
Figure shows a long rectangular strip of paper, one corner of which has been folded over along \[AC\] to meet the opposite edge, thereby creating angle \[\angle CAB = \theta \]. (all diagram are drawn using paint)
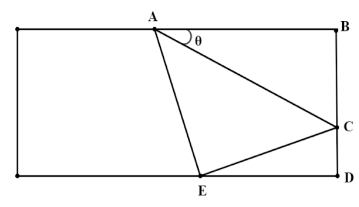
Given that the width of the strip, i.e., \[BD\] is \[w\]inches, express the length of the crease \[AC\]in terms of \[w\] and \[\theta \], assume that \[\theta \] is between \[{0^ \circ }\] and \[{45^ \circ }\].

Answer
511.8k+ views
Hint: Here in this question, we have to find the length of \[AC\] in a long rectangular strip of paper and express it in terms of \[w\] and \[\theta \], where \[\theta \] is the angle made by the folded strip and \[w\] is the width of the paper strip. On using a definition of the cosine trigonometric ratio we get the required solution.
Complete step by step answer:
Given a rectangular strip of paper, one corner of paper has been folded over along \[AC\] to meet the opposite edge and it creates an angle \[\angle CAB = \theta \].Now, we have found and expressed the length of \[AC\] in terms of \[w\] and \[\theta \].In figure, As we know all the corner of rectangle forms an angle \[{90^0}\] and given the angle \[\angle CAB = \theta \], then the \[\angle CAE = 90 - \theta \].
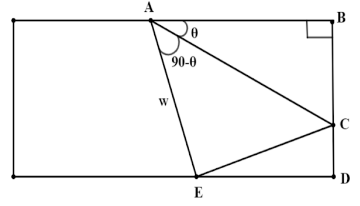
In triangle \[\vartriangle \,ACE\], the angle \[\angle CAE = 90 - \theta \]
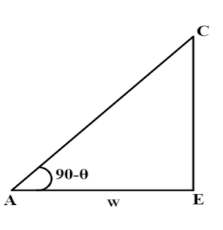
The side \[AF\] is the adjacent side and \[AC\] is the hypotenuse side with respect to the angle \[\angle CAE\]. As we know the definition of cosine trigonometric ratio is the ratio of the adjacent and hypotenuse side i.e., In, \[\vartriangle \,ACE\]
\[\cos \left( {\angle CAE} \right) = \dfrac{{AE}}{{AC}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \,\,\,\cos \left( {90 - \theta } \right) = \dfrac{{AE}}{{AC}}\]
The angle \[{90^ \circ }\] is a complementary angle then \[\cos \left( {90 - \theta } \right) = \sin \theta \], then
\[ \Rightarrow \,\,\,\sin \theta = \dfrac{w}{{AC}}\]
On cross multiplication, we get
\[\therefore \,\,\,AC = \dfrac{w}{{\sin \theta }}\]
Hence, it’s a required solution
Note: On identifying the angle student must be careful on it and should know the definitions of all six trigonometric ratios sine, cosine, tangent, secant, cosecant and cotangent choose the ratio depending on the known value of the sides. Remember when the sum of two angles is \[{90^ \circ }\], then the angles are known as complementary angles at that time the ratios will change like \[\sin \leftrightarrow \cos \], \[sec \leftrightarrow cosec\] and \[\tan \leftrightarrow cot\].
Complete step by step answer:
Given a rectangular strip of paper, one corner of paper has been folded over along \[AC\] to meet the opposite edge and it creates an angle \[\angle CAB = \theta \].Now, we have found and expressed the length of \[AC\] in terms of \[w\] and \[\theta \].In figure, As we know all the corner of rectangle forms an angle \[{90^0}\] and given the angle \[\angle CAB = \theta \], then the \[\angle CAE = 90 - \theta \].

In triangle \[\vartriangle \,ACE\], the angle \[\angle CAE = 90 - \theta \]

The side \[AF\] is the adjacent side and \[AC\] is the hypotenuse side with respect to the angle \[\angle CAE\]. As we know the definition of cosine trigonometric ratio is the ratio of the adjacent and hypotenuse side i.e., In, \[\vartriangle \,ACE\]
\[\cos \left( {\angle CAE} \right) = \dfrac{{AE}}{{AC}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \,\,\,\cos \left( {90 - \theta } \right) = \dfrac{{AE}}{{AC}}\]
The angle \[{90^ \circ }\] is a complementary angle then \[\cos \left( {90 - \theta } \right) = \sin \theta \], then
\[ \Rightarrow \,\,\,\sin \theta = \dfrac{w}{{AC}}\]
On cross multiplication, we get
\[\therefore \,\,\,AC = \dfrac{w}{{\sin \theta }}\]
Hence, it’s a required solution
Note: On identifying the angle student must be careful on it and should know the definitions of all six trigonometric ratios sine, cosine, tangent, secant, cosecant and cotangent choose the ratio depending on the known value of the sides. Remember when the sum of two angles is \[{90^ \circ }\], then the angles are known as complementary angles at that time the ratios will change like \[\sin \leftrightarrow \cos \], \[sec \leftrightarrow cosec\] and \[\tan \leftrightarrow cot\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




