
What is fertilization? Explain double fertilization and mention the changes which occur in the flowers after fertilization.
Answer
599.4k+ views
Hint: It occurs naturally through the reproductive process. As a result, it forms zygote which is diploid in nature. Sometimes fertilization occurs in a repetitive process and several changes occur in plants especially in flowers.
Complete answer
Fertilization: When two gametes with opposite sex fuse together and produce new life form, the process is called fertilization. Here, the gametes are haploids (n) and the zygotes are diploid (2n) in nature.
Double fertilization: A complex fertilization process in flowering plants mainly in angiosperms is called double fertilization. When a female gametophyte fuses with two male gametes it involves the joining of two. Here, the female gametophyte is known as megagametophyte and it forms embryo sac. It begins when the pollen grain nicked into the stigma of gynoecium i.e. the reproductive organ of the flower. When the pollen grains start to germinate it forms a pollen tube which goes through style to ovary. There is an opening called micropyle and to the ovule. Pollen tubes then release two sperm from the female megagametophyte. Ovules that are unfertilized are 8 in number and form antipodal cells, polar cells, egg cells and synergid cells. They are respectively 3, 2, 1, 2 in number. At first, the egg cell is fertilized by one sperm cell and binds with the polar nucleus. When egg and sperm fuse together it forms diploid zygote. This process is called syngamy. Besides, the other sperm binds with polar nuclei for forming a triple nucleus. Thus the whole double fertilization process occurs.
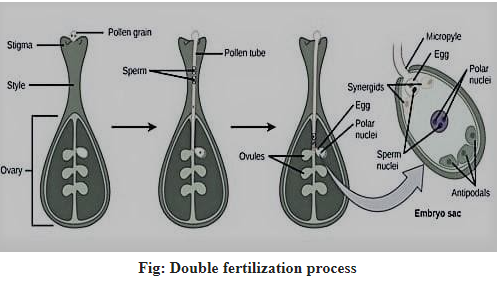
Note:New adults are formed as a result of fertilization. Double fertilization is mainly found in plants. Such an example is Arabidopsis thaliana.
Complete answer
Fertilization: When two gametes with opposite sex fuse together and produce new life form, the process is called fertilization. Here, the gametes are haploids (n) and the zygotes are diploid (2n) in nature.
Double fertilization: A complex fertilization process in flowering plants mainly in angiosperms is called double fertilization. When a female gametophyte fuses with two male gametes it involves the joining of two. Here, the female gametophyte is known as megagametophyte and it forms embryo sac. It begins when the pollen grain nicked into the stigma of gynoecium i.e. the reproductive organ of the flower. When the pollen grains start to germinate it forms a pollen tube which goes through style to ovary. There is an opening called micropyle and to the ovule. Pollen tubes then release two sperm from the female megagametophyte. Ovules that are unfertilized are 8 in number and form antipodal cells, polar cells, egg cells and synergid cells. They are respectively 3, 2, 1, 2 in number. At first, the egg cell is fertilized by one sperm cell and binds with the polar nucleus. When egg and sperm fuse together it forms diploid zygote. This process is called syngamy. Besides, the other sperm binds with polar nuclei for forming a triple nucleus. Thus the whole double fertilization process occurs.

Note:New adults are formed as a result of fertilization. Double fertilization is mainly found in plants. Such an example is Arabidopsis thaliana.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




