
Find net force due to the ring on mass m of radius R and mass M?
\[\begin{align}
& A)+\dfrac{2}{3\pi }\dfrac{GmM}{{{R}^{2}}}\widehat{\left\{ j \right\}} \\
& B)+\dfrac{3}{2\pi }\dfrac{GmM}{{{R}^{2}}}\widehat{\left\{ j \right\}} \\
& C)+\dfrac{3}{\pi }\dfrac{GmM}{{{R}^{2}}}\widehat{\left\{ j \right\}} \\
& D)+\dfrac{2}{\pi }\dfrac{GmM}{{{R}^{2}}}\widehat{\left\{ j \right\}} \\
\end{align}\]

Answer
525k+ views
Hint: In this of questions when mass is uniformly distributed over the entire body then we will calculate the force due to small portion of body then we integrate that portion so to get the net force on the other body and for integration we use the simple rule of definite integration and we get the required result.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Consider a small portion in the form of arc on the ring of mass\[dM\]and due to this mass \[dM\] and mass m placed at point O a small force \[dF\]is acting between them.
Suppose that portion of mass\[dM\] is making a small angle\[da\].
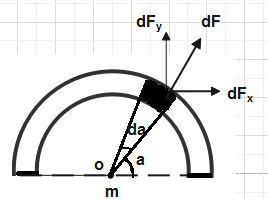
This small force \[dF\]is resolved into two components: -
1.\[d{{F}_{x}}\]- Horizontal Component of force.
2. \[d{{F}_{y}}\]- Vertical Component of force.
Since if we take small portion on the other side of the ring then this \[d{{F}_{x}}\]component of force will cancelled out and only effective component of force is\[d{{F}_{y}}\].
The value of this component of force \[d{{F}_{y}}\] is given as:
\[d{{F}_{y}}=dFSina\]
This \[dF\]is representing a small force between \[m\]and\[dM\].
So the value of \[d{{F}_{y}}\]can be written mathematically as: -
\[d{{F}_{y}}=\dfrac{G(m)(dM)Sina}{{{R}^{2}}}--Equation(1)\]
Since the mass of the whole ring is the length of the ring\[\pi R=M\].
So, mass of 1 unit length of ring \[=\dfrac{M}{\pi R}\]
mass of this arc of length \[Rda\]\[=\dfrac{M}{\pi R}\times Rda\]
mass of this small portion \[dM\]=\[\dfrac{M}{\pi }da\]
Put the value of mass \[dM\]in equation 1 then we get,
\[d{{F}_{y}}=\dfrac{G(m)(\dfrac{M}{\pi }da)Sina}{{{R}^{2}}}\]
on simplifying the above expression we get,
\[d{{F}_{y}}=\dfrac{GmMSina}{\pi {{R}^{2}}}da\]
This is the force exerted by small portion of the ring of mass \[dM\]and we have to calculate the force due to the whole ring so we integrate this above expression so the we can find the net force on mass m due to whole ring of mass M and radius R. So we integrate it from \[0to\pi \] because it is a semicircular ring.
We get ,
\[{{F}_{net}}=\int\limits_{0}^{\pi }{\left( d{{F}_{y}} \right)}\]
\[\begin{align}
& {{F}_{net}}=\int\limits_{0}^{\pi }{\dfrac{GmMSina}{\pi {{R}^{2}}}}da \\
& \Rightarrow {{F}_{net}}=\dfrac{GmM}{\pi {{R}^{2}}}\int\limits_{0}^{\pi }{\left( Sina \right)da} \\
& \Rightarrow {{F}_{net}}=\dfrac{GmM}{\pi {{R}^{2}}}\left[ -Cosa \right]_{0}^{\pi } \\
& \Rightarrow {{F}_{net}}=-\dfrac{GmM}{\pi {{R}^{2}}}[Cos\pi -Cos0] \\
\end{align}\]
On Simplifying we get,
\[{{F}_{net}}=-\dfrac{GmM}{\pi {{R}^{2}}}[-1-1]\]
\[\therefore {{F}_{net}}=+\dfrac{2}{\pi }\dfrac{GmM}{{{R}^{2}}}\widehat{j}\].
