
Eye defect in which a person cannot see near objects clearly.
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: As we have learnt that the human eye is a sensory organ and reacts to light to allow the vision. There are chiefly three types of eye defects which makes us unable to see clearly and these are named as Myopia, Hypermetropia and Astigmatism.
Complete answer:
As we all know, light enters the eye through the cornea which is a curved surface. It passes through a pupil which is the central hole in the iris. Light is further focused by the lens of the eye on the retina which contains rods and cones cells. It senses the light’s intensity and colour and transmits the signals to the brain through the optic nerve. When the light focused by the lens doesn’t fall on the retina, it causes Myopia or Hypermetropia.
Myopia, also known as near-sightedness, occurs when the light from a distant object arriving at the eye lens may get converged at a point in front of the retina. In this defect we are able to see nearby objects but not the far objects. We can use a concave lens to correct this defect.
Hypermetropia, also called Farsightedness, occurs when the eye lens focuses the incoming light from a distant object at a point behind the retina rather than directly falling on it. We can see the far objects clearly but not the near objects when having this defect of eye. This defect can be corrected by using a converging lens.
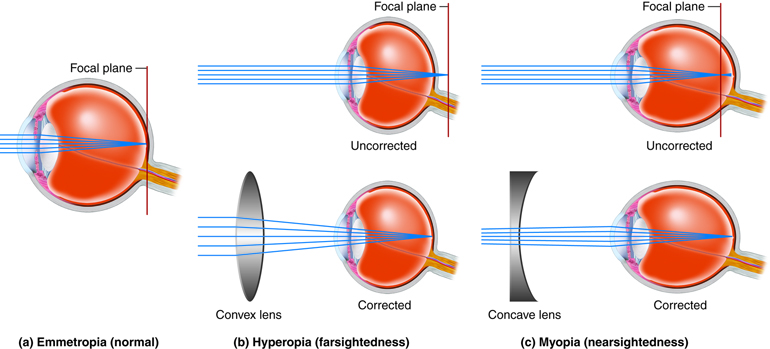
Hence, the eye defect in which a person cannot see the near objects clearly is Hypermetropia.
Note: The least distance of distinct vision is the closest distance for where the eye can focus light on the retina. It is normally 25cm. You must have seen minus or plus signs in eyeglass prescription. The minus sign denotes that the person is near-sighted while the plus sign denotes farsightedness.
Complete answer:
As we all know, light enters the eye through the cornea which is a curved surface. It passes through a pupil which is the central hole in the iris. Light is further focused by the lens of the eye on the retina which contains rods and cones cells. It senses the light’s intensity and colour and transmits the signals to the brain through the optic nerve. When the light focused by the lens doesn’t fall on the retina, it causes Myopia or Hypermetropia.
Myopia, also known as near-sightedness, occurs when the light from a distant object arriving at the eye lens may get converged at a point in front of the retina. In this defect we are able to see nearby objects but not the far objects. We can use a concave lens to correct this defect.
Hypermetropia, also called Farsightedness, occurs when the eye lens focuses the incoming light from a distant object at a point behind the retina rather than directly falling on it. We can see the far objects clearly but not the near objects when having this defect of eye. This defect can be corrected by using a converging lens.

Hence, the eye defect in which a person cannot see the near objects clearly is Hypermetropia.
Note: The least distance of distinct vision is the closest distance for where the eye can focus light on the retina. It is normally 25cm. You must have seen minus or plus signs in eyeglass prescription. The minus sign denotes that the person is near-sighted while the plus sign denotes farsightedness.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




