
Fill in the blanks:
A thin filament of myofibril contains 2 ‘F’ actin and two other proteins namely …………, and …………?
Answer
573k+ views
Hint: The two proteins attached and among them, one lies in the groove between actin filaments in muscle tissues, and the other blocks the attachment site for the myosin crossbridge, in a relaxed muscle, and thus prevents contraction.
Complete answer:
A basic rod-like unit of a muscle cell in our body is known as myofibril (also known as a muscle fibril). Muscles in our body are composed of tubular cells which are called myocytes which contain many chains of myofibrils. During embryonic development, these myofibrils are created in a process known as myogenesis which consists of long proteins including actin, myosin, and titin, and other proteins that hold them together. When myofilaments are synthesized by these proteins by organizing together into thick and thin filaments that repeat along the length of the myofibril in sections called sarcomeres. The contraction of muscles occurs by sliding the thick (myosin) and thin (actin) filaments along with each other.
The two other proteins that are present in a thin filament of myofibril are troponin and tropomyosin, where troponin is a complex of three regulatory proteins that are integral to muscle contraction in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle but not smooth muscle, and tropomyosin is a two-stranded alpha-helical coiled-coil protein that is found in cell cytoskeletons. muscle contraction is regulated by these two proteins. The calcium ions bind to the troponin and remove the tropomyosin from the actin myosin-binding site which allows muscle contraction and the muscle relaxes when the calcium ions are not attached to the troponin and it pushes the tropomyosin to block the binding site.
Additional Information: 1)The protein troponin itself has three subunits which play a role in force regulation: TnC(Troponin C) that binds to calcium ions to produce a conformational change in TnI; TnI(Troponin I) which binds to actin in thin myofilaments to hold the actin-tropomyosin complex in place and the last one TnT (Troponin T) binds to tropomyosin, interlocking them to form a troponin-tropomyosin complex.
2) Troponin was discovered in 1965 and to detect serum troponin, a sensitive and reliable radioimmunoassay was developed in the late 1990s.
3) Crustaceans and mollusks include Shellfish where tropomyosin is a protein primarily responsible for shellfish allergy.
4) In 1946 Bailey discovered tropomyosin and isolated it in the year 1948.
So, the correct answer is, ‘troponin and tropomyosin’.
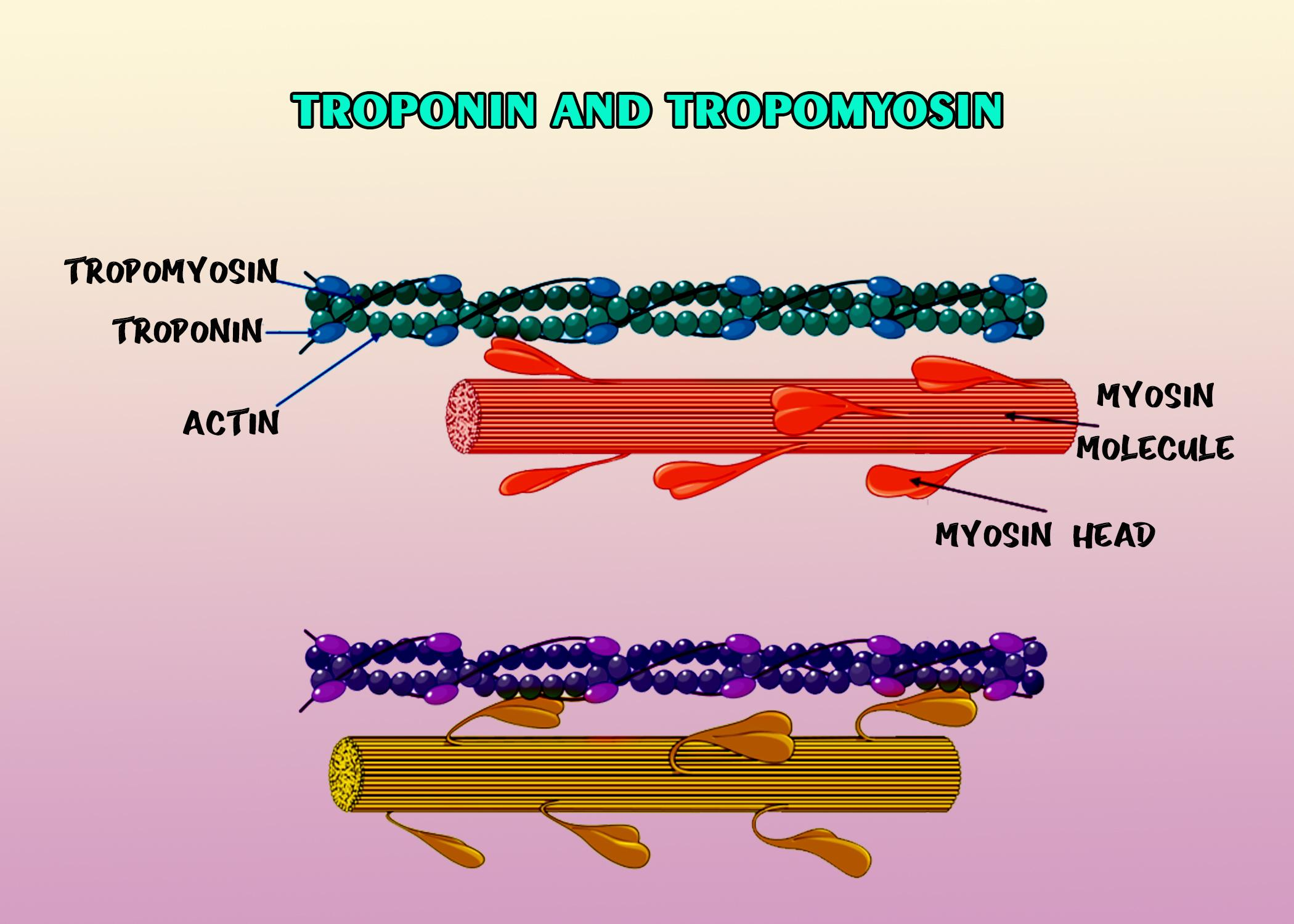
Note: In both skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, the protein troponin is found but the specific versions of troponin differ between types of muscle; and the main difference of the TnC subunit is that in cardiac muscle there are only three sites for calcium ion-binding, whereas four sites in skeletal muscle. And in the process of skeletal muscle contraction, the protein tropomyosin has involved that wraps around actin and prevents myosin from grabbing it which prevents muscle contractions until the proper signal arrives. The calcium is released when the nervous system tells the muscle cell to contract.
