
How do you find all the six trigonometric functions of $\theta $ if the given point $\left( 5,0 \right)$ is on the terminal side of $\theta $ ?
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: To find all the six trigonometric functions of $\theta $ if the point $\left( 5,0 \right)$ is on the terminal side of $\theta $, we will plot the point on the graph. The y coordinate of the point is 0. Therefore, the point $\left( 5,0 \right)$ will be X-axis. Hence, we can say that the distance of this point to the origin will be 5. Also, we can see that the angle $\theta $ will be equal to 0 degrees. Therefore, the adjacent side and hypotenuse will be similar and is equal to 5 units while the opposite side will be 0 units. Now, we have to find the trigonometric functions using the definition that $\sin \theta $ is the ratio of opposite side to the hypotenuse, $\cos \theta $ is the ratio of adjacent side to the hypotenuse, $\tan \theta $ is the ratio of opposite side to the adjacent, $\cot \theta $ is the reciprocal of $\tan \theta $, $\csc \theta $ is the reciprocal of $\sin \theta $ and $\sec \theta $ is the reciprocal of $\cos \theta $.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We have to find all the six trigonometric functions of $\theta $ if the given point $\left( 5,0 \right)$ is on the terminal side of $\theta $ . Let us graph the point $\left( 5,0 \right)$ .
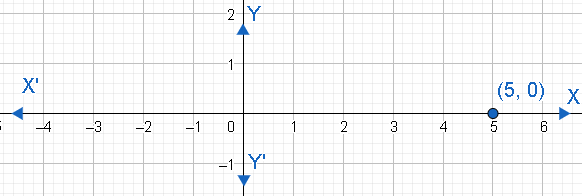
We know that the point $\left( 5,0 \right)$ will be X-axis. Therefore, the distance of this point to the origin will be 5. Also, we can see that the angle $\theta $ will be equal to 0 degrees. Therefore, the adjacent side and hypotenuse will be similar and is equal to 5 units while the opposite side will be 0 units.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \text{Adjacent side}=5\text{units} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{Opposite side}=0\text{units} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{Hypotenuse side}=5\text{units} \\
& \Rightarrow \theta =0{}^\circ \\
\end{align}\]
We know that $\sin \theta =\dfrac{\text{Opposite side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$ . Let us substitute the values.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \sin 0{}^\circ =\dfrac{0}{5} \\
& \Rightarrow \sin 0{}^\circ =0 \\
\end{align}$
We know that $\cos \theta =\dfrac{\text{Adjacent side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$ . Let us substitute the values.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos 0{}^\circ =\dfrac{5}{5} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos 0{}^\circ =1 \\
\end{align}$
We know that $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Opposite side}}{\text{Adjacent side}}$ .
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \tan 0{}^\circ =\dfrac{0}{5} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan 0{}^\circ =0 \\
\end{align}$
We know that $\cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{\tan \theta }$ .
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cot 0{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{0} \\
& \Rightarrow \cot 0{}^\circ =\infty \text{ (undefined)} \\
\end{align}$
We know that $\sec \theta =\dfrac{1}{\cos \theta }$ .
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \sec 0{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{1} \\
& \Rightarrow \sec 0{}^\circ =1 \\
\end{align}$
We know that $\csc \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }$ .
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \csc 0{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{0} \\
& \Rightarrow \csc 0{}^\circ =\infty \text{ (undefined)} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, $\sin 0{}^\circ =0,\cos 0{}^\circ =1,\tan 0{}^\circ =0,\cot 0{}^\circ =\infty ,\sec 0{}^\circ =1,\csc 0{}^\circ =\infty $.
Note: Students must know the definitions of the trigonometric functions in terms of triangles. They must know how sine and cosecant, tangent and cotangent, and cosine and secant are related. We can also find $\tan 0{}^\circ $ using the definition $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }$ .
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \tan 0{}^\circ =\dfrac{0}{1} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan 0{}^\circ =0 \\
\end{align}$
If the angle is $90{}^\circ $ , then the length of the adjacent side is equal to 0 and the length of the opposite side is equal to the length of the hypotenuse.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We have to find all the six trigonometric functions of $\theta $ if the given point $\left( 5,0 \right)$ is on the terminal side of $\theta $ . Let us graph the point $\left( 5,0 \right)$ .

We know that the point $\left( 5,0 \right)$ will be X-axis. Therefore, the distance of this point to the origin will be 5. Also, we can see that the angle $\theta $ will be equal to 0 degrees. Therefore, the adjacent side and hypotenuse will be similar and is equal to 5 units while the opposite side will be 0 units.
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \text{Adjacent side}=5\text{units} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{Opposite side}=0\text{units} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{Hypotenuse side}=5\text{units} \\
& \Rightarrow \theta =0{}^\circ \\
\end{align}\]
We know that $\sin \theta =\dfrac{\text{Opposite side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$ . Let us substitute the values.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \sin 0{}^\circ =\dfrac{0}{5} \\
& \Rightarrow \sin 0{}^\circ =0 \\
\end{align}$
We know that $\cos \theta =\dfrac{\text{Adjacent side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$ . Let us substitute the values.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos 0{}^\circ =\dfrac{5}{5} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos 0{}^\circ =1 \\
\end{align}$
We know that $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Opposite side}}{\text{Adjacent side}}$ .
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \tan 0{}^\circ =\dfrac{0}{5} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan 0{}^\circ =0 \\
\end{align}$
We know that $\cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{\tan \theta }$ .
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cot 0{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{0} \\
& \Rightarrow \cot 0{}^\circ =\infty \text{ (undefined)} \\
\end{align}$
We know that $\sec \theta =\dfrac{1}{\cos \theta }$ .
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \sec 0{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{1} \\
& \Rightarrow \sec 0{}^\circ =1 \\
\end{align}$
We know that $\csc \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }$ .
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \csc 0{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{0} \\
& \Rightarrow \csc 0{}^\circ =\infty \text{ (undefined)} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, $\sin 0{}^\circ =0,\cos 0{}^\circ =1,\tan 0{}^\circ =0,\cot 0{}^\circ =\infty ,\sec 0{}^\circ =1,\csc 0{}^\circ =\infty $.
Note: Students must know the definitions of the trigonometric functions in terms of triangles. They must know how sine and cosecant, tangent and cotangent, and cosine and secant are related. We can also find $\tan 0{}^\circ $ using the definition $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }$ .
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \tan 0{}^\circ =\dfrac{0}{1} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan 0{}^\circ =0 \\
\end{align}$
If the angle is $90{}^\circ $ , then the length of the adjacent side is equal to 0 and the length of the opposite side is equal to the length of the hypotenuse.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