Because net force acts in an upward direction along the y-axis.
This is the required expression for force on mass m placed at point O of the ring.
So, the correct option is D.
Note: Newton’s Universal law of gravitation is applied only for small objects in the universe and it's always a attractive force in nature and this attraction is due to the earth and this gravitation force is also called force of gravity when in the two bodies one body is treated as earth .Earth always attract each object towards its centre.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Consider a small portion in the form of arc on the ring of mass\[dM\]and due to this mass \[dM\] and mass m placed at point O a small force \[dF\]is acting between them.
Suppose that portion of mass\[dM\] is making a small angle\[da\].

This small force \[dF\]is resolved into two components: -
1.\[d{{F}_{x}}\]- Horizontal Component of force.
2. \[d{{F}_{y}}\]- Vertical Component of force.
Since if we take small portion on the other side of the ring then this \[d{{F}_{x}}\]component of force will cancelled out and only effective component of force is\[d{{F}_{y}}\].
The value of this component of force \[d{{F}_{y}}\] is given as:
\[d{{F}_{y}}=dFSina\]
This \[dF\]is representing a small force between \[m\]and\[dM\].
So the value of \[d{{F}_{y}}\]can be written mathematically as: -
\[d{{F}_{y}}=\dfrac{G(m)(dM)Sina}{{{R}^{2}}}--Equation(1)\]
Since the mass of the whole ring is the length of the ring\[\pi R=M\].
So, mass of 1 unit length of ring \[=\dfrac{M}{\pi R}\]
mass of this arc of length \[Rda\]\[=\dfrac{M}{\pi R}\times Rda\]
mass of this small portion \[dM\]=\[\dfrac{M}{\pi }da\]
Put the value of mass \[dM\]in equation 1 then we get,
\[d{{F}_{y}}=\dfrac{G(m)(\dfrac{M}{\pi }da)Sina}{{{R}^{2}}}\]
on simplifying the above expression we get,
\[d{{F}_{y}}=\dfrac{GmMSina}{\pi {{R}^{2}}}da\]
This is the force exerted by small portion of the ring of mass \[dM\]and we have to calculate the force due to the whole ring so we integrate this above expression so the we can find the net force on mass m due to whole ring of mass M and radius R. So we integrate it from \[0to\pi \] because it is a semicircular ring.
We get ,
\[{{F}_{net}}=\int\limits_{0}^{\pi }{\left( d{{F}_{y}} \right)}\]
\[\begin{align}
& {{F}_{net}}=\int\limits_{0}^{\pi }{\dfrac{GmMSina}{\pi {{R}^{2}}}}da \\
& \Rightarrow {{F}_{net}}=\dfrac{GmM}{\pi {{R}^{2}}}\int\limits_{0}^{\pi }{\left( Sina \right)da} \\
& \Rightarrow {{F}_{net}}=\dfrac{GmM}{\pi {{R}^{2}}}\left[ -Cosa \right]_{0}^{\pi } \\
& \Rightarrow {{F}_{net}}=-\dfrac{GmM}{\pi {{R}^{2}}}[Cos\pi -Cos0] \\
\end{align}\]
On Simplifying we get,
\[{{F}_{net}}=-\dfrac{GmM}{\pi {{R}^{2}}}[-1-1]\]
\[\therefore {{F}_{net}}=+\dfrac{2}{\pi }\dfrac{GmM}{{{R}^{2}}}\widehat{j}\].
Because net force acts in an upward direction along the y-axis.
This is the required expression for force on mass m placed at point O of the ring.
So, the correct option is D.
Note: Newton’s Universal law of gravitation is applied only for small objects in the universe and it's always a attractive force in nature and this attraction is due to the earth and this gravitation force is also called force of gravity when in the two bodies one body is treated as earth .Earth always attract each object towards its centre.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




