \right)=-\left( \dfrac{{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}-4\left( 1 \right)\left( 1 \right)}{4} \right) $ . Thus, the minimum value of $ f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{-3}{4} $ . Now, the minimum value of $ f\left( x \right) $ occurs at $ x=\dfrac{-b}{2a} $ . Thus, $ x=\dfrac{-1}{2} $ . Thus, the rough graph of $ y={{x}^{2}}+x+1 $ is:
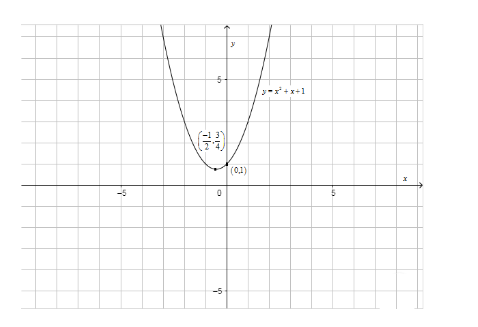
Now, we have to determine the value of $ \sin x $ at $ x=\dfrac{-1}{2} $ . We know that in $ \left[ \dfrac{-\pi }{2},0 \right) $ , $ \sin x $ is negative i.e. it is not possible for $ \sin x $ to interest $ f\left( x \right) $ in that interval. Also, the maximum value of $ \sin x $ is 1. Thus, the combined graph of $ y=\sin x\ and\ y={{x}^{2}}+x+1 $ is shown below:
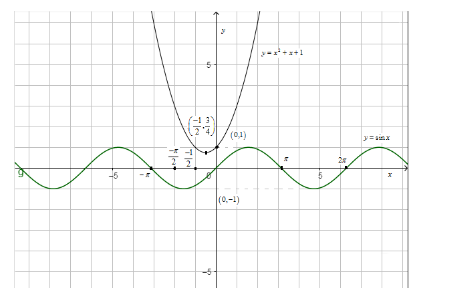
Thus, we can see that both the graphs do not intersect at all. Thus, there will be no solution of $ \sin x={{x}^{2}}+x+1 $ .
Hence, there are 0 solutions of the equation $ \sin x={{x}^{2}}+x+1 $ .
Note: he minima of $ f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}+x+1 $ can also be find out by an alternate method as shown below:
We know that if $ f\left( x \right) $ is a quadratic function of the form $ a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c $ , where $ a>0 $ then its minimum value will occur at $ x=\alpha $ where $ \alpha $ is solution of $ f'\left( x \right)=0 $ . Thus, we have:
$ f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}+x+1 $
On differentiating both sides, we have:
$ \Rightarrow f'\left( x \right)=2x+1 $
Now, $ f'\left( x \right)=0 $ . So, we have
$ \begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2x+1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-1}{2} \\
\end{align} $
At $ x=\dfrac{-1}{2} $ , there will be minima. The value of this minima will be $ =f\left( \dfrac{-1}{2} \right) $ . Thus,
$ \begin{align}
& f\left( \dfrac{-1}{2} \right)={{\left( \dfrac{-1}{2} \right)}^{2}}+\left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)+1 \\
& f\left( \dfrac{-1}{2} \right)=\dfrac{-3}{4}+\dfrac{3}{2}=\dfrac{3}{4} \\
\end{align} $
Complete step-by-step answer:
To start with, we will first find out the range of the function $ f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}+x+1 $ . Now, to find the range of $ f\left( x \right) $ we will find its maximum value and minimum value. We can clearly see that the maximum value of $ f\left( x \right) $ will be infinite. Now, we know that the minimum value of the equation $ a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0\ as\ -\left( \dfrac{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}{4a} \right) $ . In our case, a = 1, b = 1 and c = 1. Thus, minimum value of $ f\left( x \right)=-\left( \dfrac{{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}-4\left( 1 \right)\left( 1 \right)}{4} \right) $ . Thus, the minimum value of $ f\left( x \right)=\dfrac{-3}{4} $ . Now, the minimum value of $ f\left( x \right) $ occurs at $ x=\dfrac{-b}{2a} $ . Thus, $ x=\dfrac{-1}{2} $ . Thus, the rough graph of $ y={{x}^{2}}+x+1 $ is:

Now, we have to determine the value of $ \sin x $ at $ x=\dfrac{-1}{2} $ . We know that in $ \left[ \dfrac{-\pi }{2},0 \right) $ , $ \sin x $ is negative i.e. it is not possible for $ \sin x $ to interest $ f\left( x \right) $ in that interval. Also, the maximum value of $ \sin x $ is 1. Thus, the combined graph of $ y=\sin x\ and\ y={{x}^{2}}+x+1 $ is shown below:

Thus, we can see that both the graphs do not intersect at all. Thus, there will be no solution of $ \sin x={{x}^{2}}+x+1 $ .
Hence, there are 0 solutions of the equation $ \sin x={{x}^{2}}+x+1 $ .
Note: he minima of $ f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}+x+1 $ can also be find out by an alternate method as shown below:
We know that if $ f\left( x \right) $ is a quadratic function of the form $ a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c $ , where $ a>0 $ then its minimum value will occur at $ x=\alpha $ where $ \alpha $ is solution of $ f'\left( x \right)=0 $ . Thus, we have:
$ f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}+x+1 $
On differentiating both sides, we have:
$ \Rightarrow f'\left( x \right)=2x+1 $
Now, $ f'\left( x \right)=0 $ . So, we have
$ \begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2x+1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-1}{2} \\
\end{align} $
At $ x=\dfrac{-1}{2} $ , there will be minima. The value of this minima will be $ =f\left( \dfrac{-1}{2} \right) $ . Thus,
$ \begin{align}
& f\left( \dfrac{-1}{2} \right)={{\left( \dfrac{-1}{2} \right)}^{2}}+\left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)+1 \\
& f\left( \dfrac{-1}{2} \right)=\dfrac{-3}{4}+\dfrac{3}{2}=\dfrac{3}{4} \\
\end{align} $
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