Complete answer:
A basic rod-like unit of a muscle cell in our body is known as myofibril (also known as a muscle fibril). Muscles in our body are composed of tubular cells which are called myocytes which contain many chains of myofibrils. During embryonic development, these myofibrils are created in a process known as myogenesis which consists of long proteins including actin, myosin, and titin, and other proteins that hold them together. When myofilaments are synthesized by these proteins by organizing together into thick and thin filaments that repeat along the length of the myofibril in sections called sarcomeres. The contraction of muscles occurs by sliding the thick (myosin) and thin (actin) filaments along with each other.
The two other proteins that are present in a thin filament of myofibril are troponin and tropomyosin, where troponin is a complex of three regulatory proteins that are integral to muscle contraction in skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle but not smooth muscle, and tropomyosin is a two-stranded alpha-helical coiled-coil protein that is found in cell cytoskeletons. muscle contraction is regulated by these two proteins. The calcium ions bind to the troponin and remove the tropomyosin from the actin myosin-binding site which allows muscle contraction and the muscle relaxes when the calcium ions are not attached to the troponin and it pushes the tropomyosin to block the binding site.
Additional Information: 1)The protein troponin itself has three subunits which play a role in force regulation: TnC(Troponin C) that binds to calcium ions to produce a conformational change in TnI; TnI(Troponin I) which binds to actin in thin myofilaments to hold the actin-tropomyosin complex in place and the last one TnT (Troponin T) binds to tropomyosin, interlocking them to form a troponin-tropomyosin complex.
2) Troponin was discovered in 1965 and to detect serum troponin, a sensitive and reliable radioimmunoassay was developed in the late 1990s.
3) Crustaceans and mollusks include Shellfish where tropomyosin is a protein primarily responsible for shellfish allergy.
4) In 1946 Bailey discovered tropomyosin and isolated it in the year 1948.
So, the correct answer is, ‘troponin and tropomyosin’.

Note: In both skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle, the protein troponin is found but the specific versions of troponin differ between types of muscle; and the main difference of the TnC subunit is that in cardiac muscle there are only three sites for calcium ion-binding, whereas four sites in skeletal muscle. And in the process of skeletal muscle contraction, the protein tropomyosin has involved that wraps around actin and prevents myosin from grabbing it which prevents muscle contractions until the proper signal arrives. The calcium is released when the nervous system tells the muscle cell to contract.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




