
Explain with the help of diagram, how a depletion layer and barrier potential are formed in a junction diode.
Answer
572.4k+ views
Hint:There are two types of semiconductors: p-type and n-type. When both p-type and n-type semiconductor fused together, a region of a certain width develops between them. Recall the term barrier potential which is the potential beyond that the depletion region breaks down.
Complete answer:
We know that there are two types of semiconductors: p-type and n-type. When both p-type and n-type semiconductor fused together, a depletion region develops between them. The word depletion meant reduction in something. We know that in p-type semiconductor, holes are majority charge carriers and in n-type semiconductor, electrons are majority charge carriers. The depletion region or pn junction separates p-region and n-region in the semiconductor device.
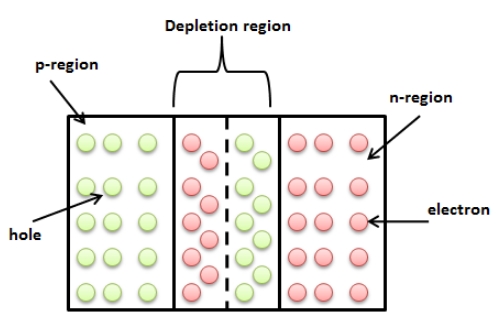
We will now discuss how the depletion region forms? Since in n-type semiconductor, electrons are charged carriers and are free to move. We know that the electrons move from high concentrated region (n-region) to low concentrated region (p-region). This is primarily due to electrostatic force which deflects electrons from n-region to p-region. In the same manner, the holes from the p-region move towards n-region. In this way, the region of electrons and holes is created at the junction of p-type and n-type semiconductor. This region we call the depletion region.
We know that in the p-region, there is a deficiency of electrons. Therefore, the atoms in the p-region gain electrons and become negatively charged. Similarly, the atoms in the n-region gain extra holes and attain positive charge. When the charge transfer attains threshold, it prevents transfer of extra electrons to the p-region due to net repulsion from the p-region. At this stage, the potential form between p-region and n-region is known as barrier potential. If we apply the voltage greater than the barrier potential, the depletion region breaks down.
Note:The depletion regions break down when we connect the semiconductor device in a forward bias and the voltage increases beyond the threshold value. When we connect the semiconductor device in a reverse bias, the width of the depletion regions gets wider until it reaches its threshold value. After a certain value of applied voltage, this depletion region also gets a break and we can see the sharp rise in the current.
Complete answer:
We know that there are two types of semiconductors: p-type and n-type. When both p-type and n-type semiconductor fused together, a depletion region develops between them. The word depletion meant reduction in something. We know that in p-type semiconductor, holes are majority charge carriers and in n-type semiconductor, electrons are majority charge carriers. The depletion region or pn junction separates p-region and n-region in the semiconductor device.

We will now discuss how the depletion region forms? Since in n-type semiconductor, electrons are charged carriers and are free to move. We know that the electrons move from high concentrated region (n-region) to low concentrated region (p-region). This is primarily due to electrostatic force which deflects electrons from n-region to p-region. In the same manner, the holes from the p-region move towards n-region. In this way, the region of electrons and holes is created at the junction of p-type and n-type semiconductor. This region we call the depletion region.
We know that in the p-region, there is a deficiency of electrons. Therefore, the atoms in the p-region gain electrons and become negatively charged. Similarly, the atoms in the n-region gain extra holes and attain positive charge. When the charge transfer attains threshold, it prevents transfer of extra electrons to the p-region due to net repulsion from the p-region. At this stage, the potential form between p-region and n-region is known as barrier potential. If we apply the voltage greater than the barrier potential, the depletion region breaks down.
Note:The depletion regions break down when we connect the semiconductor device in a forward bias and the voltage increases beyond the threshold value. When we connect the semiconductor device in a reverse bias, the width of the depletion regions gets wider until it reaches its threshold value. After a certain value of applied voltage, this depletion region also gets a break and we can see the sharp rise in the current.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




